创新背景
传统社会学理论认为文化偏好更多地受到家庭、经历等外部环境的影响,基因很难影响这些选择。基因作为自然的传承和客观个人条件,影响我们的性别、身高和其他生理特征,审视自然与养育,会发现基因对于人的社会特征也有一定的影响。
创新过程
哥本哈根大学的研究人员从基因的角度探究了文化偏好的形成和影响因素,估计了文化偏好和活动在多大程度上由每个人的基因影响或由环境创造,将遗传印记纳入社会特征的考虑之中。社会学普遍认为父母通过社会化和社会互动,将他们的文化偏好完全转移给孩子。新研究则表明,一个家庭整体的文化偏好和消费存在重要的遗传因素。在家庭中,对流行、阳春白雪或是下里巴人文化的偏好主要通过共享基因传播。也就是说,通过朋友、媒体等在家庭之外遇到的个人经历也非常重要。因此,文化偏好不是只有遗传或环境的影响,二者兼而有之。


研究调查了对1200对丹麦双胞胎,其中466对是同卵双胞胎,734对是双卵双胞胎。通过描绘他们对12种文化活动的品味和参与情况,比较遗传上相同的单卵双胞胎和共享50%分离基因的双卵双胞胎受到基因的影响情况。结果表明,受访者对一些雅文化如古典音乐、戏剧、芭蕾舞和艺术的品味的54%的差异可归因于遗传倾向,家庭的影响只占16%,剩下的30%是外部社会因素。
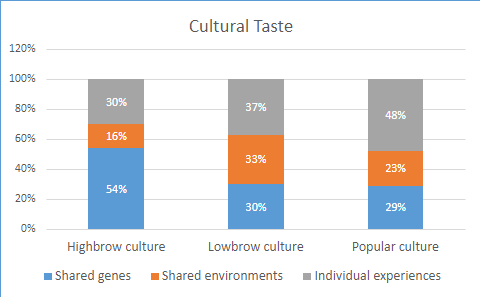
对流行文化的品味背后的因素分布更均匀,从受访者的实际文化参与来看,家庭内部的社会影响甚至更小。当这项研究测试基因在我们发展各种流派的广泛音乐和文学品味中的重要性时,同样,遗传因素同样是显著的。
研究人员认为,可遗传的基因对认知技能和人格特质的影响为各种文化偏好奠定了基础,个别的倾向会转化为每个人在与不同环境中对特定文化活动和流派的品味和参与。
创新关键点
创新从基因遗传的角度探究文化偏好的塑造和形成。
创新价值
拓展文化偏好研究方向,有助于在不同的社会背景下传播文化,深刻了解文化的多样性成因。
Explore the causes of cultural preferences from a genetic perspective
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen explored the formation and influencing factors of cultural preferences from a genetic perspective, estimating the extent to which cultural preferences and activities are genetically influenced by each individual or created by the environment, incorporating genetic imprints into consideration of social characteristics. Sociology generally believes that parents completely transfer their cultural preferences to their children through socialization and social interaction. New research suggests that there are important genetic factors in the cultural preferences and consumption of a family as a whole. In the family, preferences for pop, yangchun white snow or lower riba culture are mainly transmitted through shared genes. That said, personal experiences encountered outside the home through friends, the media, etc. are also very important. Thus, cultural preferences are not just genetic or environmental influences, but both.
The study looked at 1200 pairs of Danish twins, of which 466 were identical twins and 734 were twins. By mapping their tastes and participation in 12 cultural activities, comparisons were made between genetically identical monozygotic twins and twins who shared 50% of the isolated genes who were affected by genes. The results showed that 54% of the differences in respondents' tastes in some asian cultures such as classical music, theatre, ballet and the arts could be attributed to genetic predispositions, with only 16% of the family influencing and the remaining 30% being external social factors.
The factors behind tastes for popular culture are more evenly distributed, with even less social impact within the family in terms of respondents' actual cultural participation. When this study tests the importance of genes in the broad musical and literary tastes we develop in various genres, similarly, genetic factors are equally significant.
The researchers argue that the effects of heritable genes on cognitive skills and personality traits lay the foundation for a variety of cultural preferences, and that individual tendencies translate into each person's taste and participation in specific cultural activities and genres in different contexts.
智能推荐
管理学创新思维 | 快速思考 聪明交谈(3)
2022-09-13涉及学科涉及领域研究方向管理科学创新思维 | 人际关系管理创新的重要性
2022-08-24以文化、第三人角度、谈判和环境四个方面入手考虑优化管理和人际关系的可行方法,研究更为有效的管理模式。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向管理科学创新思维 | 运用系统思维帮助改进墨西哥啤酒厂的运营模式
2022-08-23使用系统思维将制造工厂已有的数据驱动和人工智能技术运用于运营,帮助解决公司生产瓶颈。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向管理科学创新思维 | 创新发现成功经验的“二次组合”可提高团队成员契合度
2022-11-04研究将有成功经验的团队成员组合起来,不以创造积极情绪为手段,创新探究有成功经验的合作双方对最终合作效果的影响,发现减少情绪障碍将减少彼此的紧张感,提高双方契合度。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向