创新背景
在传统的用于图像识别的神经网络中,目标物体的图像首先在图像传感器上形成,例如智能手机中的数码相机。然后,图像传感器将光转换成电信号,最终转换成二进制数据,然后使用计算机芯片对这些数据进行处理、分析、存储和分类。提高这些能力是改善许多应用程序的关键,比如人脸识别、自动检测照片中的文字或帮助自动驾驶汽车识别障碍。
创新过程
人工智能在许多系统中扮演着重要的角色,从预测文本到医疗诊断。受人脑的启发,许多人工智能系统都是基于人工神经网络实现的,其中生物神经元的电等效物相互连接,用一组已知数据(如图像)进行训练,然后用于识别或分类新的数据点。
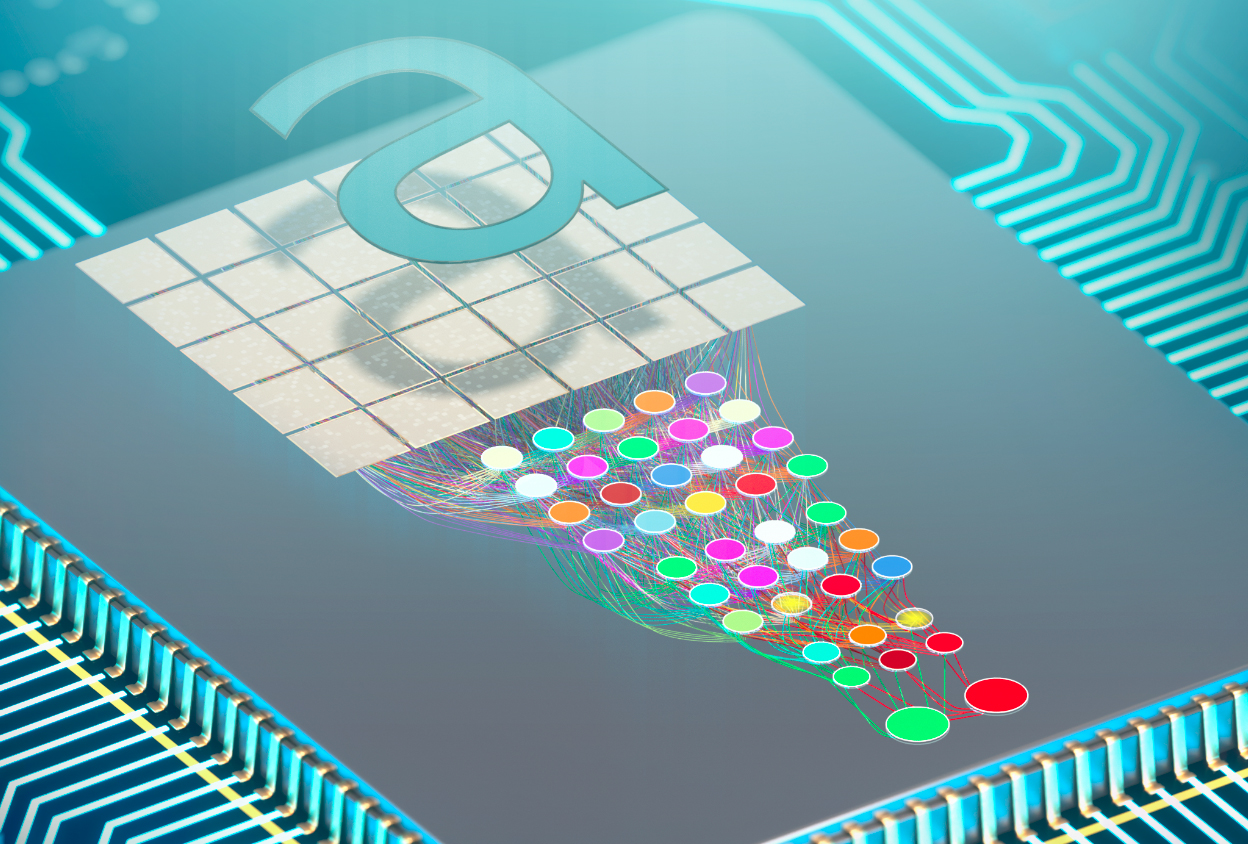
在数字芯片上的消费级图像分类技术每秒可以执行数十亿次的计算,使其足够快于大多数应用程序,更复杂的图像分类,如识别移动物体,3D物体识别,或对体内微观细胞的分类,正在挑战即使是最强大的技术的计算极限。这些技术的当前速度限制是由计算机处理器中基于时钟的计算步骤计划设置的,其中计算在线性计划中一个接一个地进行。
他们通过在一个9.3平方毫米芯片上实现的光学深度神经网络直接处理从感兴趣的物体接收的光来实现这一点。
该芯片的一大部分光神经元是通过光缆或“波导”相互连接,形成一个模仿人脑的许多“神经元层”的深层网络。信息通过网络的各个层,每一步都有助于将输入的图像分类到它所学到的类别中。在研究人员的研究中,芯片分类的图像是手绘的、类似字母的字符。
创新关键点
该芯片的一大部分光神经元是通过光缆或“波导”相互连接,形成一个模仿人脑的许多“神经元层”的深层网络。信息通过网络的各个层,每一步都有助于将输入的图像分类到它所学到的类别中。
创新价值
这是研究人员创造的第一个可扩展的芯片,它几乎可以立即分类和识别图像,消除了传统计算机芯片中四个耗时的主要问题:光电信号转换、输入数据转换为二进制格式的需要、大内存模块和基于时钟的计算。
The new chip uses optical waveguides to process images in a nanosecond
Artificial intelligence plays an important role in many systems, from predicting text to medical diagnosis. Inspired by the human brain, many AI systems are implemented based on artificial neural networks, where electrical equivalents of biological neurons are connected to each other, trained with a set of known data, such as images, and then used to identify or classify new data points.
Consumer-grade image classification technologies on digital chips can perform billions of calculations per second, making them fast enough to outpace most applications, and more sophisticated image classification, such as identifying