创新背景
曲霉病是由烟曲霉引起的霉菌感染,通常会影响肺部,在免疫功能低下的个体中致死率高治疗该病需要模型帮助,以往常用动物实验寻找合适的方法。
创新过程
侵袭性曲霉病通常发生在真菌菌丝侵入血管中,能对抗这种真菌感染的只有少数活性物质,所以建立模型帮助研究治疗曲霉病需要能够代表这种侵入性增长。
莱布尼茨自然科学研究所的研究人员开发了可以实时跟踪真菌菌丝扩散以及免疫细胞反应的算法和基于芯片的肺部感染模型,可以实时观察由侵袭性真菌感染曲霉病引起的肺组织损伤并帮助减少实验动物的数量,相关研究成果《侵袭性曲霉病芯片:人类烟曲霉菌感染的定量治疗研究》发表在《生物材料》上。

器官模型由两层由人工膜隔开的细胞组成。一层暴露在空气中,由肺的表面细胞组成;另一层由血管细胞组成,血液样营养液不断流过它们。研究人员通过在模型中添加真菌使器官模型变成感染模型。研究人员表示,模型转变的困难在于确定感染的准确严重程度,如果在模型中添加过多的烟曲霉菌,就会导致肺细胞死亡。如果太少,就无法观测到任何东西。
“芯片肺”模型创建了一个由与巨噬细胞共培养的肺泡上皮细胞层和三维灌注微环境中的内皮衬里组成的气液界面,并且具有显微成像和高级图像分析,令研究者可以在显微镜下观察和量化3D现场曲霉病。通过表征真菌药物有效地干扰已经在治疗相关的最小抑制浓度下的菌丝形成,证明了IAC模型在抗真菌药物测试中的转化潜力,以及人类免疫细胞或各种药物可以添加到这个系统中。
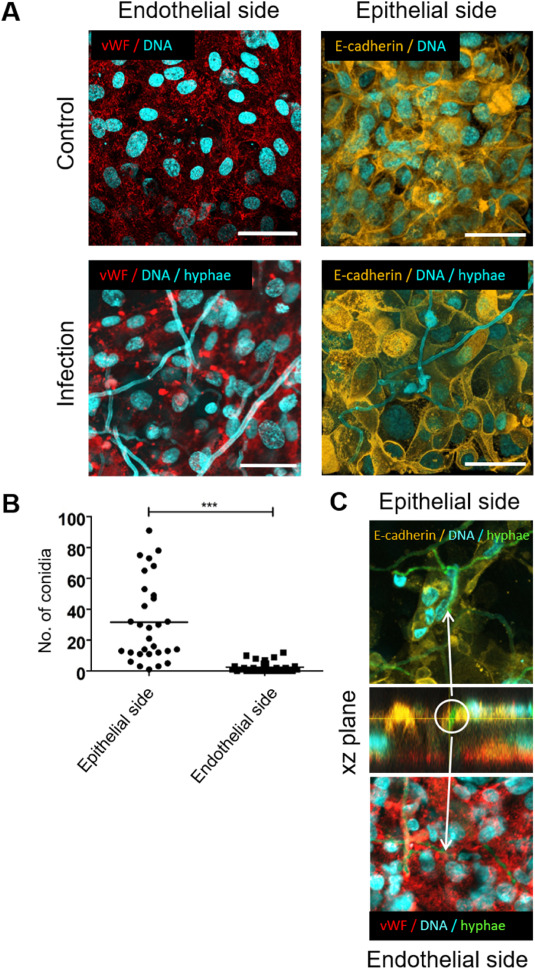
在得到图像之后,可以感受到感染状况的变化,但无法量化。研究开发出能将真菌菌丝或免疫细胞与组织细胞以及周围环境区分开来的算法,使用荧光染料对不同的细胞类型进行颜色编码区分,然后用荧光的强度来确定免疫细胞吃了多少真菌。
新的模型目前只是一种简化的感染模型,无法和完整的器官一对一进行比较,研究将进一步优化模型。
创新关键点
添加真菌将器官模型转变为感染模型,帮助研究侵袭性曲霉病的感染状况。
创新价值
研究对更好地研究真菌感染做出贡献,可以取代部分动物实验。
The new infection model provides real-time microscopic observation of lung tissue conditions
Invasive aspergillosis usually occurs in fungal hyphae invading blood vessels, and only a few active substances can fight this fungal infection, so modeling to help study the treatment of aspergillosis needs to be representative of this invasive growth.
Researchers at the Leibniz Institute for Natural Sciences have developed algorithms and chip-based lung infection models that can track fungal hyphal diffusion and immune cell response in real time, which can observe lung tissue damage caused by invasive fungal infection with aspergillosis in real time and help reduce the number of laboratory animals.
The organ model consists of two layers of cells separated by artificial membranes. A layer exposed to air, consisting of cells on the surface of the lungs; The other layer consists of vascular cells through which a blood-like nutrient solution is constantly flowing. The researchers turned the organ model into an infection model by adding fungi to the model. The researchers say the difficulty in model transition is determining the exact severity of the infection, and adding too much Aspergillus fumigatus to the model can lead to lung cell death. If there are too few, nothing can be observed.
The "lung on chip" model created a gas-fluid interface consisting of a co-cultured alveolar epithelial cell layer with macrophages and an endothelial lining in a three-dimensional perfusion microenvironment, and featured microscopic imaging and advanced image analysis that allowed researchers to observe and quantify 3D field aspergillosis under a microscope. By characterizing fungal drugs to effectively interfere with hyphae formation already at treatment-related minimum inhibitory concentrations, demonstrating the translational potential of IAC models in antifungal drug testing, and that human immune cells or various drugs can be added to this system.
After obtaining the image, the change in the infection status can be felt, but it cannot be quantified. Research has developed algorithms that can distinguish fungal hyphae or immune cells from histiocytes and their surroundings, using fluorescent dyes to color-code different cell types, and then using the intensity of the fluorescence to determine how much fungus the immune cells ate.
The new model is currently just a simplified model of infection and cannot be compared with the complete organ one-on-one, and the study will further refine the model.
智能推荐
创新可穿戴成像帽为婴儿大脑成像
2022-08-03由伦敦大学学院的研究人员领导的一个团队展示了一种新的可穿戴的、对婴儿友好的大脑测绘技术,它对理解自闭症谱系障碍和脑瘫等发育状况具有重要意义。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向创新人工智能应用程序帮助更准确地诊断艾滋病毒
2022-08-01伦敦大学学院和非洲卫生研究所(AHRI)的研究人员开发的开创性技术可以改变准确解读艾滋病毒检测结果的能力,特别是在低收入和中等收入国家。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向医学影像学创新 | 利用功能性磁共振成像技术开发婴儿扫描仪
2022-08-29研究团队开发了一种专门为婴儿设计的扫描仪,创新性地利用功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)技术,从婴儿身上扫描到了以往难以达到的大量数据,这项技术将推动整个领域的发展。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向物联网技术创新 | 弹性粘合剂配对传感器创新超声成像设备
2022-07-29结合弹性粘合剂和刚性传感器制作超声成像贴纸,弹性体延长贴纸监测时间,为医疗成像技术拓展新方法。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向