创新背景
MicroRNAs是一种短RNA分子,它针对某些信使RNA(用于合成蛋白质的遗传物质)来阻止它们编码特定的蛋白质。miRNA活性受损与癌症肿瘤的形成和转移(癌症扩散到身体其他部位)有关。
创新过程
研究小组使用纳米颗粒锁定靶向microRNAs (miRNAs),使它们能够很容易地被提取。其中一个主要的好处是,即使在血液样本中miRNA的含量很低的情况下,它也是有效的。以前,需要更大的样本才能提取类似的量。

这项新技术有可能通过手指刺血测试来确定microRNA的水平
研究人员用DNA修饰镀金磁性纳米颗粒(Au@MNPs),以匹配他们想要检测的miRNA。
纳米颗粒实际上是可分散的电极。当它们在血液中循环时,它们会捕获miRNA,然后用磁铁重新捕获带有新附着的microRNA的纳米颗粒。研究人员可以得到更多的microRNA,因为分散电极几乎捕获了样本中的所有东西。
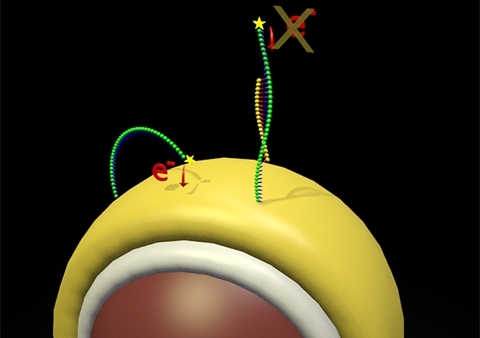
构成可分散电极的镀金纳米颗粒的计算机表示。这些被DNA修饰,产生电化学信号。当微RNA结合时,电化学信号被关闭。电流变化的大小与miRNA的浓度有关。
速度快的优点之一是成本低。它可能会便宜好几个数量级。新方法只需30分钟,而定量聚合酶链式反应只需近12小时。
这项新技术的关键不仅在于检测较低浓度的miRNA,而且在于检测大范围浓度的能力。这对于确定不同的microrna的水平是增加了还是减少了非常重要。
创新关键点
研究人员用DNA修饰镀金磁性纳米颗粒(Au@MNPs),以匹配他们想要检测的miRNA。
纳米颗粒实际上是可分散的电极。当它们在血液中循环时,它们会捕获miRNA,然后用磁铁重新捕获带有新附着的microRNA的纳米颗粒。
创新价值
这项技术有可能仅通过手指穿刺测试就能确定microRNA的水平。
Innovative use of nanoparticles to effectively detect ultra-low levels of micrornas in blood samples
The research team used nanoparticles to lock and target microRNAs (miRNAs) so that they could be easily extracted. One of the main benefits is that it is effective even at very low levels of miRNA in blood samples. Previously, larger samples were needed to extract similar amounts.
The researchers modified gold-plated magnetic nanoparticles (Au@MNPs) with DNA to match the miRNA they wanted to detect.
Nanoparticles are actually dispersible electrodes. As they circulate in the blood, they capture the miRNA and then use magnets to recapture the nanoparticles with the newly attached microRNA. The researchers can get more micrornas because the scatter electrodes capture almost everything in the sample.
One of the advantages of speed is low cost. It could be orders of magnitude cheaper. The new method takes just 30 minutes, compared with nearly 12 hours for quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
The key to this new technique is the ability to detect not only lower concentrations of mirnas, but also a wide range of concentrations. This is important to determine whether the levels of different micrornas are increasing or decreasing.
智能推荐
细胞学创新 | 应用新型全息系统可捕捉到细胞的高速运动并进行成像
2022-09-28杜克大学的生物医学工程师设计了一种全息系统,该系统能够每分钟成像和分析数以万计的细胞,从而发现并识别疾病的迹象。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向新材料 | 开发新型生物材料可加速身体自愈过程
2022-09-29研究团队为外科医生设计了一种绷带,植入骨折部位可加速自然愈合过程。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向生物医学工程创新 | 将抗生素涂层创新应用于骨科植入物可降低感染机会
2022-09-28杜克大学的生物医学工程师等人发明了一种抗生素涂层,可以在手术前几分钟涂在骨科植入物上,从而消除植入物周围感染的机会。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向医学成像技术创新 | 新型诊断成像技术可将切割精度提高10倍
2022-10-11加州理工学院的研究人员开发的一种新的诊断成像技术使外科医生能够将切割精度提高10倍,使他们能够保留多达1000倍的健康组织,并使患者更容易康复。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向