moving objects, 3D object recognition, or sorting microscopic cells in the body, is challenging the computational limits of even the most powerful technologies. The current speed limits for these techniques are set by a clock-based computation step schedule in a computer processor, where the computations take place one after the other in a linear schedule.
They do this by directly processing the light received from the object of interest with an optical deep neural network implemented on a 9.3 sq mm chip.
A large part of the chip's optical neurons are connected to each other via optical cables, or "waveguides," forming a deep network that mimics the many "neuronal layers" of the human brain. The information passes through the layers of the network, each step helping to classify the input image into the categories it has learned. In the researchers' study, the images the chips sorted were hand-drawn, letter-like characters.
智能推荐
使用硫化学气相沉积制备超高折射率的聚合物
2022-08-05通过一步法气相沉积工艺提高折射聚合物薄膜的高透明度。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向利用原子的缺失打造不同强度的复合半导体材料
2022-08-16来自麻省理工学院的研究团队通过使用硫化锌和另外两种半导体进行的研究发现,半导体材料中缺陷或缺失的原子使得材料在对光的反应中会变得更加坚硬,当光关闭后,这种坚硬的效果是可逆的。并提出了通过引入特定缺陷的方式来制造不同强度的半导体材料的新研究方向。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向声学创意 | 以声学功能设计建筑形态
2022-07-06创新以声学功能作建筑的首要元素,融合自然与人为的声音,突破原有的建筑类型。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向化学工程创新 | 通过确定催化位点的最佳结构加快催化剂设计
2022-08-18通过统计催化纳米颗粒不同位置位点的相邻数来确定铂基催化剂的催化位点,进而开发快速设计催化剂的方法。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向