创新背景
睡眠对人类健康至关重要,有助睡眠的相关药物和产品开发层出不穷,反向考虑大脑自身的物质和清醒的原因,对于相关研究会有积极作用。
创新过程
伦敦帝国理工学院生命科学系和神经技术中心的Stephen Brickley博士、Nick Franks教授和Bill Wisden教授领导的研究团队通过改变小鼠的神经化学结构,研究其睡眠机制和控制清醒的物质,帮助探究这两种状态之间的平衡和作用如何影响注意力和记忆力等大脑功能以及一般健康,相关研究成果《清醒度受GABA和组胺协同传播的支配》发表在2015年7月出版的《神经元》上。

此前已有科学家证明化学组胺向大脑发送信号以使其清醒。下丘脑后部区域管氨基核(TMN)中的组胺能神经元可以维持清醒,它们是神经元组胺的唯一来源,将轴突发送到整个大脑,其活性在睡眠期间受到抑制,在醒来后会变得活跃。基于此,很多抗组胺药的使用会导致使用者嗜睡。研究团队对小鼠和人类大脑高度相似的原始部分进行探究,最终把研究目标定为组胺和GABA。
组胺可以通过激活末端的异质H3代谢受体来抑制谷氨酸或GABA对局部电路的输入,或者通过H1和H2代谢受体使细胞去极化或引起影响放电速率的离子通道的磷酸化。研究人员发现,GABA和组胺是在相同的脑细胞中产生的,称为组胺神经元。
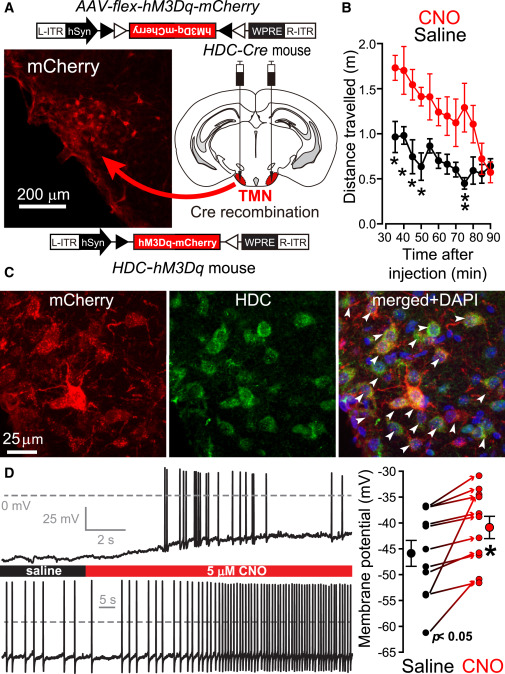
研究首先用DREADD hM3Dq-mCherry受体和氯氮平-N-氧化物在体内选择性地刺激组胺能神经元的行为兴奋性。组氨酸能神经元因为具有组氨酸脱羧酶(hdc)基因的独特表达,可以被遗传靶向,产生HDC-Cre小鼠。
研究通过改变小鼠大脑中的GABA水平并测量其在白天和黑夜对大脑活动的影响来探究GABA的作用。没有GABA化学物质的小鼠会经历不安和失眠,发展出类似于躁狂症的特征,在人类身上体现为双相情感障碍的症状。
研究发现,没有GABA的小鼠的奔跑速度比正常小鼠快一倍,跑得也更远,在30分钟内会保持甚至增加它们的活性。并且小鼠在白天保持清醒的时间延长,睡觉时只经历深度睡眠的65%。
研究人员表示,通常失去5个小时睡眠的小鼠在被剥夺睡眠后会睡得更久,活动水平更低,但缺少GABA的小鼠在接下来的16小时内保持清醒多动状态,似乎根本不需要任何恢复睡眠。
研究根据目前的成果探索睡眠不足与记忆丧失之间的联系,希望能够理清睡眠质量和人类心理健康之间的联系。
创新关键点
研究组胺和GABA对清醒状态的影响,反向思考其对睡眠的影响。
创新价值
有助于开发促进睡眠质量变好的新药,或控制患有躁狂症的人的多动症。
Effects of brain chemicals on waking and sleeping states
The research team led by Dr Stephen Brickley, Professor Nick Franks and Professor Bill Wisden, From the Department of Life Sciences and the Centre for Neurotechnology at Imperial College London, helped explore how the balance and effect between these two states affects brain function such as attention and memory and general health by altering the neurochemistry of mice, studying their sleep mechanisms and controlling the substances that are awake. Published in the July 2015 issue of Neurons.
Scientists have previously demonstrated that chemical histamine sends signals to the brain to wake it up. Histamine neurons in the tubal amino nucleus (TMN) in the posterior region of the hypothalamus can maintain lucidity, and they are the only source of neuronal histamine, sending axons throughout the brain, whose activity is suppressed during sleep and becomes active after waking up. Based on this, the use of many antihistamines can cause the user to be drowsy. The team explored primitive parts of the mouse and human brains that were highly similar, and finally set the research targets histamine and GABA.
Histamine can inhibit glutamate or GABA input to local circuits by activating heterogeneous H3 metabolic receptors at the terminals, or depolarize cells or cause phosphorylation of ion channels that affect the rate of discharge by the H1 and H2 metabolic receptors. The researchers found that GABA and histamine are produced in the same brain cells called histamine neurons.
The study first used the DREADD hM3Dq-mCherry receptor and clozapine-N-oxide in vivo to selectively stimulate the behavioral excitability of histamine neurons. Histidineergic neurons, because of their unique expression of the histidine decarboxylase (HDC) gene, can be genetically targeted to produce HDC-Cre mice.
The study explored the role of GABA by altering GABA levels in mouse brains and measuring their effects on brain activity day and night. Mice without the GABA chemical experienced restlessness and insomnia, developing features similar to mania, manifesting in humans as symptoms of bipolar disorder.
Mice without GABA were found to run twice as fast and farther than normal mice, maintaining or even increasing their activity for 30 minutes. And the mice stayed awake during the day for longer, experiencing only 65 percent of deep sleep when sleeping. The researchers said the mice, which typically lost 5 hours of sleep, slept longer and had lower activity levels after being deprived of sleep, but the mice lacking GABA remained awake and hyperactive for the next 16 hours and didn't seem to need anything to regain their sleep at all.
Based on the current results, the study explores the link between sleep deprivation and memory loss, hoping to clarify the link between sleep quality and human mental health.
智能推荐
全球健康学创新思维 | 反向思考压力对睡眠的影响和作用
2022-08-02反向思考压力和睡眠的关系,探索压力诱导睡眠的机制。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向涂料工程创新思维 | 新型耐用涂料结合聚氨酯和油可杀灭COVID病毒和细菌
2022-09-05来自密歇根大学的研究团队利用创新方法将油与聚氨酯很好的结合在一起,研发了一种具有耐用性和杀菌能力新型的涂料。这项创新研究成果可能会在疫情大流行的情况下,让公共空间变得更安全,进而减少疫情的扩散。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向医学创新思维 | 增加睡眠时长可减少能量摄入,帮助减少体重
2022-08-03美国芝加哥大学医学院和和威斯康星大学麦迪逊分校的研究人员通过对80个超重样本的对照试验结果进行分析发现,平均睡眠时长增加1.2小时,可以减少270千卡的能量摄入,这些减少的能量摄入就会帮助人们减重。相反,睡眠不足会影响食欲,导致食物摄入量增加,从而加重肥胖风险。该研究发现了睡眠和能量摄入量之间的关系,为肥胖人群的健康减肥提供了新思路。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向