创新背景
细胞膜在生命中至关重要,因为它们可以形成隔膜,从而将不同类型的组织和细胞分离开来。
此前,科学家们一直在努力为脂质和脂质体寻找合适的缓冲条件,以确保它们的DNA“计算机”能够吸附在脂质体上。
创新过程
科学家们已经研究出了如何最好地让DNA与我们体内的细胞膜进行通信,这为在液滴中创建“迷你生物计算机”铺平了道路,这种计算机在生物传感和mRNA疫苗方面有潜在用途。
它发现了设计和构建DNA“纳米结构”的最佳方法,可以有效地操纵合成脂质体——传统上用来输送治疗癌症和其他疾病的药物的微小气泡。
通过改变脂质体的形状、孔隙度和反应性,还有更大的应用,比如构建小分子系统,这些系统可以感知周围环境,并对信号做出反应,释放物质,比如当药物分子接近目标分子时。
新南威尔士大学生物技术和生物分子科学学院的首席作者马特·贝克博士表示,该研究发现了如何从DNA中构建“小块”,并研究出了如何用胆固醇最好地标记这些小块,以使它们粘附在植物和动物细胞的主要成分脂类上。
此项研究的一个主要应用是生物传感:将一些液滴插入一个人或病人体内,当液滴在身体中移动时,它会记录下当地的环境,对其进行处理并输出结果,这样就可以“读出”当时所处的环境。
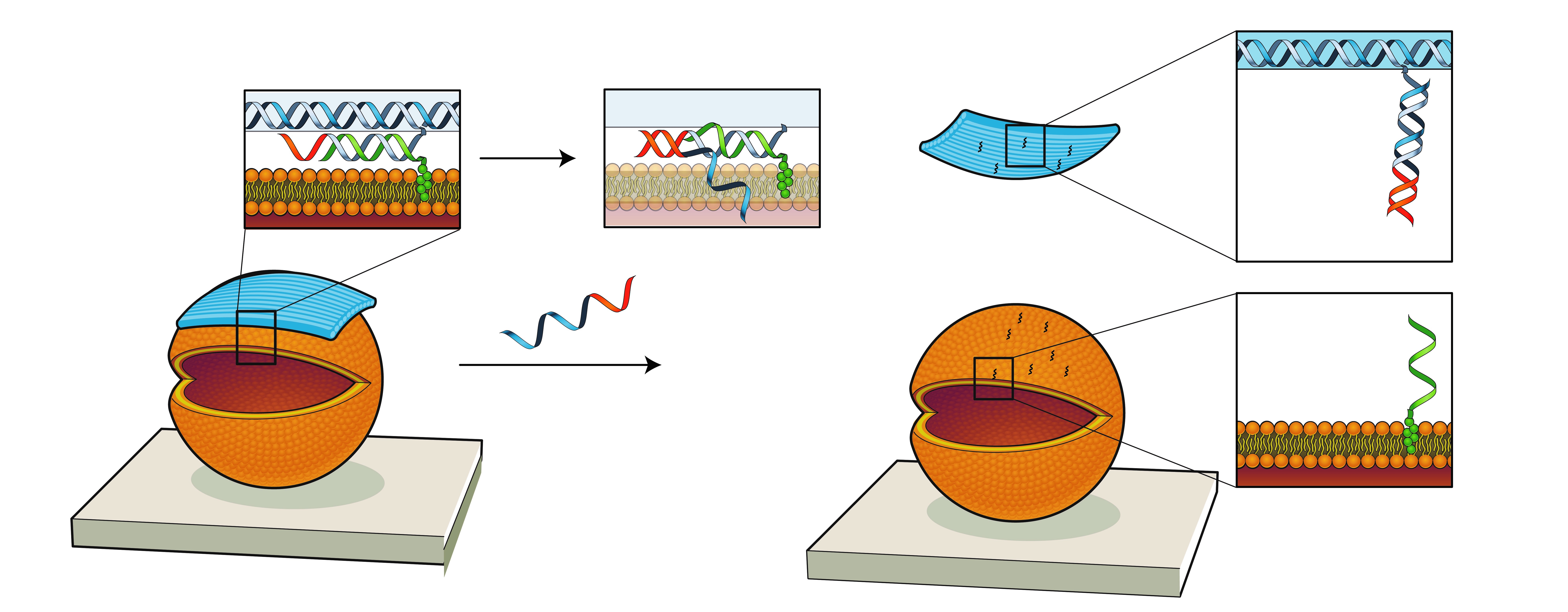
图像显示了如何构建DNA“纳米结构”以有效操纵合成的脂质体。(左)DNA链被编织以将DNA纳米桩(蓝色)与脂质体(橙色)结合,然后(右)在给定特定信号时释放它。
脂质体纳米技术随着脂质体与RNA疫苗(如辉瑞和Moderna COVID-19疫苗)一起使用而崭露头角。研究人员建立了全新的DNA纳米技术,可以根据需要在膜上打孔,从而能够通过膜传递重要信号。
这最终是细胞如何相互交流的生命基础,以及研究如何在一个细胞中制造有用的东西,然后输出到其他地方使用。
创新关键点
通过改变脂质体的形状、孔隙度和反应性,还有更大的应用,比如构建小分子系统,这些系统可以感知周围环境,并对信号做出反应,释放物质,比如当药物分子接近目标分子时。
创新价值
如何在DNA中构建纳米结构并使其粘附在脂质上的发现对生物传感和信使rna疫苗具有重要意义。
Construct "nanostructures" to manipulate synthetic liposomes to facilitate cell communication
Scientists have worked out how best to get DNA to communicate with cell membranes in our bodies, paving the way for the creation of "mini biological computers" in droplets with potential uses in biosensing and mRNA vaccines.
It has found the best way to design and build DNA "nanostructures" that can efficiently manipulate synthetic liposomes - tiny air bubbles traditionally used to deliver drugs to treat cancer and other diseases.
There are larger applications by changing the shape, porosity, and reactivity of liposomes, such as building small molecule systems that sense their surroundings and respond to signals to release substances, such as when a drug molecule approaches a target molecule.
