创新背景
在现代电信中,无线电波通过空中传输信息,用于无线电广播、雷达和导航系统等应用。但是波长较短的无线电波有其局限性:它们传输的信号在很长的距离内会变得很弱,不能通过水传播,而且很容易被岩石层阻挡。
创新过程
加利福尼亚州门洛帕克——美国能源部SLAC国家加速器实验室研发的一种新型口袋大小的天线,可以在传统无线电无法工作的情况下实现移动通信,比如在水下、在地面以及在空气中很长的距离。
该设备发出的超低频率(VLF)辐射波长为几十到数百英里。这些波能在视界之外传播很长一段距离,并能穿透阻隔短波长的无线电波的环境。虽然当今最强大的VLF技术需要巨大的发射器,但这种天线只有4英寸高,所以它可能用于需要高机动性的任务,包括救援和防御任务。

VLF技术也面临着重大挑战。当天线的大小与它发射的波长相当时,它的效率最高;VLF的长波长要求巨大的天线阵列绵延数英里。较小的VLF发射器效率低得多,重量可达数百磅,限制了它们作为移动设备的预期用途。另一个挑战是VLF通信的低带宽,这限制了它可以传输的数据量。
新天线的设计考虑到了这些问题。它小巧的体积使得制造只有几磅重的发射机成为可能。在从发射机向100英尺外的接收器发送信号的测试中,研究人员证明,他们的设备产生VLF辐射的效率比以前的紧凑天线高出300倍,传输数据的带宽几乎增加了100倍。
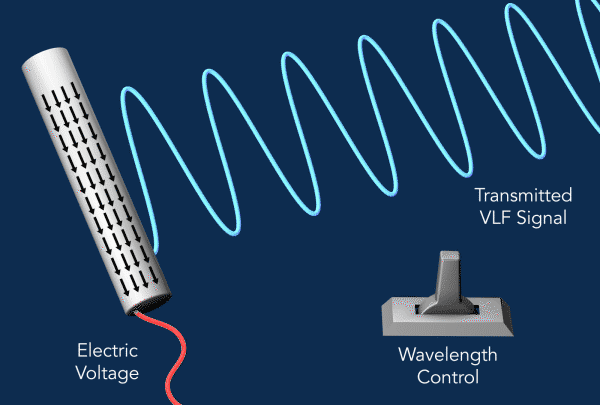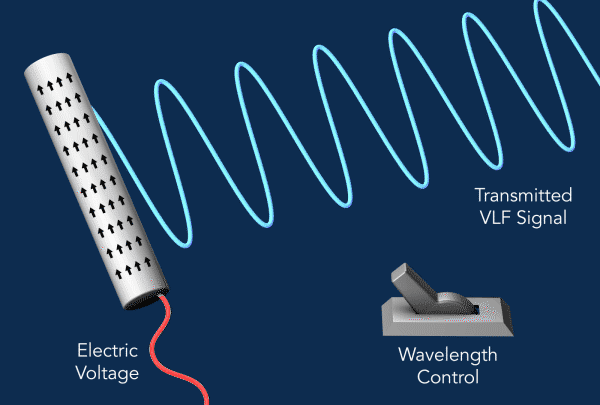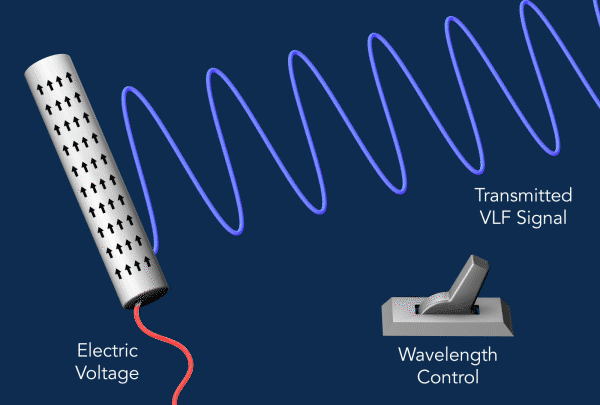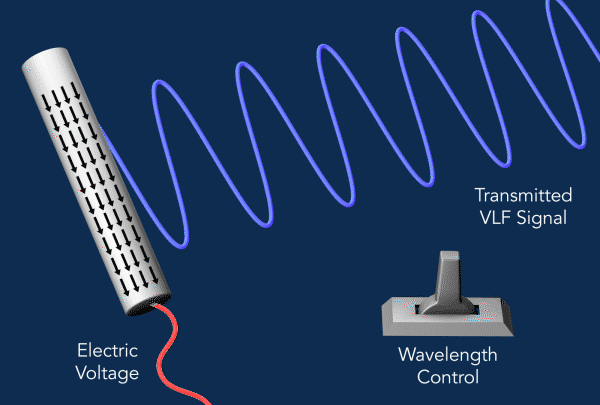
为了产生VLF辐射,该装置利用了所谓的压电效应,它将机械应力转化为电荷的积聚。
研究人员使用了一种压电材料的棒状晶体,即铌酸锂,作为他们的天线。当他们对杆子施加振荡电压时,杆子就会振动,交替收缩和扩张,这种机械应力触发了振荡电流,其电磁能量就会以甚低频辐射的形式释放出来。
电流是由于电荷在杆子上上下移动而产生的。在传统的天线中,这些运动与它们产生的辐射波长接近相同的大小,而更紧凑的设计通常需要比天线本身更大的调谐单元。另一方面,新方法需要有效地激发电磁波,其波长比沿晶体运动的波长大得多,而且没有大型调谐器,这就是这种天线如此紧凑的原因。
创新价值
我们的设备的效率也比以前同等尺寸的设备提高了数百倍,传输数据的速度更快。”“它的性能推动了技术上的极限,使便携式VLF应用,比如在具有挑战性的情况下发送短信息,变得触手可及。
创新关键点
该设备发出的超低频率(VLF)辐射波长为几十到数百英里。这些波能在视界之外传播很长一段距离,并能穿透阻隔短波长的无线电波的环境。
The new compact antenna is used for communication in case of radio failure
Menlo PARK, Calif. - A new pocket-sized antenna developed by the U.S. Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory could enable mobile communication in situations where traditional radios don't work, such as underwater, on the ground and over long distances in the air.
The device emits ultra-low frequency (VLF) radiation at wavelengths ranging from tens to hundreds of miles. These waves can travel long distances beyond the event horizon and penetrate environments that block short wavelength radio waves. While today's most powerful VLF technology requires huge transmitters, this antenna is only 4 inches tall, so it could potentially be used for missions that require high mobility, including rescue and defense missions.
VLF technology also faces significant challenges. The antenna is most efficient when its size corresponds to the wavelength at which it emits; The VLF's long wavelengths require a huge array of antennas stretching for miles. Smaller VLF emitters are much less efficient and can weigh hundreds of pounds, limiting their intended use as mobile devices. Another challenge is the low bandwidth of VLF communications, which limits the amount of data it can transmit.
