创新背景
城市环境中的绿色植物起到优化环境、保护身心的作用,但并非每种类型的绿色植物都对人们产生积极影响。
创新过程
鲁汶大学的研究人员详细绘制了比利时首都布鲁塞尔的树木,将城市生活环境中的树木和人体健康状况联系,研究树木与流行病学、心血管疾病、呼吸、睡眠等的关系,相关研究成果《比利时布鲁塞尔的住宅暴露于城市树木和药物销售情绪障碍和心血管疾病:生态研究》发表在《环境健康展望》上。
以往的城市环境研究多使用卫星图像、树木寄存器甚至Google街景绘制绿色空间,但这并不能给出生活环境中可靠直观真实的绿色植物类型。卫星图像无法区分草、灌木丛、乔木等,只能显示景观的绿色程度。而在Google街景上,无法看到私人花园中隐藏了多少绿色。
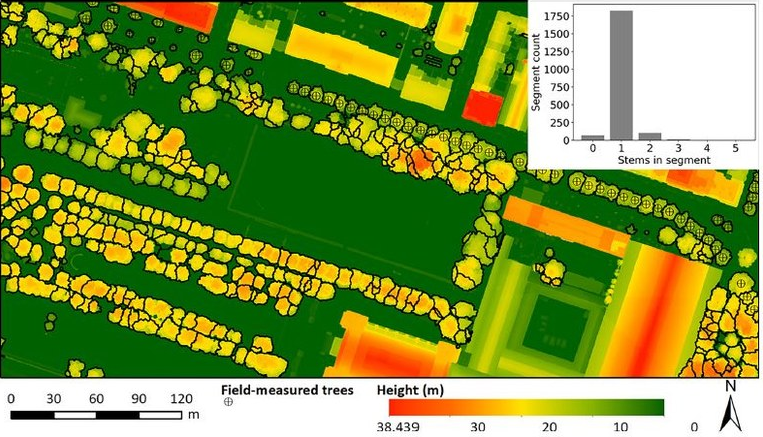
研究使用基于LiDAR技术的航空图像,与独特的数据处理算法相结合,可以在城市环境中创建详细的树木3D图像,确定整个布鲁塞尔地区的树木类型和数量以及树冠大小,并量化给定区域的树干数量。
研究将布鲁塞尔的树木详细信息和药品销售数据进行比较,并将社会经济因素考虑在内,发现城市绿色情况跟心血管疾病处方药和报销药物的销售情况与情绪障碍之间的联系。比如,富裕的社区更有可能是绿色的,社会经济地位在很大程度上决定了心血管健康。

研究发现,高冠体积的存在与所研究药物的使用率联系较低,但如果高冠量与许多小树相对应,该联系的强度就会减弱。研究结果表明,在城市环境中,一棵树冠健壮的大树比十棵幼树具有更大的影响力。
创新关键点
利用结合独特数据算法和LiDAR技术的航空图像创建布鲁塞尔地区的城市树木情况,研究城市环境中的树木与销售情绪障碍和心血管疾病之间的关系。
创新价值
为城市规划和房地产开发提出新的见解,开拓植物环境与人类健康之间的研究方向。
The relationship between urban tree types and human health
Researchers at the University of Leuven have mapped trees in Brussels, belgium, linking trees in urban living environments to human health, studying the relationship between trees and epidemiology, cardiovascular disease, breathing, sleep, etc. The relevant research results "Residential Exposure to Urban Trees and Drug Sales in Brussels, Belgium Emotional Disorders and Cardiovascular Diseases: Ecological Research" was published in the Environmental Health Outlook.
Previous urban environmental studies have used satellite imagery, tree registers, and even Google Street View to map green spaces, but this does not give a reliable and intuitive type of green plant in the living environment. Satellite imagery cannot distinguish between grass, bushes, trees, etc., and can only show how green the landscape is. On Google Street View, it's impossible to see how much green is hidden in the private garden.
Using aerial imagery based on LiDAR technology, combined with unique data processing algorithms, the study can create detailed 3D images of trees in an urban environment, determine the type and number of trees across the Brussels region, as well as the size of the canopy, and quantify the number of trunks in a given area.
The study compared tree details and drug sales data in Brussels and took socioeconomic factors into account and found a link between urban green conditions and sales of prescription and reimbursed drugs for cardiovascular disease and mood disorders. For example, wealthy communities are more likely to be green, and socioeconomic status largely determines cardiovascular health.
The study found that the presence of high crown volume was associated with low use of the drug under study, but the strength of the link weakened if the high crown volume corresponded to many small trees. The findings suggest that in an urban environment, a large tree with a strong crown has a greater impact than ten young trees.
智能推荐
血液病学创新 | 创新开发新型基因编辑技术可治疗儿童耐药性白血病
2022-11-03研究人员设计了供体T细胞,试图治疗患有耐药性白血病的重症儿童,这些儿童已经用尽了所有可用的治疗方法。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向靶向tau可减轻肌萎缩侧索硬化症中的线粒体碎裂
2022-06-28麻省总医院神经退行性疾病研究所 Healey ALS 中心的神经遗传学实验室主任 Ghazaleh Sadri-Vakili 博士和她的同事研究了这种异常 tau 蛋白与 DRP1 之间的相互作用是否也会促进渐冻症的线粒体功能障碍,以及减少 tau 蛋白是否可以成为对抗渐冻症的一种新的治疗方法。该研究提供了对肌萎缩侧索硬化症(ALS)既渐冻症发病背后机制的更好理解,并指出了潜在的治疗策略。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向大数据+公共卫生 | 使用大数据可制定有效防御新冠疫情的社会卫生政策
2022-09-20大数据技术可从巨量信息中心快速获取有价值的信息,将其使用在防控新冠疫情的公共卫生政策制定过程中,有助于为各地提供参考建议,并帮助预测各种措施的可行性。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向药学创新 | 利用氘化过程开发治疗心房颤动的新药物
2022-09-24创新使用氘原子替换药物分子上存在的原子,以氘化过程消除治疗心房颤动的药物的副作用,满足治疗需求。研究成果有助于进行安全有效的抗心律失常治疗,减少世界各地不断增长的AF患者数量。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向