创新背景
医生和研究人员使用光学相干断层扫描(OCT)来诊断各种眼睛疾病,包括青光眼、糖尿病视网膜病变和老年性黄斑变性。在成像过程中,探头向眼睛发送一束光,并测量各种反射需要多长时间才能反射回来,以破译组织内的结构。
在临床上,OCT系统是传统的大型桌面系统,训练有素的技术人员使用它来捕捉眼睛的多个图像。患者必须牢固地安置在头部和下巴托上,以确保正确的位置和限制任何动作。除了不舒服之外,这种头部和下巴托架并不适合所有人,这使得某些人很难接受扫描。
而且,并不是所有地方都有受过高度训练的专业技术人员,比如眼科摄影师。
创新过程
使用新型扫描仪时,病人只需走近机器,站在机械臂前。放置在机器人左右两侧的3D摄像机有助于在空间中找到患者,而机器人手臂上的小型摄像机则搜索眼睛上的地标,以精确定位扫描仪。该系统能够扫描黄斑(视网膜中负责中心视觉的部分)和角膜(眼睛的透明前部),这是许多眼病发生的部位。
该工具扫描和成像每只眼睛的时间不到10秒,整个过程在50秒内完成。
机械臂给人们带来了手持OCT扫描仪的灵活性,而且不需要担心操作者的任何颤抖。如果人移动,机器人也会跟着移动。只要扫描器对齐到距离瞳孔所需位置不到一厘米的位置,扫描器就能获得与台式扫描仪一样好的图像。
由于患者从不与系统进行身体接触,他们的工具避免了传统OCT系统中共享下巴和头枕所引起的任何卫生和传染病问题。研究人员还证明,他们的机器人系统是非常安全的,特别是考虑到它可以非常接近患者的脸。
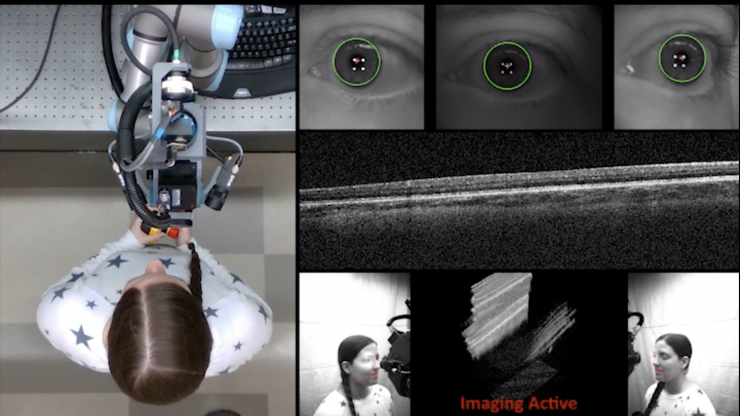
该团队已经开始了下一阶段的临床工作,他们已经开始对志愿者的眼睛进行成像,以继续改进机器人的瞄准能力。接下来,他们希望对患有视网膜或角膜疾病的患者进行成像,以测试他们的机器人捕捉异常情况的能力。
他们还在努力改善视网膜扫描仪的视野,因为他们的第一次迭代能够捕捉关键特征,但需要将多个图像拼接在一起,才能获得视网膜的完整视图。
创新关键点
这种新工具结合了成像扫描仪和机械臂,可以在不到一分钟的时间内自动跟踪和成像患者的眼睛,并产生与专业眼科诊所的传统扫描仪一样清晰的图像。
创新价值
人们不需要经过高级培训就能使用该新工具。它可以很容易地用于验光师办公室、初级保健诊所甚至急诊科等地方。
由于患者从不与系统进行身体接触,新工具也避免了传统OCT系统中共享下巴和头枕所引起的任何卫生和传染病问题。
Innovative development of robotic scanners to automate diagnostic eye imaging
With the new scanners, patients simply walk up to the machine and stand in front of the robotic arm. 3D cameras placed on the left and right sides of the robot help find patients in space, while small cameras on the robot's arm search for landmarks on the eyes to pinpoint the scanner. The system is able to scan the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision, and the cornea, the clear front of the eye, where many eye diseases occur.
The tool scans and images each eye in less than 10 seconds, and the entire process is completed in 50 seconds.
The robotic arm brings the flexibility of a handheld OCT scanner without the need to worry about any tremors from the operator. If the person moves, the robot moves with him. As long as the scanner is aligned to within a centimeter of the desired position of the pupil, the scanner can obtain images as good as those obtained with a benchtop scanner.
Because patients never have physical contact with the system, their tool avoids any of the hygiene and infectious disease issues that arise from sharing the chin and headrest in traditional OCT systems. The researchers also demonstrated that their robotic system is very safe, especially considering that it can get very close to the patient's face.
The team has moved on to the next phase of clinical work, where they have begun imaging volunteers' eyes to continue improving the robot's aiming ability. Next, they hope to image patients with retinal or corneal diseases to test their robot's ability to pick up abnormalities.
They are also working to improve the visual field of the retina scanner, as their first iteration was able to capture key features but required stitching together multiple images to get a complete view of the retina.
智能推荐
利用基因疗法制备可挽救眼部疾病的迷你视网膜
2022-08-04根据伦敦大学学院和都柏林三一学院对实验室培养的“迷你视网膜”的一项新研究,一种新的基因疗法有望治疗一组常见的遗传性眼病。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向通过眼科血液测定开发非侵入式颅内压监测方法
2022-08-15利用眼睛与颅内压之间的关系,在传统颅内压监测的基础上开发新技术,通过测量眼睛内的血管动态来检查创伤后的脑部高压状况。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向细胞学创新 | 从成体细胞而非人类胚胎中可提取干细胞
2022-09-21新南威尔士大学悉尼分校的生物医学工程师和医学研究人员已经独立地发现了胚胎血液干细胞的创造,有一天可能会消除对干细胞献血者的需求。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向眼视光医学创新思维 | 创新应用基因疗法恢复视网膜视锥受体的功能
2022-09-26伦敦大学学院的研究人员领导的一项研究报告称,基因疗法可部分恢复两名天生完全色盲儿童视网膜锥受体的功能。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向