创新背景
语言的生成、发展和灭绝与地区的历史变化密切相关,同一个地区会衍生出不同的语言,但大都可以归在一个语言类型中。人类的语言多样性远比现存的已知语言类型要多得多,不断充实语言类型对于探索文明进程具有重要意义。
创新过程
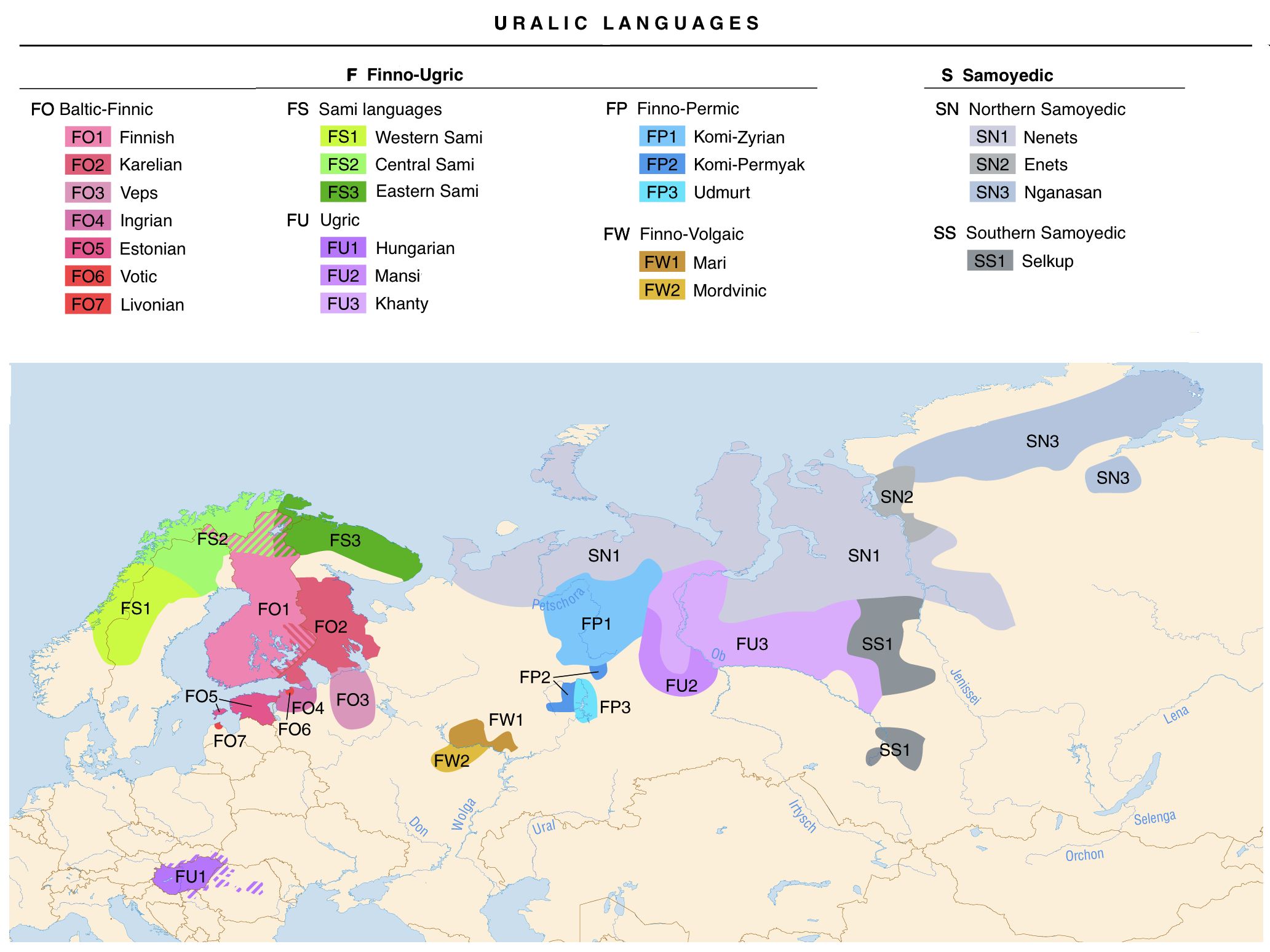
乌拉尔语起源于乌拉尔山脉,是分布于从斯堪的纳维亚往东经乌拉尔山脉到亚洲西北部广大地区的一组语言,分为芬兰-乌戈尔语族和萨莫耶德语族。芬兰-乌戈尔语族包括芬兰语支和乌戈尔语支,共约15种语言。萨莫耶德语族分南 、北两个语支,有4种语言。
乌拉尔语由几个独立的分支组成,除了已知的芬兰语、爱沙尼亚语和匈牙利等民族语言外,还包括挪威、瑞典、波罗的海地区以及包括西伯利亚在内的俄罗斯不同地区的较小语言。慕尼黑大学的语言学教授Ksenia Shagal从现有的已知语言着手,深入到一些偏远地区甚至已经灭绝的语言,探索乌拉尔语的类型学和多样性。

研究员对于乌拉尔语最深的感受是其复杂句子形成的不同方式。句法结构的分布遵循清晰的空间模式,这些模式表现了不同乌拉尔语变体之间的接触故事。根据研究,西方乌拉尔语系与其他欧洲语言有许多共同特性,而伏尔加-卡马地区的语言则更像突厥语。西伯利亚的乌拉尔语与北欧亚语言如通古斯语和叶尼塞语相似。语言接触互相影响,驯鹿牧民之间的接触令语言明显带有驯鹿背景。
语言在地区接触和时间变化中不断发展,不同地区的乌拉尔语之间存在细微的差异。东部的乌拉尔语系的“主语-宾语-谓语”结构仍然符合原始乌拉尔语,但芬兰语和爱沙尼亚语等西方变体已经采用了“主语-谓语-宾语”结构。
研究乌拉尔语必须从已知语言着手,面对一些濒临灭绝的语言,研究人员进行了深入详细的田野调查,尽可能记录下一些相关的语言。田野调查需要录制现场母语人士的语言样本,目前先进的科技和智能设备减轻了工作人员远程携带专业设备的压力,用智能手机存储视频和音频文件,然后通过机器学习或者深度学习帮助研究人员对语言样本进行转录、分析和注释,提高翻译效率。

通过智能设备和技术,大量收集语言信息,语言研究可以搭建庞大的体系并进行模拟,为研究者提供方便快速的语言相似度和差异性辨别,提供可行的参考意见。或者帮助研究者对比反馈检测错误,在乌拉尔语和语言类型学之间架起桥梁,扩展全球语言多样性。
创新关键点
利用智能设备和技术帮助语言田野调查研究,提高语言存储和翻译效率,帮助语言研究顺利进行。
Smart devices help study the Ural language
Originating in the Ural Mountains, urals are a group of languages that spread east from Scandinavia through the Ural Mountains to a vast area of northwestern Asia, divided into Finnish-Ugric and Samoyed German. The Finnish-Ugric language family includes Finnish and Ugric languages, with a total of about 15 languages. The Samoyed Germans are divided into two branches, the north and the south, and there are 4 languages.
The Ural language consists of several separate branches, including, in addition to the known national languages of Finnish, Estonian and Hungarian, but also the smaller languages of Norway, Sweden, the Baltic region, and different parts of Russia, including Siberia. Ksenia Shagal, a professor of linguistics at the University of Munich, began with existing known languages and went deep into some remote areas that are even extinct, exploring the typology and diversity of Ural languages.
