创新背景
以前关于物质变形的工作通常不是编程,而是被编程。也就是说,配备了设计的主动元素的软表面可以在几种形状之间变换形状,就像折纸一样,在光、热或其他刺激触发下做出反应。相比之下,研究人员想要创造一种更可控的东西,可以随时变形和重新配置成任何物理上可能的形状。
创新过程
为了创造可伸缩的软表面,研究人员首先布置了一个蛇形梁网格,它由一层薄薄的聚合物包裹的薄薄的金制成。单个光束只有8微米厚——大约是棉纤维的厚度——不到一毫米宽。光束的重量使磁力容易而迅速地使它们变形。
为了产生局部力,表面被置于低水平的静态磁场中。电压的变化会沿着黄金电网产生复杂但容易预测的电流,驱动电网的平面外位移。
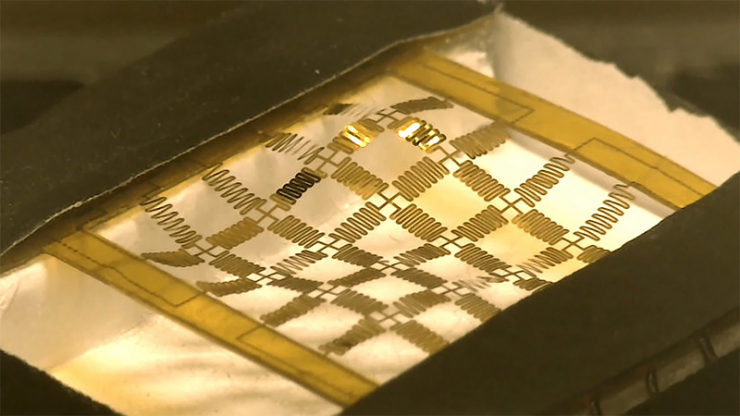
这是第一个速度足够快的人造软表面,可以精确地模拟自然界中连续的形状变化过程。一个关键的进步是结构设计,使电气输入和结果形状之间具有不同寻常的线性关系,这使得很容易找出如何施加电压来实现各种各样的目标形状。
新型“超表面”展示了广泛的变形和模仿技能。它创造了凸起,并在表面上移动,就像一只猫试图从毯子下找到出路,振荡的波模式,以及液体滴落和扑向固体表面的令人信服的复制品。它可以在任何需要的速度或加速度下产生这些形状和行为,这意味着它可以重新想象被困住的猫或滴落的液滴以慢动作或快进。
通过摄像头监控变形的表面,扭曲的表面也可以学会自己重建形状和图案。通过缓慢调整施加的电压,学习算法接收3D成像反馈,并找出不同输入对超表面形状的影响。
由于表面通过试验和错误自学移动,它也可以适应损伤、意外的物理约束或环境变化。在一项实验中,尽管它的一根横梁被切断,但它很快学会了模仿一个鼓胀的土堆。在另一种情况下,尽管在网格的一个节点上附加了重量,它仍然能够模仿出类似的形状。
创新关键点
为了创造可伸缩的软表面,研究人员首先布置了一个蛇形梁网格,它由一层薄薄的聚合物包裹的薄薄的金制成。单个光束只有8微米厚——大约是棉纤维的厚度——不到一毫米宽。光束的重量使磁力容易而迅速地使它们变形。
为了产生局部力,表面被置于低水平的静态磁场中。电压的变化会沿着黄金电网产生复杂但容易预测的电流,驱动电网的平面外位移。
创新价值
这项新技术有希望创建具有集成形状传感功能的机器人超表面,对自然界中复杂的动态表面进行实时形状模拟,如水波纹、鱼鳍或人脸。该实验室还可能研究在原型机上嵌入更多组件,如机载电源、传感器、计算资源或无线通信能力。
这种软表面可以应用于远程操作机器人、动态3D显示、伪装、外骨骼或其他智能功能表面,可以在恶劣、不可预测的环境中工作。有许多直接的机会来扩展软表面的规模和配置。例如,一个表面阵列可以缩放到触摸屏的大小。或者,更高精度的制造技术可以将尺寸缩小到一毫米,使其更适合于生物医学应用。
Developing self-reinventing artificial soft surfaces to mimic objects in nature
To create the stretchy soft surface, the researchers first laid out a mesh of serpentine beams made of thin gold wrapped in a thin layer of polymer. Individual beams are just eight microns thick - about the thickness of cotton fibres - and less than a millimetre wide. The weight of the beams allows magnetic forces to deform them easily and quickly.
To generate local forces, the surface is subjected to a low level of static magnetic field. Voltage changes generate complex but easily predictable currents along the gold grid, driving out-of-plane displacement of the grid.
This is the first artificial soft surface fast enough to accurately mimic the continuous process of shape change in nature. A key advance has been structural design that enables an unusual linear relationship between electrical inputs and the resulting shape, which makes it easy to figure out how to apply voltage to achieve a wide variety of target shapes.
The new "metasurface" exhibits a wide range of metamorphosis and imitation skills. It creates bumps and moves across the surface like a cat trying to find its way out from under a blanket, oscillating wave patterns, and a convincing replica of liquid dripping and swooping on solid surfaces. It can produce these shapes and behaviors at any required speed or acceleration, meaning it can reimagine a trapped cat or a dripping droplet in slow motion or fast forward.
By monitoring the deformed surface with a camera, the distorted surface can also learn to reconstruct shapes and patterns on its own. By slowly adjusting the applied voltage, the learning algorithm receives 3D imaging feedback and finds out how different inputs affect the metasurface shape.
Since a surface teaches itself to move by trial and error, it can also adapt to damage, unexpected physical constraints, or environmental changes. In one experiment, it quickly learned to mimic a bulging mound, despite having one of its beams cut off. In the other case, it was able to mimic a similar shape despite attaching weight to one node of the grid.
智能推荐
使用硫化学气相沉积制备超高折射率的聚合物
2022-08-05通过一步法气相沉积工艺提高折射聚合物薄膜的高透明度。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向新材料 | 创新利用”catholyte”开发新材料可使植入式电池更持久
2022-11-07研究人员提出了一种新方法来提高这些不可充电电池的能量密度,种技术可以使使用寿命增加50%。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向智能制造 | 新型“材料显微外科”技术可提高废物回收效率
2022-09-27新南威尔士大学可持续材料研究与技术中心(SMaRT)的“微回收科学”先驱们开发出了一项有望提升先进制造业的新技术。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向热中子的核反应让二维材料的掺杂更清洁
2022-07-27研究团队首次实现通过NTD掺杂二维层状硒化铟。他们成功地缩小了带隙并增加了锡掺杂层状硒化铟的电子迁移率,将场效应电子迁移率从 1.92cm2·V-1·s-1 提高到195cm2·V-1·s-1。同时,光电探测器的响应度提高了约 50 倍,达到了397 A/W。NTD工艺具有巨大的应用前景,它将为材料技术带来新的重大机遇。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向