创新背景
在传统的细胞诊断过程中,从组织刮刮或细针活检中获得的细胞被放在载玻片上,并被染色,以便训练有素的医生仔细放大和检查。但在某些情况下,染色过程可能会损伤细胞,将切片送到训练有素的专家的眼睛可能需要几天甚至几周的时间。
创新过程
在新的全息成像方法中,样本细胞可以从收集仪器中冲洗到生物兼容的溶液中,并插入微流控芯片中。这个小装置将样品转移到一系列平行通道中,这些通道在直线相机下方通过,有点像传送带在自动扫描仪下通过新制造的物品进行检测。当放慢速度时,细胞图像的移动会让人想起《黑客帝国》(the Matrix)中电脑屏幕上层叠而下的绿色字符。
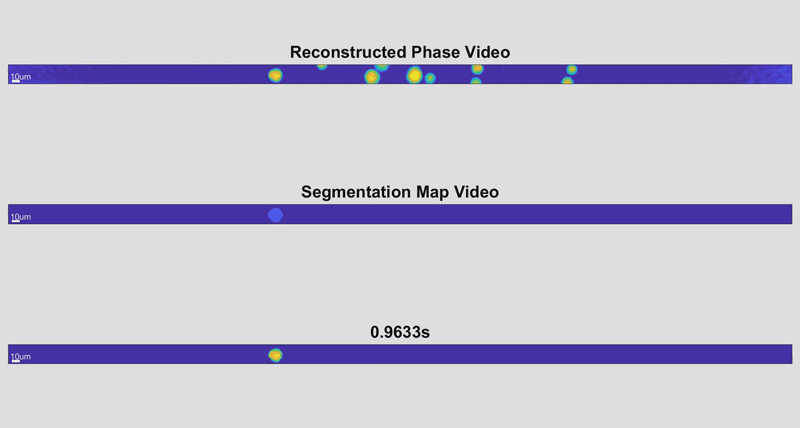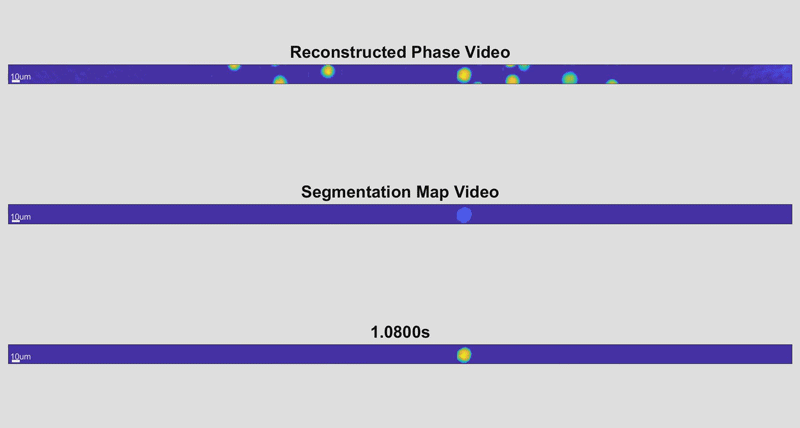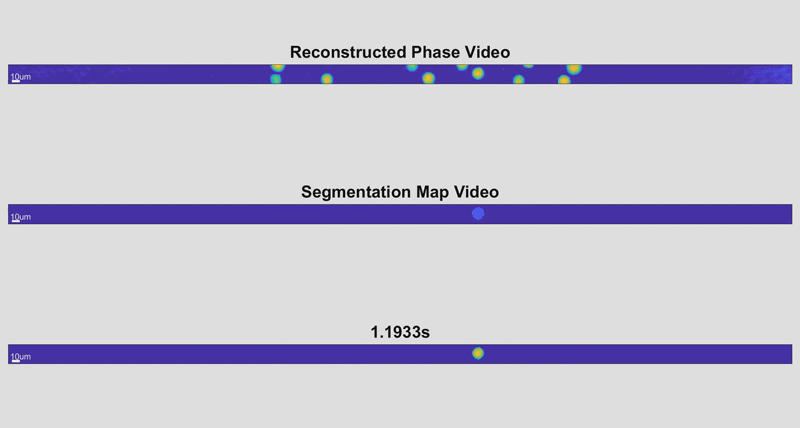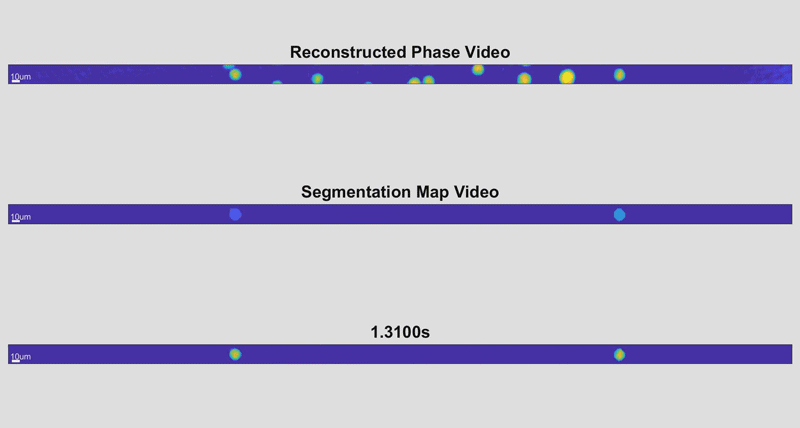
底线包含整个单元格,因为它们被识别。中间线显示每个像元扫描的区域参数。顶线显示每个细胞的最终扫描,颜色编码以指示厚度。
当这些细胞飞过时,该设备会自动挑选出整个细胞,并通过它们发光。根据光从旅途返回所需时间的差异和一个畅通的参考光束,相机可以确定每个细胞的地形,并计算其形状和高度等特征。虽然这些听起来像是简单的测量,但当它们与数以万计的数据点和先进的深度学习技术相结合时,它们可以成为发现疾病的灯塔。
处理一毫升的样本大约需要30秒,其中可能包含50多万个细胞。一旦完成,病理学家可以提取任何被成像的细胞的单个数据,以便更仔细地检查。
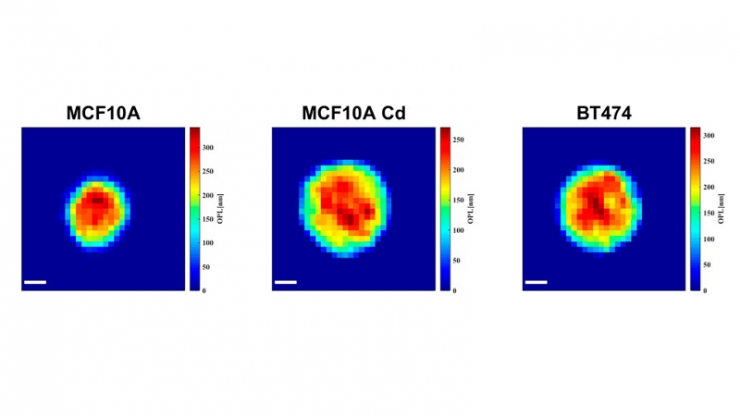
由新的高速细胞全息设备拍摄的三张单细胞图像。通过测量细胞的物理方面,研究人员可以识别疾病的迹象。此处,较深、较红的颜色表示较高的单元格高度,而较浅的蓝色表示较短的单元格高度。
为了证明这种方法的潜力,Wax和Chen使用它对来自三个不同细胞系的8500个细胞进行了成像,这些细胞系分别是健康的乳腺细胞、癌变的乳腺细胞和暴露于已知的强致癌物镉中的癌前乳腺细胞。虽然这项技术捕获了细胞的25种独立物理特征,但研究人员发现,在这种情况下,区分这三种类型只需要4种。
使用机器学习算法,该设备能够成功地对每个细胞进行分类,准确率为98%至99%,仅利用其占据的2D面积、3D空间、形状和平均高度。
创新关键点
在新的全息成像方法中,样本细胞可以从收集仪器中冲洗到生物兼容的溶液中,并插入微流控芯片中。当这些细胞飞过时,该设备会自动挑选出整个细胞,并通过它们发光。
创新价值
在概念验证演示中,该技术仅使用25个全息面板中的4个基本细胞物理参数,就能以接近100%的准确率区分健康样本和癌变或暴露于致癌物的癌前细胞。研究结果指向了一种很有前景的筛查或诊断技术,它比目前的标准做法更简单、更便宜,使其成为在偏远、低资源环境中使用的潜在目标。
The high speed movement of cells can be captured and imaged by a new holographic system
In the new holographic imaging method, sample cells can be flushed from the collection instrument into a biocompatible solution and inserted into a microfluidic chip. The gadget transfers samples into a series of parallel channels that pass under a straight-line camera, a bit like a conveyor belt passing newly manufactured items under an automated scanner. When slowed down, the movement of the cell image recalls the cascading green characters on a computer screen in "The Matrix."
