创新背景
谷物生长和储存过程中都需要使用杀虫剂来杀灭害虫保护作物,但杀虫剂无区别地杀灭虫类不可避免地对一些益虫甚至鸟类和蜜蜂都有副作用。应用天然物质研发农药作为杀虫剂的替代品是农药更迭的必然趋势。
创新过程
目前保护作物免受害虫侵害最常用的是一些化学杀虫剂,比如来自新烟碱类的内吸性杀虫剂吡虫啉。杀虫剂的灭杀性不仅是害虫的天敌,也对其他生物具有破坏性影响,德国昆虫研究所Thomas Schmitt教授和同事合作,测试研究了两种天然物质,试图令其成为化学杀虫剂的替代品,相关研究成果《增强型硅藻土、吡虫啉和Beauveria bassiana对3种鞘翅目和1种伪蚜粒昆虫的持久性和有效性》发表在2021年1月5日出版的《环境科学与污染研究》上。
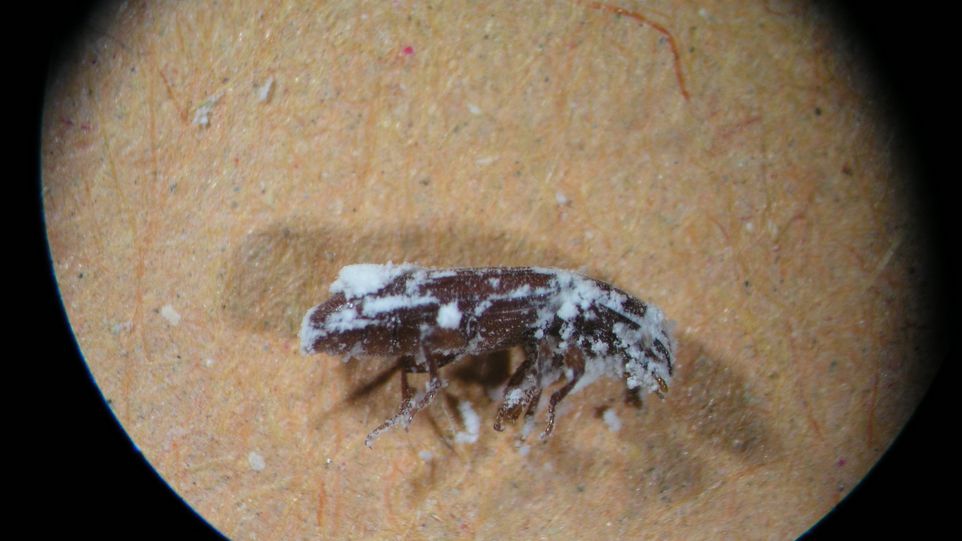

研究将硅藻土、昆虫致病的寄生真菌Beauveria bassiana和杀虫剂吡虫啉用于红粉甲虫、小加林螟虫和锈纹甲虫,比较测试3种物质对虫子的有效性。研究将3种药物的处理方式、双向组合效果一一对照,比较了处理后害虫的存活数量和种类,发现硅藻土和真菌这两种天然物质还是存在各自的不足与长处。
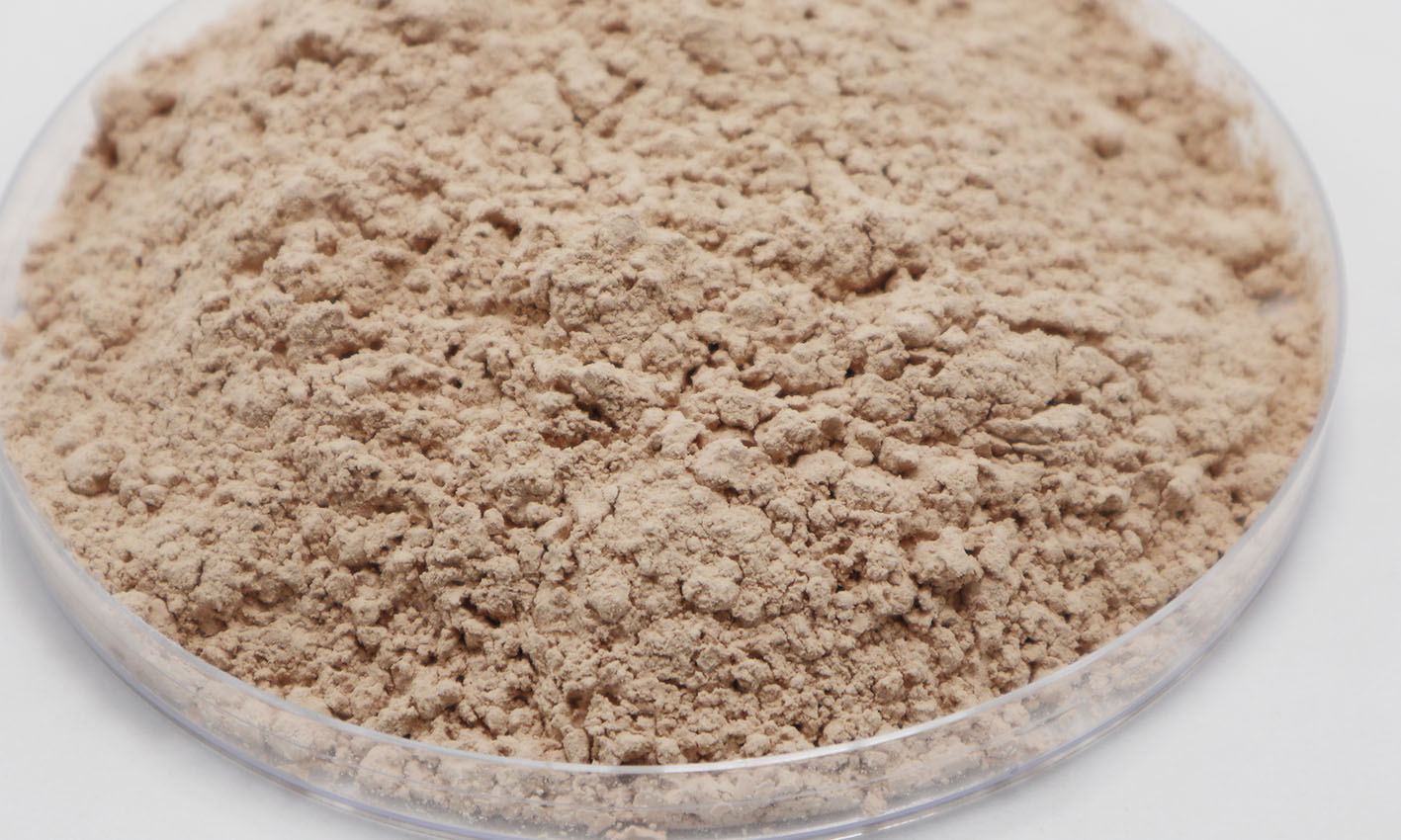

硅藻土来源于硅藻化石,常用于食品添加剂来保护头发和指甲,但它与昆虫接触会吸收昆虫角质层的表皮脂质,导致它们因为干燥而死亡,且尖颗粒会伤害幼虫和更健壮的成虫。而Beauveria真菌的孢子会粘附在害虫的皮肤上,在发芽后穿透宿主导致感染个体死亡,这些真菌对脊椎动物绝对无害。
发现不同活性物质组合,如杀虫剂和真菌、硅藻土和真菌组合使用的效果比单一药物更好。并且,活性物质组合生成的化合物表现出良好的长期效果。测试系列刚刚开始时,吡虫啉和Beauveria bassiana真菌的组合对害虫表现出最佳效果,但在谷物储存100天后,硅藻土与真菌的组合呈现出同样良好的效果。

研究人员表示,从150到180天的储存期,用硅藻土和Beauveria bassiana处理的小麦的害虫感染更少。谷物储存时间通常在半年以上,因此研究测试的天然杀虫剂可能是化学杀虫剂的良好替代品。
创新关键点
通过对比化学杀虫剂和两种天然物质,寻找有效杀虫且副作用较小的天然杀虫剂。
Natural pesticide combinations are effective in protecting grains in the long term
Currently, the most commonly used to protect crops from pests are chemical pesticides, such as the systemic insecticide imidacloprid from neonicotinoids. The killing of insecticides is not only a natural enemy of pests, but also has a destructive effect on other organisms, Professor Thomas Schmitt of the German Entomological Institute collaborated with colleagues to test and study two natural substances in an attempt to make them alternatives to chemical insecticides, and the related