The researchers' deepest feeling about the Ural language is the different ways in which its complex sentences are formed. The distribution of syntactic structures follows clear spatial patterns that represent the story of contact between different Ural variations. According to research, Western Ural languages have many characteristics in common with other European languages, while the languages of the Volga-Kama region are more Turkic. The Ural language of Siberia is similar to Norse sub-languages such as Tunguska and Yenisei. Language contact influences each other, and contact between reindeer herders makes the language clearly have a reindeer background.
Languages continue to evolve in regional contact and temporal variations, with subtle differences between Ural languages in different regions. The subject-object-predicate structure of the eastern Ural language family still conforms to the Proto-Uralic language, but Western variants such as Finnish and Estonian have adopted a subject-predicate-object structure.
The study of Ural languages must start with known languages, and in the face of some endangered languages, researchers have conducted in-depth and detailed fieldwork to record some relevant languages as much as possible. Fieldwork requires recording language samples of native speakers on the spot, and advanced technology and smart equipment reduce the pressure on staff to remotely carry professional equipment, store video and audio files with smartphones, and then help researchers transcribe, analyze and annotate language samples through machine learning or deep learning to improve translation efficiency.
Through smart devices and technologies, a large number of language information is collected, and language research can build a huge system and simulate, providing researchers with convenient and rapid language similarity and difference discrimination, and providing feasible reference opinions. Or help researchers detect errors by comparing feedback, build bridges between Uralic and linguistic typology, and expand global linguistic diversity.
智能推荐
AI+管理学 | 人工智能应用于企业管理应以“预测”为最大功能
2022-07-29考虑人工智能的缺陷和风险,在企业管理中正确使用人工智能,利用它的数据处理能力为决策提供可行的预测和建议。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI+管理科学 | 应用AI工具优化急诊床位的分配方案
2022-09-23由UCL的研究人员与UCLH的工作人员一起开发的人工智能工具创新应用于预测有多少患者需要通过急诊室入院,来帮助规划者管理床位需求。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向“AI+城市管理”打造低碳出行模式
2022-06-29AI+城市管理控制城市能源利用和排放,促进低碳出行发展。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向