创新背景
癌症治疗是目前医学领域的难题,而癌细胞的扩散是癌症常见的死因。由于癌细胞迁移机制复杂,至今对其了解甚少。纳米金刚石由于其良好的生物相容性和易于被功能化修饰的特性,使其作为药物载体材料在生物医学领域具有广泛的应用。
创新过程
中国科学院理化技术研究所光电功能界面材料实验室自2010年开始研究基于纳米金刚石的癌症治疗体系,发现在酸性细胞环境内,纳米金刚石-顺铂体系可实现顺铂药物的缓释效果,能显著抑制HeLa细胞的增殖(Small 2010, 6, 1514-1519)。后续研究发现了高压高温法制备的纳米金刚石对HepG2细胞的迁移抑制效果(Physica Status Solidi A 2016, 213, 2131-2137)。
特定浓度的羧基化纳米金刚石可显著抑制癌细胞中波形蛋白的表达,从而抑制HeLa和C6细胞的迁移(Diam Relat Mater 2020, 105, 107809)。近期,该课题组合成了纳米金刚石-二氧化钛复合材料,可在可见光下对癌细胞进行选择性杀伤,并抑制癌细胞的迁移。该研究为开发低毒性、多功能的光敏剂提供了新思路,在细胞诊疗与迁移方面具有潜在应用价值(Carbon 2021, 174, 90-97)。
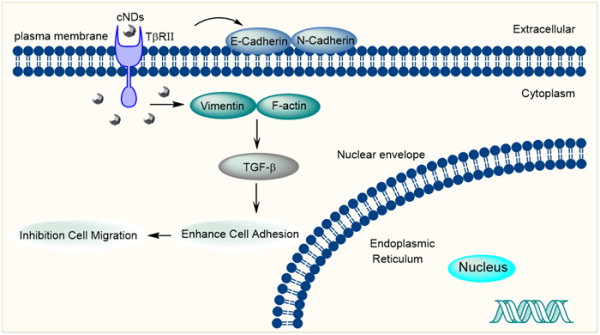
羧基化纳米金刚石抑制肿瘤细胞迁移过程示意图
此外,该课题组还对纳米金刚石对肿瘤细胞迁移的抑制机制及其在体内的作用展开了深入探讨。结果表明,羧基化纳米金刚石可以提高肿瘤细胞与基底的粘附能力,从而导致细胞运动受限。在分子机理上主要表现在羧基化纳米金刚石能够下调N-钙粘蛋白和波形蛋白的表达,上调E-钙粘蛋白的表达,通过TGF-β信号通路逆转EMT过程。通过Phalloidin染色实验证实了羧基化纳米金刚石会损害F-肌动蛋白细胞骨架的组装,减少应力纤维和板状伪足的形成,进而抑制肿瘤细胞的迁移。利用小鼠肺转移模型验证了羧基化纳米金刚石在体内对肿瘤转移的抑制作用。未来,羧基化纳米金刚石有望作为简单的载体和探针,并在生物医学领域作为肿瘤细胞迁移的新型抑制剂,在调控细胞行为方面发挥积极作用。
创新价值
该课题组合成了纳米金刚石-二氧化钛复合材料,可在可见光下对癌细胞进行选择性杀伤,并抑制癌细胞的迁移。该研究为开发低毒性、多功能的光敏剂提供了新思路,在细胞诊疗与迁移方面具有潜在应用价值。
创新关键点
在分子机理上主要表现在羧基化纳米金刚石能够下调N-钙粘蛋白和波形蛋白的表达,上调E-钙粘蛋白的表达,通过TGF-β信号通路逆转EMT过程。通过Phalloidin染色实验证实了羧基化纳米金刚石会损害F-肌动蛋白细胞骨架的组装,减少应力纤维和板状伪足的形成,进而抑制肿瘤细胞的迁移。
New carbon - based nanomaterials have been innovatively applied in the field of biomedicine as drug carrier materials
Since 2010, the Laboratory of Optoelectronic Functional Interface Materials, Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences has been researching the cancer treatment system based on nanodiamond. It has been found that the nanodiamond-cisplatin system can achieve the sustained release effect of cisplatin in acidic cell environment. It can significantly inhibit the proliferation of HeLa cells (Small 2010, 6, 1514-1519). Subsequent studies found that the nano-diamond prepared by high pressure and high temperature method had the inhibitory effect on migration of HepG2 cells (Physica Status Solidi A 2016, 213, 2131-2137). Specific concentrations of carboxylated nanodiamond can significantly inhibit the expression of vimentin in cancer cells, thereby inhibiting the migration of HeLa and C6 cells (Diam Relat Mater 2020, 105, 107809). Recently, the research group synthesized nanodiamond-titanium dioxide composites, which can selectively kill cancer cells under visible light and inhibit the migration of cancer cells. This study provides a new idea for the development of low-toxicity, multifunctional photosensitizers with potential applications in cell diagnosis, treatment and migration (Carbon 2021, 174, 90-97).
In addition, the inhibition mechanism of nano-diamond on tumor cell migration and its role in vivo were also discussed. The results showed that carboxylated nanodiamond could improve the adhesion ability of tumor cells to the substrate, resulting in cell movement limitation. In terms of molecular mechanism, carboxylated nanodiamond can down-regulate the expression of N-cadherin and vimentin, up-regulate the expression of E-cadherin, and reverse the EMT process through TGF-β signaling pathway. Phalloidin staining assay confirmed that carboxylated nanodiamond could impair the assembly of F-actin cytoskeleton, reduce the formation of stress fibers and laminodia, and then inhibit the migration of tumor cells. The inhibitory effect of carboxylated nanodiamond on tumor metastasis in vivo was verified using a mouse lung metastasis model. In the future, carboxylated nanodiamond is expected to play a positive role in regulating cell behavior as a simple carrier and probe, and as a novel inhibitor of tumor cell migration in the biomedical field.
智能推荐
生物医学创新思维 | 使用新型跨学科技术研究病毒的进化与组装
2022-11-13来自约克大学的研究人员与苏黎世联邦理工学院的希尔弗特实验室合作,研究了病毒的组装和进化。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向医学创新思维 | 类固醇会影响新型冠状病毒治疗效果
2022-11-06发表在《柳叶刀》上的一篇文章得出结论,基于以往类似类型感染(如SARS)爆发的事例,类固醇对患者几乎没有好处,而且可能弊大于利。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向生物医学创新思维 | 通过自监督学习实验发现AI模型与人脑的相似性
2022-07-28Meta AI、美国哥伦比亚大学、多伦多大学等的研究人员完成了一个关于深度学习模型和人脑之间相似性的研究。研究发现,AI模型Wav2Vec 2.0与人类大脑处理语音的方式非常相似,甚至AI也像人类一样,对“母语”有更强的辨别能力,如法语模型就比英语模型更容易感知来自法语的刺激。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向生物医学创新思维 | 揭示细菌内部ATP水平与耐药性的关联
2022-11-13科学家们揭示了细菌如何从蛋白质中产生微小的液滴,以帮助它们在恶劣的环境中生存,从而减少被抗生素杀死的机会。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向