research results "Enhanced Diatomaceous Earth, Imidacloprid and Beauveria bassiana on the Persistence and Effectiveness of 3 Coleoptera and 1 Pseudo-Aphid Insects" published in the January 5, 2021 issue of "The Persistence and Effectiveness of Enhanced Diatomaceous Earth, Imidacloprid and Beauveria Bassiana on 3 Coleoptera and 1 Pseudo-Aphid Insects" published in the January 5, 2021 issue of the journal Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Diatomaceous earth, insect-causing parasitic fungi Beauveria bassiana and the insecticide imidacloprid were used for pink beetles, petty carlin borers and rusty beetles, and the effectiveness of the three substances on insects was compared to test the effectiveness of the three substances against insects. The study compared the treatment methods and two-way combination effects of the three drugs one by one, compared the number and type of pests surviving after treatment, and found that diatomaceous earth and fungi still have their own shortcomings and advantages.
Diatomaceous earth is derived from fossil diatomaceous bodies and is often used as a food additive to protect hair and nails, but when it comes into contact with insects, it absorbs the epidermal lipids of the insect stratum corneum, causing them to die from dryness, and the spiked particles can harm larvae and more robust adults. While the spores of the Beauveria fungus adhere to the skin of the pest, penetrating the host after germination and causing death to the infected individual, these fungi are absolutely harmless to vertebrates.
