创新背景
社会认知是个体与他人互动中涉及的过程,是个体根据环境中的社会信息形成对他人或事物的判断和推论。 头部受损引起的脑损伤可能会影响社会认知,导致一些无法被轻易观察到的残疾。目前评估这种残疾的测试方法不够完善,需要进一步改善提高。
创新过程
目前脑损伤引起的残疾的评估测试在日常互动中使用时缺少对正确认知过程的开发研究,导致测试结果会出现偏差。法国国家科学技术中心的研究人员Maud Champagne-Lavau带领团队,开发并测试了一项新的测试方法,使用名为Marie和Pierre的虚拟人类再现社交互动,开发新工具EVICog,相关研究成果《与虚拟人类对话:用第二人称视角任务评估创伤性脑损伤中的社会认知》发表在2021年6月28日出版的《神经心理学杂志》上。
以往的研究通过传统人物探究创伤性脑损伤患者的社会认知改变,以第三人称视角对角色的精神状态进行有意识地推理。新方法让参与者积极参加互动,以第二人称在更接近现实生活的条件下评估社会认知,将患者置于比传统测试更加有代入感的环境中,致力于了解社会认知过程的更多隐形作用和过程。
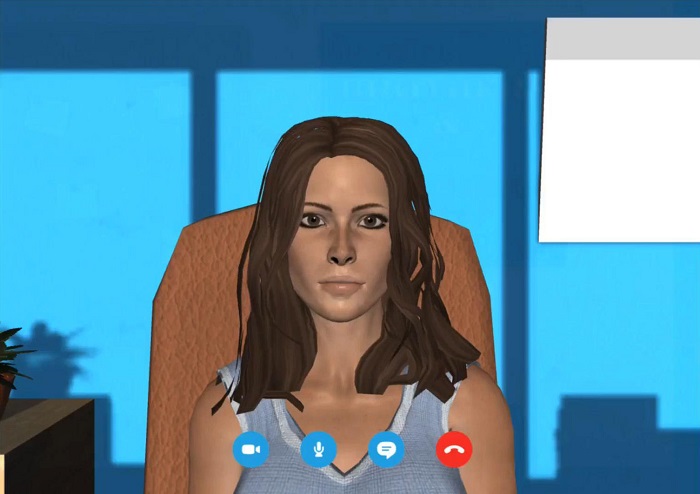
研究人员和心理学家指导变成,使虚拟人具有接近人类的言语和情感反应。EVICog让参与者与两个虚拟人进行真实的视听对话,虚拟人积极表达情感并制作语音内容,研究要求参与者对角色的精神状态进行推断。然后研究人员通过照片评估参与者对情感的识别判断,并使用短连环画来测试参与者对意图的归属。
研究结果表明,与对照组参与者相比,创伤性脑损伤(TBI)参与者表现出显着的社会认知缺陷。ROC分析表明,与其他测试相比,EVICog具有很高的鉴别能力。
研究进一步证实了即使在实际互动中,TBI参与者的社会认知也会发生变化。研究一旦适应临床要求和需要,测试任务可以成为评估头部损伤对社会互动影响的新参考。
创新关键点
将社会认知纳入脑损伤的后续影响,利用虚拟人模仿真实情景评估测试脑损伤对社会认知的影响。
Virtual human talk helps assess the consequences of brain injury tested
The current assessment test for disability caused by brain injury lacks development studies of correct cognitive processes when used in daily interactions, resulting in biased test results. Maud Champagne-Lavau, a researcher at France's National Centre for Science and Technology, led a team that developed and tested a new test method, using virtual humans called Marie and Pierre to reproduce social interactions, developed a new tool EVICog, and the research result "Dialogue with Virtual Humans: Assessing Social Cognition in Traumatic Brain Injury with a Second-Person Perspective Task" was published in the June 28, 2021 issue of the Journal of Neuropsychology.
Previous research has used traditional characters to explore the social cognitive changes of patients with traumatic brain injury, and consciously reasoned about the mental state of the characters from a third-person perspective. The new approach involves participants actively engaging, assessing social cognition in the second person under conditions closer to real life, placing patients in a more empathetic environment than traditional tests, and working to understand more invisible roles and processes of social cognitive processes.
Researchers and psychologists guide the transformation into a verbal and emotional response that makes virtual humans have a proximity to that of humans. EVICog had participants engage in real-life audiovisual dialogue with two virtual people who actively expressed emotions and produced spoken content, and the study asked participants to extrapolate the mental state of the characters. The researchers then assessed participants' recognition judgments about emotions through photographs and used short comic strips to test participants' attribution to intent.
The findings showed that participants with traumatic brain injury (TBI) exhibited significant social cognitive deficits compared to participants in the control group. ROC analysis shows that EVICog has a high discriminating power compared to other tests.
The study further confirmed that the social perceptions of TBI participants changed even during actual interactions. Once research is adapted to clinical requirements and needs, the testing task can serve as a new reference for assessing the impact of head injuries on social interactions.
智能推荐
医学创新思维 | 镜像核酸的定向进化以及在疾病诊疗中的应用
2022-07-01该研究报道了一种镜像核酸的定向进化与镜像DNA适配体的直接筛选方法,为其在疾病诊疗领域的应用提供了新的技术平台。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向临床医学创新思维 | 嗅觉丧失或预示着认知功能下降
2022-08-01通过嗅觉和记忆之间的关系探索嗅觉变化与大脑结构变化以及阿尔兹海默症之间的联系。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向