创新背景
花的香味实际上是一种挥发性有机化合物的复杂混合物,会影响自身与微生物、传粉媒介和食草动物之间的相互作用。大多数花挥发物在花瓣的细胞质中合成,在一天中的特定时间释放到顶空。当授粉媒介比授粉活跃时,许多开花植物会调整其气味排放率。比如牵牛花和野生烟草会在夜间散发香味,吸引夜间活跃的传粉媒介。各种花香采样方法配合气相色谱-质谱法已被用于测量花卉挥发物的质量和数量,但还是无法让人们了解花香的排放模式。
创新过程
研究花香会广泛使用到质谱法,但质谱法无法直接测量花香的释放频率。KAIST机械工程师和生物科学家使用激光干涉测量方法,实现百合花释放挥发性有机化合物的频率可视化,相关研究成果《气味积累的实时可视化揭示了花香排放的频率》发表在2022年4月18日出版的《植物科学前言》上。
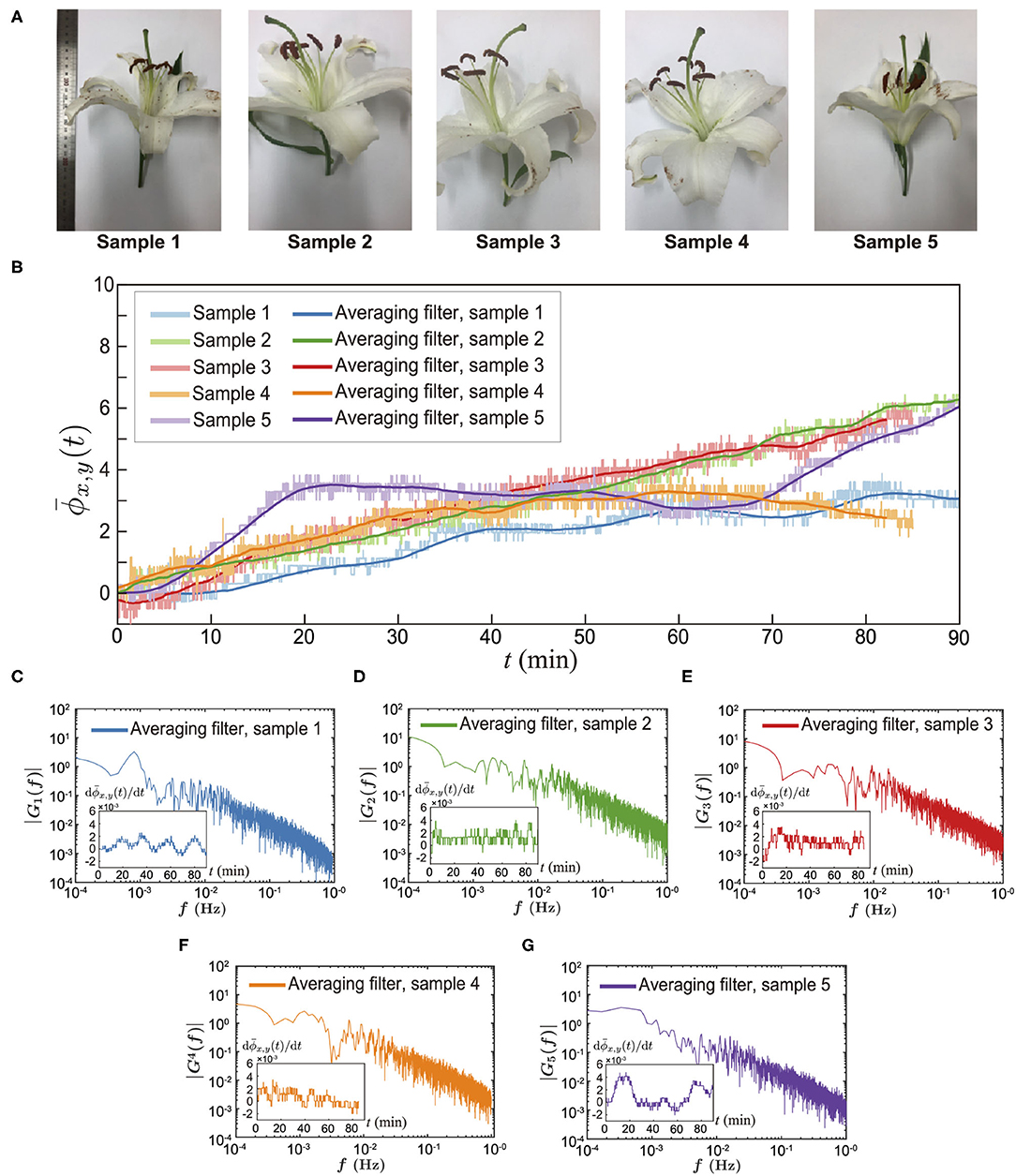
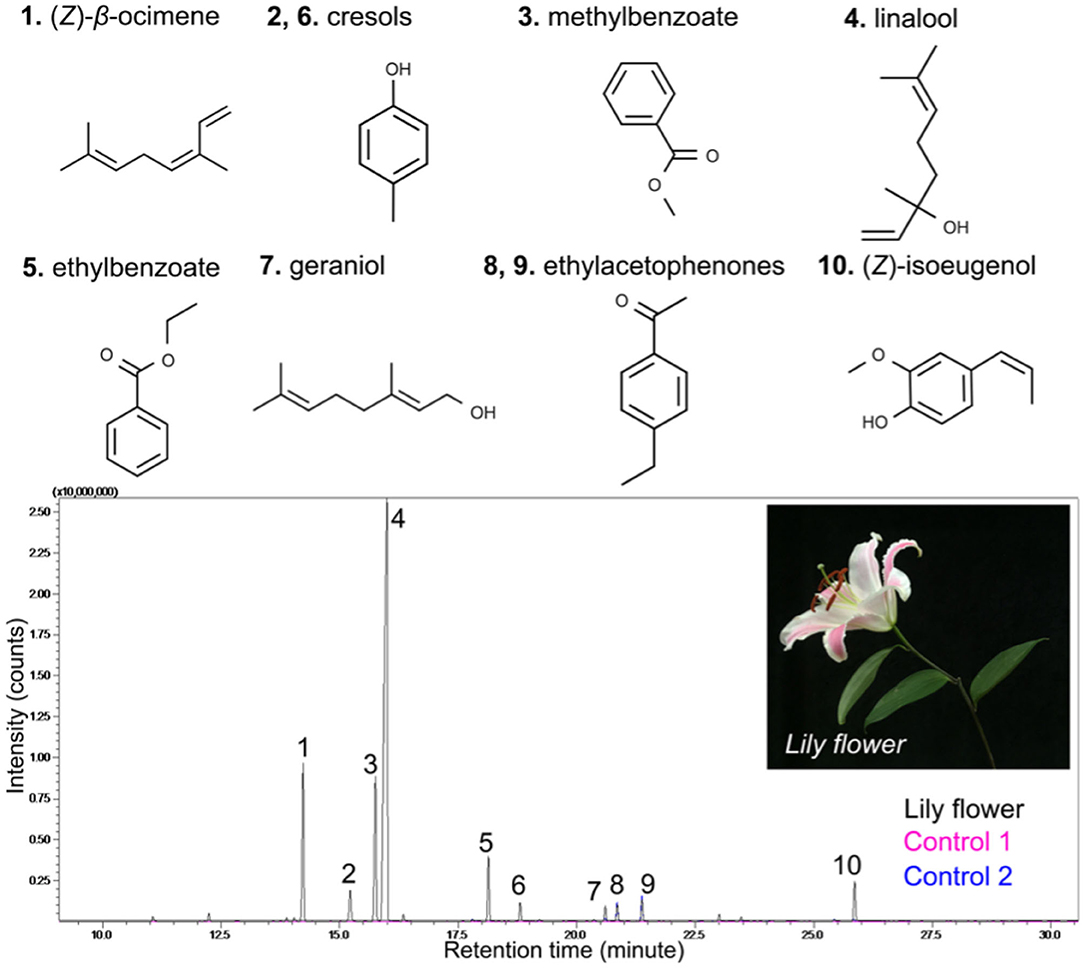
研究用GC-MS测量百合花中VOC的成分,发现芳樟醇是主要成分之一,使用带有封闭百合罩盒的激光干涉测量仪进行探索。因为分子会因为重力作用向下趁机,研究为了了解芳樟醇蒸气沉降的更多详细信息,将百合倒挂,设计让百合花挥发性有机化合物沿着测量容器狭窄的通道沉积在底部被测量到。
研究人员在测量区域记录百合花VOC的干扰信号,观察到折射率随时间而变化,并监测到折射率差的信号。研究通过测量百合花VOC和空气的蒸汽之间的折射率差,以测量发射频率。

结果检测到花香蒸汽,空气折射率为1.0,芳樟醇百合的主要花香率为1.46。时间功率谱表明,每朵百合都有自己的花香,每朵花的发射频率可能因基因型或生长条件而异,但所有百合花的发射速率小于1小时。
创新关键点
利用光学干涉测量显示百合花释放挥发性有机化合物的频率,可视化气味排放可以帮助了解植物和传粉媒介的相互作用。
创新价值
为理解和进一步探索花挥发物的生物合成和排放机制提供新的见解,有助于进一步探究植物的生态进化和演变。
Visualize the floral release process using optical interferometry
Mass spectrometry is widely used in the study of floral fragrances, but mass spectrometry cannot directly measure the release frequency of floral fragrances. KAIST mechanical engineers and bioscientists