As the cells fly by, the device automatically picks out the entire cell and lights through it. Based on differences in the time it takes light to return from the journey and a smooth reference beam, the camera can determine the topography of each cell and calculate features such as its shape and height. While these may sound like simple measurements, when combined with tens of thousands of data points and advanced deep learning techniques, they can be a beacon for disease discovery.
It takes about 30 seconds to process a one-milliliter sample, which can contain more than half a million cells. Once this is done, the pathologist can extract individual data from any cell being imitated for closer examination.
To demonstrate the potential of this approach, Wax and Chen used it to image 8,500 cells from three different cell lines: healthy breast cells, cancerous breast cells, and precancerous breast cells exposed to cadmium, a known potent carcinogen. While the technique captures 25 separate physical features of cells, the researchers found that in this case, only four were needed to distinguish the three types.
Using machine learning algorithms, the device was able to successfully classify each cell with 98 to 99 percent accuracy using only the 2D area, 3D space, shape, and average height it occupied.
智能推荐
生物医学工程创新 | 创新利用铝制成可在液态金属中分解的医学设备
2022-11-09麻省理工学院的研究人员利用一种导致金属断裂的现象,设计了一种更简单的移除不再需要的医疗设备的方法。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向生物医学工程创新 | 利用活细胞构建“半互穿聚合物网络”使药物输送更安全
2022-09-30杜克大学的生物医学工程师已经证明了一种被称为半互穿聚合物网络的交织复合材料可以由活细胞产生。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向生物医学创新 | 创新利用“双轴法”增加OCT在生物组织中的视野深度
2022-09-28杜克大学的生物医学工程师展示了一种增加光学相干断层扫描(OCT)对皮肤下结构成像的深度的新方法——双轴法。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向新材料 | 开发新型生物材料可加速身体自愈过程
2022-09-29研究团队为外科医生设计了一种绷带,植入骨折部位可加速自然愈合过程。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向