创新背景
执行太空任务的宇航员若是换上疾病,治疗方法非常有限,需要快速可靠的方法准确识别引起疾病的微生物,进行有效的治疗措施。
创新过程
CRISPR系统是细菌对病毒的免疫系统,是存在于大多数细菌与所有的古菌中的一种防御机制,可以消灭外来的质体或者噬菌体的DNA。 CRISPR 序列可以检测并摧毁能引起相似感染的其他噬菌体中相似的DNA;CAS是一种核酸内切酶,通过利用CRISPR序列中间隔序列对应的RNA指引,可以识别并切割特定与其序列互补的DNA链。细菌使用CRISPR-Cas系统作为一种分子搜索引擎,可以定位病毒序列并切割它们从而使病毒失效。
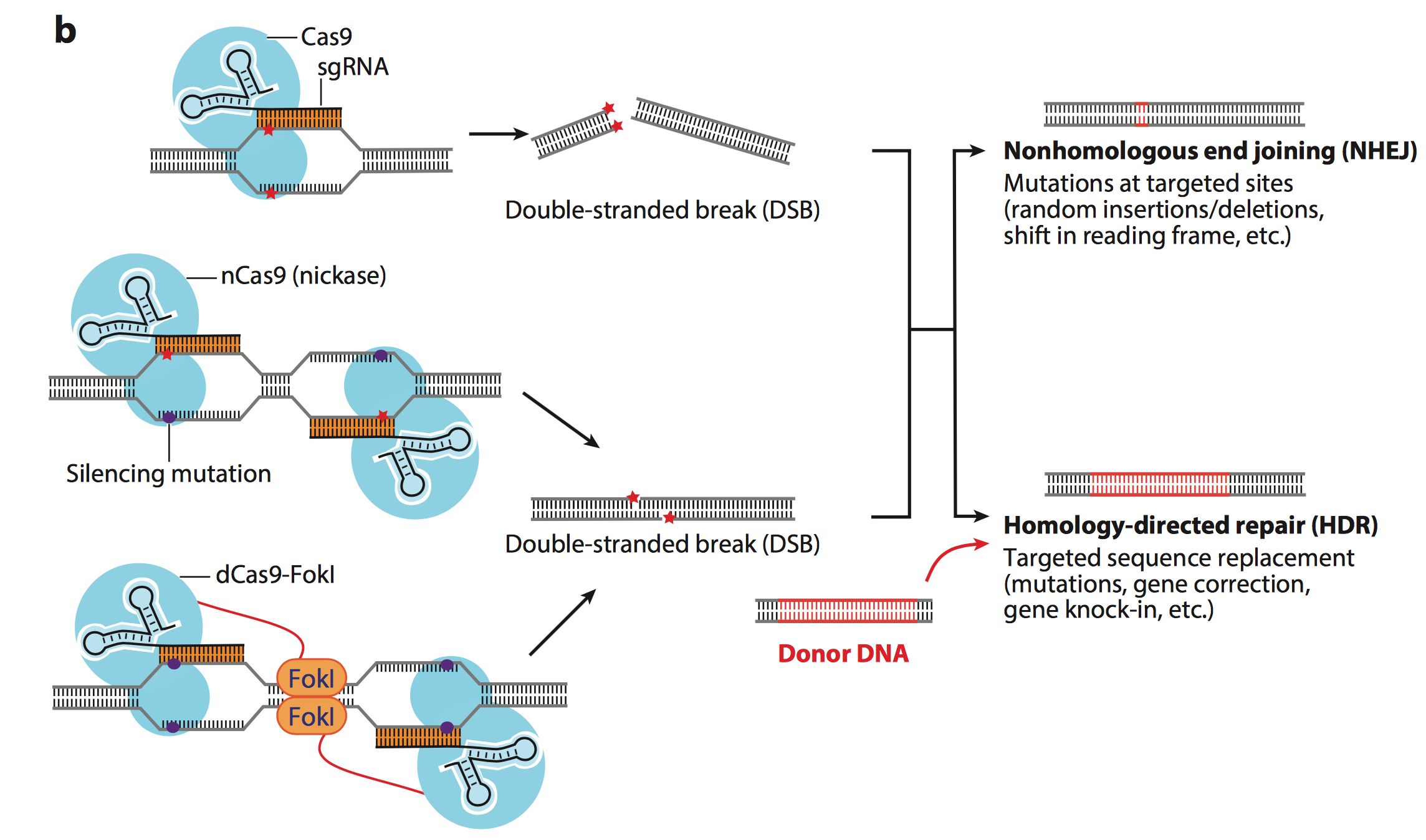
特拉维夫大学Shmunis生物医学和癌症研究学院的Dudu Burstein博士以及Volcani研究所的Gur Pines博士在Ramon基金会和以色列航空局的支持下让以色列宇航员将一个试剂盒带到太空,在国际空间站进行了一项独特的研究。研究旨在在微重力条件下进行基因诊断,发现细菌免疫的现有技术系统CRISPR可用于在太空任务期间识别感染机组人员的病毒和细菌。
CRISPR技术进行的基因诊断和PCR测试不同,PCR需要经过专门训练且操作熟练的人员和相对复杂的设备。研究人员假设,CRISPR进行基因诊断只需基本而且易于操作的设备,适用于长时间的太空任务。

实验过程先增加DNA,多次重复复制每个目标DNA分子;然后CRISPR-Cas系统开始行动,识别到目标DNA时就会激活荧光分子标记,荧光时片段样本中是否存在细菌或病毒的的根据。整个过程在一个小试管中进行,符合航空环境的需求。实验达到预期结果后,研究人员将CRISPR-Cas系统和探测所需的其它组件放入测试盒中,让宇航员将测试盒带进国际空间站。

研究下一步将尝试从样本中简单提取DNA,是整个诊断系统高效运作,能够在一个是观众测试多种生物,并诊断更复杂的样本。
创新关键点
利用CRISPR系统在微重力环境中实现简单快速诊断病原体,开发太空环境中的疾病治疗方法。
创新价值
为宇航员提供执行任务时可用的疾病诊断方法,帮助未来太空任务执行。
CRISPR systems help enable the diagnosis of genes under microgravity conditions
The CRISPR system is the bacterial immune system against viruses, a defense mechanism present in most bacteria and all archaea, which can destroy the DNA of foreign plastids or bacteriophages. CRISPR sequences can detect and destroy similar DNA in other bacteriophages that can cause similar infections; CAS is a nucleic acid endonuclease that identifies and cleaves specific strands of DNA that are complementary to their sequences by using RNA guidelines corresponding to spacer sequences in CRISPR sequences. Bacteria use the CRISPR-Cas system as a molecular search engine that can locate viral sequences and cut them to render the virus ineffective.
Dr. Dudu Burstein of the Shmunis School of Biomedical and Cancer Research at Tel Aviv University and Dr. Gur Pines of the Volcani Institute, with the support of the Ramon Foundation and the Israel Aviation Agency, have led Israeli astronauts to carry out a unique study on the International Space Station with the support of the Ramon Foundation and the Israel Aviation Agency. The study aims to perform genetic diagnostics under microgravity conditions, discovering that CRISPR, an existing technology system for bacterial immunity, can be used to identify viruses and bacteria that infect crews during space missions.