It was found that different combinations of active substances, such as pesticides and fungi, diatomaceous earth and fungi combined, worked better than a single drug. Moreover, the compounds produced by the combination of active substances exhibit good long-term effects. At the beginning of the test series, the combination of imidacloprid and Beauveria bassiana fungi showed the best results for pests, but the combination of diatomaceous earth with fungi showed equally good results after 100 days of grain storage.
The researchers said wheat treated with diatomaceous earth and Beauveria bassiana had fewer pest infections during storage periods ranging from 150 to 180 days. Grains are usually stored for more than half a year, so the natural pesticides tested in the study may be a good alternative to chemical pesticides.
智能推荐
机器人+植物保护 | 利用机器人培育新型葡萄品种
2022-11-25自主机器人以便种植者可以比以往任何时候都更大规模地监测疾病以及葡萄园中葡萄藤生长的许多其他方面。研究人员正在帮助育种者实现根本性的改进,同时使他们能够更快地对变化做出反应,无论是否进行预测。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向月壤中生长的植物呈现与火山灰中植株不同水平的基因
2022-06-30这项研究探讨了植物在月球上生长的可行性。他们用常见的植物拟南芥进行研究,使其在十二个由阿波罗11号、12号和17号月球任务收集的月壤样本中生长。该研究表明月壤虽可用于种植,但它支持植物生长的水平不及火山灰,尤其是那些更暴露于月球表面的月壤。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向利用人工智能帮助兽医编写笔记
2022-08-18由医学院科学家领导的一个团队开发了一种算法,可以读取兽医打印的记录,并预测动物可能患有的特定疾病。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI+农业 | 创造未来农场和农场工人
2022-08-23将先进技术应用于农场,未来的农场将比以往任何时候生产更多的食物,以土地、劳动力、能源或材料的投入来衡量,而且使用的水更少,对环境和气候的影响也更小。它还为新一代农场工人提供技术职业。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向