创新背景
科技水平的发展为人造材料带来了先进的性能,但材料要保持活性并适应情况变化自我进行改变、拓展功能性作用还有很长的路要走。大多数技术和工程使用的激光器由晶体材料组成,具有精确的静态特性,如果能制造出融合结构和功能的激光器,使其像生物材料一样根据情况变化重新配置自身并进行合作,将有助于技术和工程发展。
创新过程
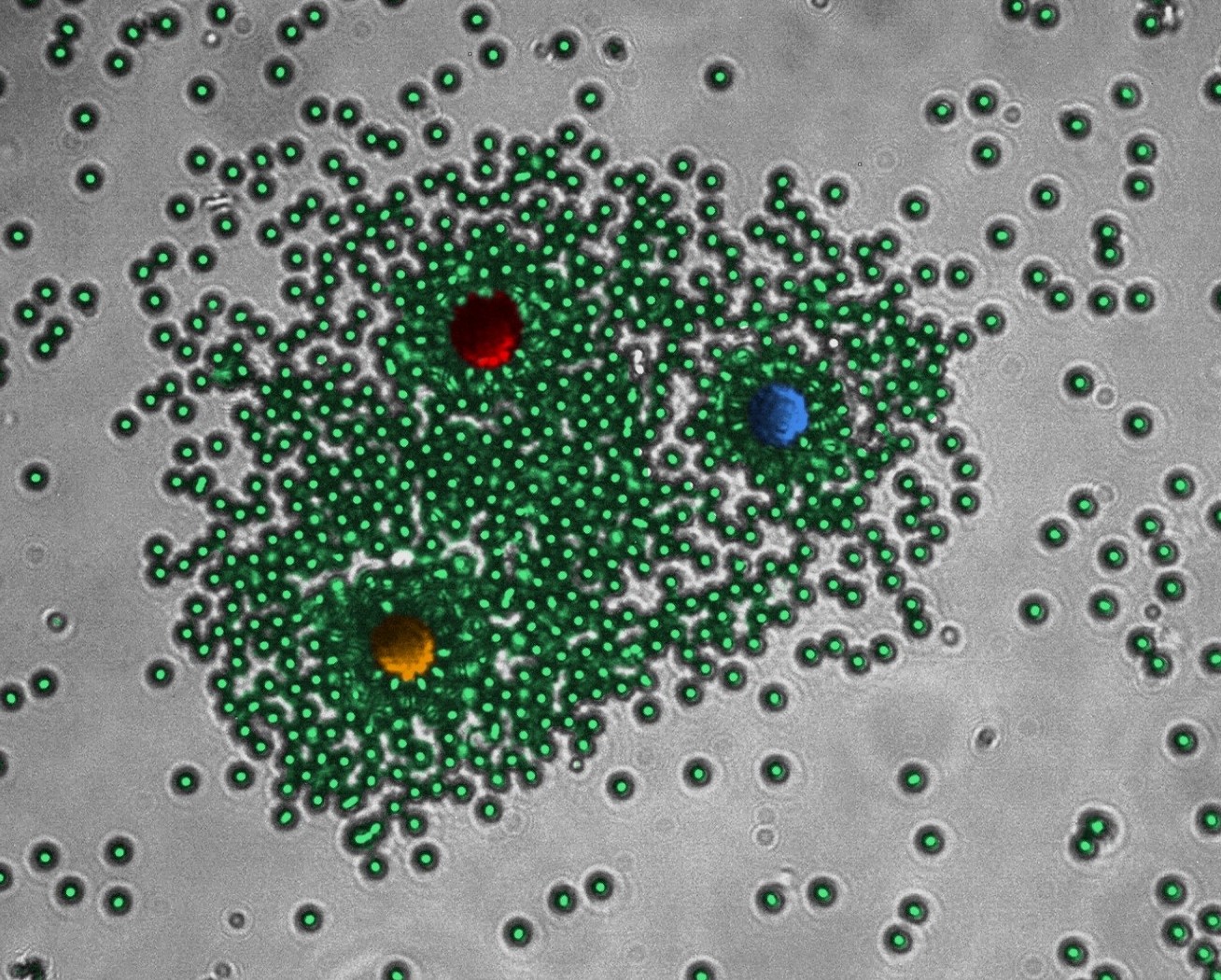
激光器是通过放大光来产生特殊形式的光的装置,伦敦帝国理工学院和伦敦大学学院的研究人员用分散在具有高增益液体中的微粒组成自组装激光器来自可重构胶体组件,在耗散胶体组件内经历多次散射的光的光学放大。当足够多的微粒聚集在一起时,就会利用外部能量产生激光。
使用外部激光加热一侧涂有光吸收材料的粒子,微粒会聚集在其周围,动态随机激光器具有响应性,呈现连续可调的激光阈值。微粒簇产生的激光会通过改变外部激光的强度来打开和关闭,反向控制簇的密度和大小。
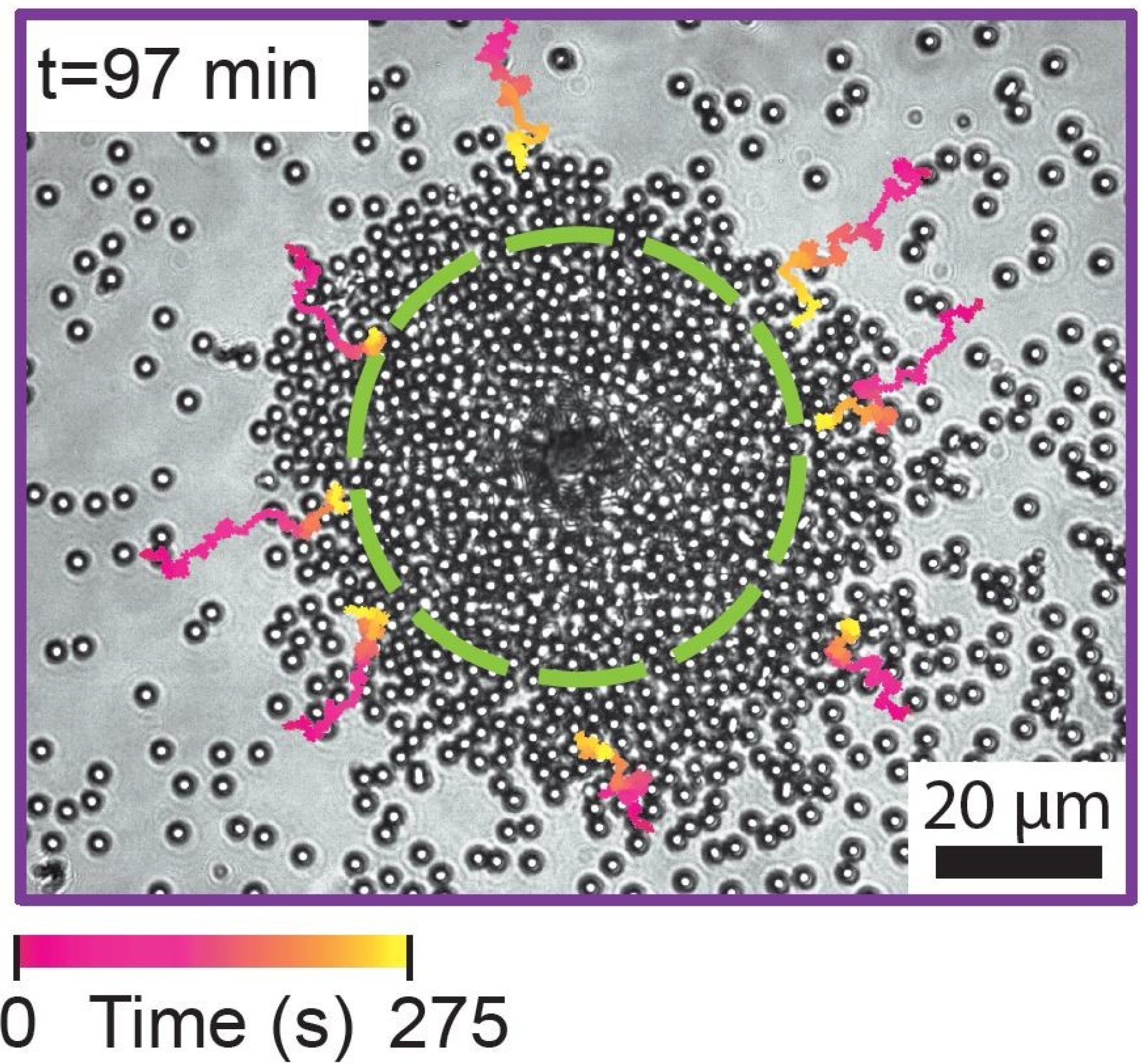
激光系统可以可以通过模拟结构和功能之间不断发展的时空关系来重新配置和组装合作,迈出模拟生活材料典型结构和功能之间发展的关系的第一步,拥有单元可利用可用能量执行任务的非平衡组件特征。
激光系统加热不同的粒子会在空间中转移激光簇,粒子之间会进行协作,创建具有两个簇以外的属性的簇,改变它们的形状和提高它们的激光能力,展现了新激光系统的适应性。研究相关成果论文发表在2022年7月14日出版的《自然物理》上。
研究人员表示,目前激光在医学、电信和工业生产中广泛使用,体现具有逼真特性的激光器将能够开发用于传感应用、非常规计算、新型光源和显示器的自主耐用的新型材料和设备。
研究团队将继续探索如何改善激光的自主行为,使它们更加逼真。新技术有助于开发能够更好地模仿生物物质特性的智能光子材料,使其具有响应性、适应性、自我修复和集体行为。
创新关键点
使用可重构的胶体组件开发自组织激光器,使其可以根据条件调整结构并配合协作。
创新价值
通过模仿生命系统的特征开发的自组织激光器可以带来用于传感、计算、光源和显示器的新材料。
Reconfigurable colloid assembly to manufacture self-organizing lasers
Lasers are devices that produce special forms of light by amplifying light, and researchers at Imperial College London and University College London assemble self-assembled lasers composed of particles dispersed in a high-gain liquid from a reconfigurable colloidal component that undergoes multiple optical amplifications of scattered light within the dissipative colloidal assembly. When enough particles come together, the laser is generated using external energy.
