创新背景
巴甫洛夫联想学习被认为是塑造人类和动物行为的一种基本学习形式,但在人工智能系统中采用这种学习方式在很大程度上是闻所未闻的。
创新过程
发表在《光学》杂志上的这项新研究的灵感来自诺贝尔奖得主伊万·巴甫洛夫发现的经典条件反射。在他的实验中,巴甫洛夫发现,通过在喂食过程中提供另一种刺激,如铃声或节拍器的声音,他的狗开始将这两种体验联系起来,并会在单独听到声音时流口水。将两个不相关的事件重复联系在一起,可以产生一种习得反应——条件反射。
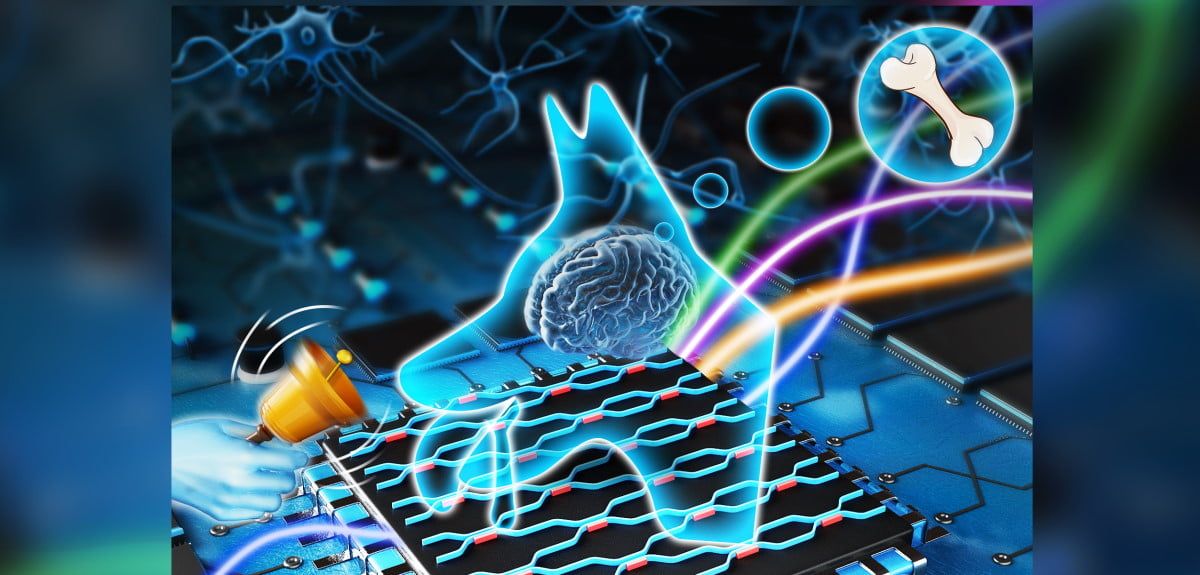
在大多数人工智能系统中使用的神经网络在学习过程中通常需要大量的数据示例——训练一个模型可靠地识别一只猫,可能需要多达1万张猫/非猫的图像——同时需要计算和处理成本。
联想一元学习元素(AMLE)不是依靠神经网络喜欢的反向传播来“调整”结果,而是使用记忆材料来学习模式,将数据集中相似的特征联系在一起——模仿巴甫洛夫在“匹配”情况下观察到的条件反射。
AMLE的输入与正确的输出配对来监督学习过程,并且可以使用光信号重置记忆材料。在测试中,仅用5对图像进行训练,AMLE就能正确识别猫/非猫图像。

与传统电子芯片相比,这种新型光学芯片的可观性能可以归结为两个设计上的关键差异:
一种独特的网络架构,将联想学习作为构建模块,而不是使用神经元和神经网络。利用“波分多路复用”在一个信道上发送不同波长的多个光信号,以提高计算速度。
芯片硬件使用光来发送和检索数据,以最大化信息密度——多个不同波长的信号同时发送,进行并行处理,这提高了识别任务的检测速度。每个波长都提高了计算速度。
创新价值
许多学习任务都是基于量的,并没有那么复杂——在这些情况下,联想学习可以更快地完成任务,并以更低的计算成本。这项工作为实现快速光学处理器铺平了道路,为特定类型的AI计算捕获数据关联。
创新关键点
新的人工智能使用联想学习技术,而不是人工智能的传统神经网络。
创新主体
牛津大学(University of Oxford),简称“牛津”(Oxford),位于英国牛津,是一所公立研究型大学,采用传统学院制。是罗素大学集团成员,被誉为“金三角名校”和“G5”。牛津大学的具体建校时间已不可考,但有档案明确记载的最早的授课时间为1096年,之后在1167年因得到了英国王室的大力支持而快速发展。
New AI systems use light for associative learning
The new study, published in the journal Optica, was inspired by the classical conditioning discovered by Nobel laureate Ivan Pavlov. In his experiments, Pavlov found that by providing another stimulus during feeding, such as the sound of a bell or metronome, his dogs began to associate the two experiences and would salivate when hearing the sound alone. The repeated association of two unrelated events can produce a learned response, a conditioned reflex.
The neural networks used in most AI systems typically require large numbers of data examples during learning - training a model to reliably identify a cat may require up to 10,000 cat/non-cat images - as well as computational and processing costs.
Instead of relying on the backpropagation preferred by neural networks to "tune" results, Associative unary Learning Elements (AMLE) use memory material to learn patterns that link similar features in a dataset together - mimicking the conditioning observed by Pavlov in "matching" situations.
AMLE's input is paired with the correct output to supervise the learning process, and optical signals can be used to reset memorized material. In tests, AMLE correctly identified cat/non-cat images when trained with just five pairs of images.
The considerable performance of the new optical chip over conventional electronic chips can be attributed to two key design differences:
A unique network architecture that uses associative learning as a building block instead of using neurons and neural networks. Wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) is used to transmit multiple optical signals of different wavelengths over a channel to improve the computational speed.
The chip hardware uses light to send and retrieve data to maximize information density -- multiple signals of different wavelengths are sent simultaneously for parallel processing, which improves detection speed for recognition tasks. Each wavelength speeds up the computation.
智能推荐
人工智能创新思维 | 3D图像转换技术可揭示更多生物系统
2022-11-21人工智能技术为生命科学带来新的可能。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI+教育创新思维 | 人工智能结合教师培训,自适应反馈帮助识别学习困难人群
2022-07-28结合人工智能和职前教师培训,帮助学习者发现自己的学习困难并增加实践机会。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向