Unlike genetic diagnostics and PCR testing performed by CRISPR technology, PCR requires specially trained and skilled personnel and relatively complex equipment. The researchers hypothesized that CRISPR requires only basic and easy-to-operate devices for genetic diagnosis, suitable for long-duration space missions.
The experimental process first increases the DNA, replicating each target DNA molecule repeatedly several times; The CRISPR-Cas system then moves, activating fluorescent molecular markers when the target DNA is identified, and the basis for the presence or absence of bacteria or viruses in the fragment sample during fluorescence. The entire process takes place in a small test tube that meets the needs of the aviation environment. After the experiments achieved their expected results, the researchers put the CRISPR-Cas system and other components needed for detection into the test box, allowing the astronauts to bring the test box into the International Space Station.
The next step in the study will be to attempt to simply extract DNA from the samples, where the entire diagnostic system operates efficiently, being able to test multiple organisms in one audience and diagnose more complex samples.
智能推荐
通过筛选优化分子开发抗登革热抗病毒药物
2022-08-09使用分子生物学方式获得可抑制登革热病毒的抗体,进而开发对其具有超强效抑制功能的药物。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向植物研究者利用反向分子遗传学方式探究植物触摸信号的传导机制
2022-08-31通过探究植物触摸信号传导的路径确定植物机械应激反应的机制,有助于探索提高植物抗性和农业产量的方法,对现代农业有着重要影响。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向融合多种技术手段揭示恐惧消退形成新记忆的动态印迹网络机制
2022-07-29该研究综合运用动物行为学、神经活性捕捉原位标记、光遗传学、神经环路示踪、电生理、在体光纤记录等多种技术手段,针对恐惧消退中形成的新记忆--消退记忆,在记忆印迹细胞群及其互相连接构成的印迹环路和印迹网络层面,揭示了消退记忆从形成到遗忘的基本演化规律,为理解抑郁症、焦虑症、创伤后应激障碍等重大情感障碍疾病治疗后复发提供了全新的思路。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向细胞学创新 | 新型化学技术可将荧光标记物添加到单个细胞中
2022-10-09研究人员开发了一种新的化学技术,可以将更广泛的荧光标记添加到单个细胞中,而在此过程中不会损坏细胞。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向