创新背景
向智能家居设备询问天气预报,设备需要几秒钟才能做出响应。出现这种延迟的一个原因是,连接的设备没有足够的内存或电力来存储和运行设备理解用户要求的内容所需的巨大机器学习模型。该模型存储在可能数百英里外的数据中心,在那里计算答案并将其发送到设备。
创新过程
麻省理工学院的研究人员创造了一种直接在这些设备上计算的新方法,这大大减少了这种延迟。他们的技术将运行机器学习模型的内存密集型步骤转移到中央服务器,其中模型的组件被编码到光波上。
这些波使用光纤传输到连接的设备,这使得大量数据能够通过网络以闪电般的速度发送。然后,接收器采用简单的光学设备,使用这些光波携带的模型部分快速执行计算。
这种方法可以使自动驾驶汽车实时做出决定,同时仅使用目前耗电量大的计算机所需能量的一小部分。它还可以允许用户与他们的智能家居设备进行无延迟的对话,用于蜂窝网络上的实时视频处理,甚至可以在距离地球数百万英里的航天器上进行高速图像分类。
每次运行神经网络都必须运行程序,而运行程序的速度取决于能以多快的速度将程序从内存中导入。数据管道是巨大的,它对应于每毫秒左右通过互联网发送一部完整的电影。
神经网络是机器学习模型,它使用连接节点或神经元层来识别数据集中的模式并执行任务,例如对图像进行分类或识别语音。但这些模型可以包含数十亿个权重参数,这些参数是在处理输入数据时转换输入数据的数值。这些权重必须存储在内存中。同时,数据转换过程涉及数十亿个代数计算,这需要大量的功率来执行。
从内存中获取数据(在这种情况下是神经网络的权重)并将其移动到计算机中执行实际计算的部分的过程是速度和能源效率的最大限制因素之一。
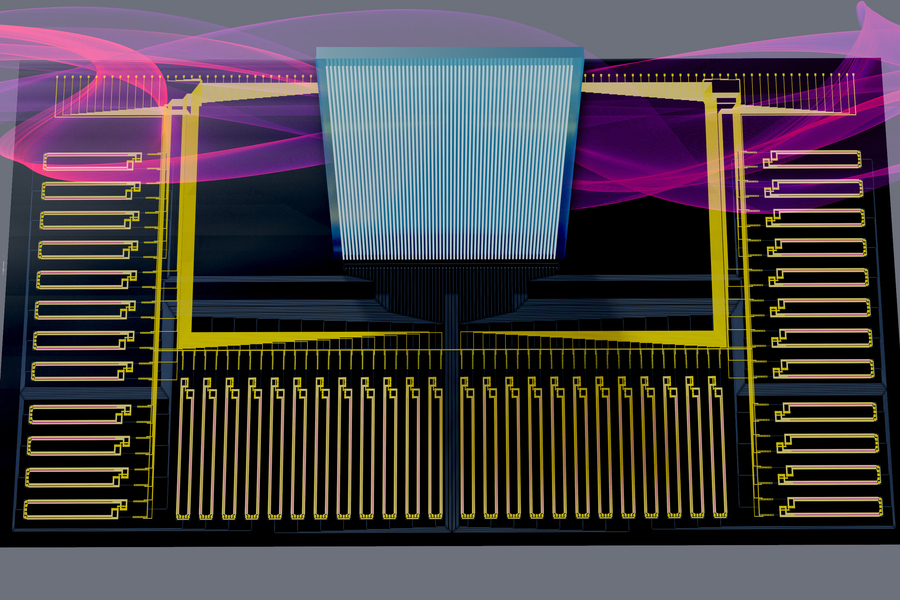
他们开发的神经网络架构Netcast涉及将权重存储在连接到称为智能收发器的新型硬件的中央服务器中。这种智能收发器是一种拇指大小的芯片,可以接收和传输数据,它使用称为硅光子学的技术每秒从内存中获取数万亿个权重。

它以电信号的形式接收重量,并将它们印在光波上。由于重量数据被编码为位(1s和0s),收发器通过切换激光器来转换它们;激光在1上亮起,在0点亮起。它结合了这些光波,然后通过光纤网络定期传输它们,因此客户端设备不需要查询服务器来接收它们。
一旦光波到达客户端设备,一个称为宽带“Mach-Zehnder”调制器的简单光学元件就使用它们来执行超快速的模拟计算。这涉及将来自设备的输入数据(如传感器信息)编码到权重上。然后,它将每个单独的波长发送到接收器,接收器检测光并测量计算结果。
创新关键点
研究人员设计了一种方法,使用这种调制器每秒进行数万亿次乘法,这大大提高了设备上的计算速度,同时仅使用少量的功率。
创新价值
这些设备的实际实现引入了一种新的实用的边缘计算方案,同时也探索了在非常低(单光子)光照水平下计算的一些基本限制。
与其他方法相比,该技术可将能源效率提高一百倍以上。它还可以提高安全性,因为用户的数据不需要传输到中心位置进行计算。
New hardware "smart transceivers" use silicon photonics to speed up computing
MIT researchers have created a new way to compute directly on these devices, which dramatically reduces this delay. Their technique moves the memory-intensive steps of running machine learning models to a central server, where the components of the model are encoded onto light waves.
These waves are transmitted to connected devices using optical fibers, which allows large amounts of data to be sent across the network at lightning speed. The receiver then employs simple optics to quickly perform calculations using parts of the model carried by these light waves.
This approach could allow self-driving cars to make decisions in real time while using only a fraction of the energy required by today's power-hungry computers. It could also allow users to have delay-free conversations with their smart home devices, for real-time video processing on cellular networks, and even for high-speed image classification on spacecraft millions of miles from Earth.
You must run the program every time you run the neural network, and the speed of running the program depends on how fast you can import the program from memory. The data pipeline is huge, and it corresponds to sending a full movie over the Internet every millisecond or so.
Neural networks are machine learning models that use layers of connected nodes or neurons to recognize patterns in a data set and perform tasks, such as classifying images or recognizing speech. But these models can contain billions of weight parameters that transform the values of the input data as it is processed. These weights must be stored in memory. Meanwhile, the data conversion process involves billions of algebraic calculations, which require a lot of power to perform.
The process of taking data from memory, in this case the weights of the neural network, and moving it to the part of the computer where the actual calculations are performed is one of the biggest constraints to speed and energy efficiency.
The neural network architecture they developed, Netcast, involves storing weights in central servers connected to new types of hardware called smart transceivers. The smart transceiver is a thumb-sized chip that receives and transmits data using a technique called silicon photonics that pulls trillions of weights from memory per second.
It receives weights in the form of electrical signals and prints them on light waves. Since the weight data are encoded as bits (1s and 0s), the transceiver converts them by switching lasers; The laser lights up at 1, lights up at 0. It combines these light waves and then transmits them periodically over a fiber-optic network, so client devices do not need to query the server to receive them.
Once the light waves reach the client device, a simple optical element called a broadband "Mach-Zehnder" modulator uses them to perform ultra-fast analog calculations. This involves encoding input data from the device, such as sensor information, onto weights. It then sends each individual wavelength to a receiver, which detects the light and measures the calculation.
智能推荐
人工智能创新思维 | 3D图像转换技术可揭示更多生物系统
2022-11-21人工智能技术为生命科学带来新的可能。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI+城市管理 | 打造低碳出行模式
2022-06-29AI+城市管理控制城市能源利用和排放,促进低碳出行发展。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向