Particles coated with light-absorbing material on one side are heated with an external laser, particles gather around it, and the dynamic random laser is responsive, presenting a continuously adjustable laser threshold. The laser generated by the particle cluster turns on and off by changing the intensity of the external laser, reversing the density and size of the cluster.
Laser systems can be reconfigured and assembled cooperatively by simulating evolving spatiotemporal relationships between structures and functions, taking the first step in simulating the evolving relationships between the typical structures and functions of living materials, possessing the characteristics of non-equilibrium components of the units that can utilize available energy to perform tasks.
Laser systems heating different particles transfer laser clusters in space, and particles collaborate to create clusters with properties other than two, changing their shape and increasing their laser capabilities, demonstrating the adaptability of the new laser system. The paper was published in the July 14, 2022 issue of Natural Physics.
Lasers, which are now widely used in medicine, telecommunications and industrial production, will be able to develop new materials and devices that are autonomously durable for sensing applications, unconventional computing, new light sources and displays, the researchers said.
The research team will continue to explore how to improve the autonomous behavior of lasers to make them more realistic. New technologies help develop smart photonic materials that better mimic the properties of biological matter, making them responsive, adaptive, self-healing, and collectively behaving.
智能推荐
数字化+农业 | 利用数字化平台对抗东非的 Striga 虫害
2022-08-24研究团队为了应对striga寄生虫,更新并调整了现有技术,开发了Field Book数字平台以帮助该植物科学家进行striga寄生虫的相关数据收集。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向使用含有数字芯片的聚合物纤维设计智能服装
2022-08-15麻省理工学院的研究人员通过将数百块方形硅微尺度数字芯片放入预制体中,再用预制体制造聚合物纤维,通过精确地控制聚合物的流动,制造出了第一种能够被缝进衣服中的具有数字功能的纤维。这种新型纤维不仅能够写入、存储并读取大量信息,还能够感知、存储、分析和推断穿着者的活动。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向悬挂式屋顶的San Giacomo Apostolo教堂
2022-07-07“San Giacomo Apostolo”教堂的落地在当地形成了新的中心和社区地标,如催化剂一般促进社区内的社交、教育活动和内部互动。教堂屋顶的起伏来源于罗马式和哥特式大殿的拱顶原型。然而,建筑师们将平行线重新组合成放射状,让祭坛位于拱顶的中心,抛物线拱顶由此辐射而出。项目为社区提供教育、会议和娱乐服务的空间,并为附近学校提供新的多功能空间。教区综合体与这些空间对话,并注重体现与周围环境的关系。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向利用光学干涉测量技术使花香释放过程可视化
2022-08-05利用光学干涉测量显示百合花释放挥发性有机化合物的频率,可视化气味排放可以帮助了解植物和传粉媒介的相互作用。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向