The new antenna has been designed with these problems in mind. Its compact size makes it possible to build transmitters that weigh only a few pounds. In tests sending signals from a transmitter to a receiver 100 feet away, the researchers demonstrated that their device produced VLF radiation 300 times more efficiently than previous compact antennas and transmitted data with almost 100 times more bandwidth.
To generate VLF radiation, the device exploits the so-called piezoelectric effect, which converts mechanical stress into a buildup of charge.
The researchers used a rod-like crystal of a piezoelectric material, lithium niobate, as their antenna. When they applied an oscillating voltage to the rod, it vibrated, alternately contracting and expanding. This mechanical stress triggered oscillating currents, whose electromagnetic energy was released as very low-frequency radiation.
Current is produced by electric charge moving up and down the rod. In conventional antennas, these motions are close to the same size as the wavelengths of radiation they produce, and more compact designs typically require tuning units larger than the antenna itself. On the other hand, the new method requires efficient excitation of electromagnetic waves at wavelengths much larger than those traveling along the crystal and without a large tuner, which is why the antenna is so compact.
智能推荐
物联网+医学 | 新型电子皮肤可通过触觉刺激唤醒植物人
2022-06-29电子技术和医学感知交叉利用,提出电子皮肤毛发刺激触觉唤醒植物人的可能。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向使用FMCW雷达的毫米波反向散射建立大规模物联网系统
2022-08-05针对毫米波反向散射和雷达解调信号的缺陷,开发新的信号处理方式和系统,构建满足物联网设备大规模连接的稳定同步通信系统。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向电子芯片创新 | 建立在塑料上的柔性薄膜电子芯片可大幅降低制造成本
2022-08-14研究团队借助 PragmatIC 技术,生产了具有 4 位和 8 位处理器的塑料涂层晶圆,并在多个程序中对它们进行了不同电压以及弯曲的测试。该研究开发的芯片可以放置在几乎任何产品的包装上或医疗贴片上,应用领域不再受到限制,而且成本甚至可以控制在一美分以下。随着如此便宜的塑料处理器和柔性电子产品成为主流,也许我们很快就会看到无处不在的电子产品。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向使用人工智能鉴定出新的多发性硬化症亚型
2022-08-02伦敦大学学院的科学家们使用人工智能(AI)确定了三种新的多发性硬化症(MS)亚型。研究人员表示,这一突破性的发现将有助于识别那些更有可能出现疾病进展的人,并有助于更有效地针对性治疗。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向