used laser interferometry to visualize the frequency of release of volatile organic compounds by lilies, and the research result "Real-time Visualization of Odor Accumulation Reveals the Frequency of Floral Emissions" was published in the April 18, 2022 issue of Introduction to Plant Science.
The study of measuring the composition of VOCs in lilies with GC-MS found that linalool was one of the main components, which was explored using a laser interferometer with a closed lily hood box. Because the molecules will be taken advantage of by gravity, the study to understand more details of linalool vapor deposition, the lily was hung upside down, designed to allow lilies to be deposited along the narrow channel of the measuring vessel at the bottom to be measured.
The researchers recorded the interference signal of the lily VOC in the measurement area, observed that the refractive index changed over time, and monitored the signal with poor refractive index. The study measures the emission frequency by measuring the refractive index difference between the VOC of the lily and the vapor of the air.
The results detected floral vapor, the air refractive index was 1.0, and the main floral index of linalool lily was 1.46. Temporal power spectra indicate that each lily has its own floral fragrance, and the emission frequency of each flower may vary depending on genotype or growth conditions, but the emission rate of all lilies is less than 1 hour.
智能推荐
C4和CAM循环的共同作用有助于打造抗旱高产植物
2022-08-15耶鲁大学的研究团队通过对马齿苋叶片内的基因表达进行分析发现,C4和CAM活性在马齿苋中是完全整合的,两种途径在相同的细胞中运作,为植物提供强力的保护。了解这一新的代谢途径可以帮助科学家设计出新的方法来改造玉米等作物,以帮助植物抵御长时间的干旱。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向利用新型基因技术研究芸薹属植物
2022-11-13约克大学的研究为科学家为了研究芸薹属植物,开发了一种新型基因技术。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向采用OsDREB1C水稻基因对多个生理过程的聚合调控实现“减氮高产”
2022-07-25中国农业科学院作物科学研究所周文彬团队以118个转录因子为切入点,逐一分析它们在水稻中光照条件和低氮条件的诱导表达情况,鉴定到一个同时受光和低氮调控的转录因子——OsDREB1C。该基因可同时调控多个重要生理过程,打破长期存在于农业生产中“高产”与“早熟”之间的矛盾;同时,OsDREB1C基因在不同作物中的保守性功能使其具有巨大的应用前景与发展潜力,对推动农业可持续集约化生产具有重要意义。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI+植物科学与技术 | 创新使用AI加工藻类以用作生物燃料
2022-11-04研究人员使用人工智能创造新的世界纪录,将藻类作为可靠,经济的生物燃料来源,可用作喷气式飞机和其他运输需求的替代燃料来源。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向