Lead author Dr Matt Baker, from the University of New South Wales School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences, said the study had discovered how to build "patches" from DNA and worked out how best to label these patches with cholesterol to make them stick to lipids, the main components of plant and animal cells.
One of the main applications of the research is biosensing: when a droplet is inserted into a person or patient, it records the local environment as it moves through the body, processes it and outputs the results so that it can "read" the environment at that moment.
Liposomal nanotechnology has come to the fore with the use of liposomes in conjunction with RNA vaccines such as the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines. Researchers have built novel DNA nanotechnology that can punch holes in membranes as needed, enabling vital signals to be transmitted through them.
This is ultimately the basis of life for how cells communicate with each other, and for figuring out how to make something useful in one cell that can then be exported for use elsewhere.
智能推荐
来自无标签 RNA 序列的新型基石模型预测RNA结构及功能
2022-07-20为了弥补标注数据的不足,本文展示了一项可为 RNA 各类研究提供丰富结构功能知识的基石模型 ——RNA foundation model (RNA-FM)。作为全球首个基于 23 million 的无标签 RNA 序列通过无监督方式训练得到的 RNA 基石模型,RNA-FM 挖掘出了 RNA 序列中蕴含的进化和结构模式。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向创新应用免疫治疗生物标志物控制1型糖尿病
2022-08-04伦敦大学学院(UCL)的科学家们发现了新的生物标志物,这些标志物可能会识别出那些将受益于免疫治疗药物Abatacept的1型糖尿病患者,这一发现最终可能会帮助数千人更有效地控制这种疾病。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向融合Cre-loxP和CRISPR-Cas9的新型基因打靶技术构建微型扰动图谱
2022-07-27研究团队提出了一种崭新的小鼠基因打靶技术——iMAP,其iMAP品系携带100个gRNA表达单位,靶向90个功能不甚清晰的基因,以此构建了一个微型扰动图谱,揭示了这90个基因分别在39个组织/细胞中对细胞存活、扩增、分化的影响。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向