
创新背景
在多个时空尺度上同时完成对完整生物系统各个方面的成像对于生物学和医学发展具有重大作用,但传统成像技术自身的局限性妨碍了这一进程。最广泛使用的光学显微镜技术是荧光显微镜,通过遗传操纵或者用荧光标记染色细胞表达荧光蛋白,但这些标记过程会对细胞的内在生理学产生一定的影响,且光谱颜色的限制带来的多重荧光信号的重叠光谱阻碍结构观察。
创新过程
数字全息显微镜是数字全息技术在显微领域的应用,这种方法记录含有被观测物体波前信息的全息图,再通过计算机对所记录的全息图进行数值重建来得到被测物体的相位和振幅信息,进而完成数字三维重构。3D全息显微镜为定量成像活细胞提供了新的方法,无需经过染色等预处理,全息切片可以准确快速地测量细胞的形态和结构信息,但这种方式提供生化和分子信息并不完整。
韩国科学技术高等研究院YongKeum Park教授的团队和初创公司Tomocube以控制光和物质相互作用的固定量(折射率)为测量手段,将3D折射率断层扫描编码,使用深度学习模型解码信息,对3D显微断层扫描进行升级。研究成果《使用可推广的深度学习对内源性亚细胞动力学进行无标记多重显微断层扫描》发表在2021年12月出版的《自然细胞生物学》上。
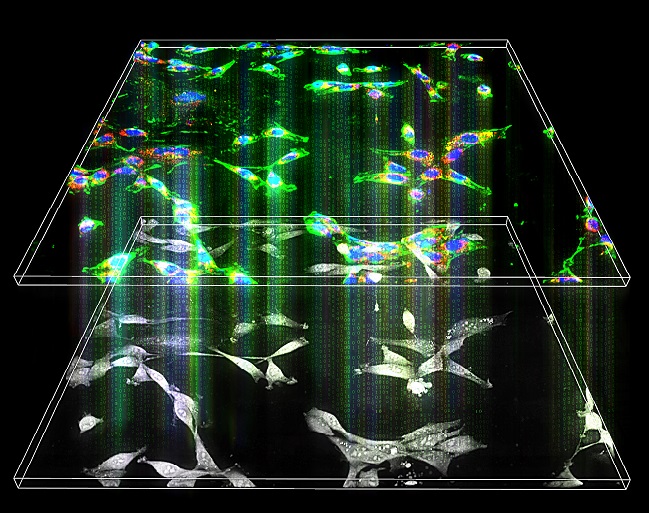
研究利用深度学习模型从相应亚细胞靶标的折射率测量值推断出多个3D荧光断层扫描,实现多重显微镜断层扫描,无需外源性标记或染色剂就可观察多颜色复用荧光成像中无标记活细胞,从中提取细胞的各种实时信息,并获得特定图像。
基于深度学习的全息显微镜继承了高特异性荧光成像和无标记RI成像的优点,可以从各种细胞和条件下的全息成像图像中直接精确地预测荧光图像,在3D中以自然状态和高达一毫秒的速度观察许多类型的细胞结构,并且还可以在几天内进行长期测量。

新显微镜将传统显微镜的优势与深度学习、光学和生物学结合,可以破译折射率的空间分布,发现折射率的空间分布与细胞中主要结构之间的定量关系。并且,无论是什么类型的细胞,这个关系都是恒定的。
研究人员表示,深度学习模型提取的分子图像信息与3D空间中荧光染色物理获得的分子图像信息一致性高达97%甚至以上,这是肉眼难以区分的水平,显示出新显微镜具有更高的性能。
创新关键点
结合传统几种显微镜和深度学习、光学以及生物学,升级3D全息显微镜,在不引入外源标记剂的情况下进行分子成像。
创新价值
新的概念显微镜将立即适用于现有数据中未包含的新型细胞,并有望广泛适用于各种生物学和医学研究。
Combined with deep learning to upgrade holographic microscopy, breaking through the limitations of cellular molecular imaging
Digital holographic microscope is the application of digital holographic technology in the field of microscopy, this method records the hologram containing the wavefront information of the observed object, and then the computer numerically reconstructs the recorded hologram to obtain the phase and amplitude information of the measured object, and then completes the digital three-dimensional reconstruction. 3D holographic microscopy provides a new method for quantitative imaging of living cells without pretreatment such as staining, and holographic sections can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but this way provides biochemical and molecular information that is incomplete.
The team of Professor YongKeum Park of the Korea Advanced Research Institute of Science and Technology and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomography using a fixed amount (refractive index) that controls the interaction between light and matter as a means of measurement, using a deep learning model to decode the information, and upgrading the 3D microtomography. The research result , Label-free multiplex microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning " was published in the December 2021 issue of Natural Cell Biology.
The study used deep learning models to infer multiple 3D fluorescence tomographies from refractive index measurements of corresponding subcellular targets to achieve multiple microscopic tomography, which can observe labelless live cells in multi-color multiplexed fluorescence imaging without exogenous labeling or stains, extract various real-time information of cells, and obtain specific images.
Deep learning-based holographic microscopy inherits the advantages of high-specific fluorescence imaging and label-free RI imaging to predict fluorescence images directly and accurately from holographic imaging images of various cells and conditions, observe many types of cellular structures in 3D in their natural state and at speeds of up to one millisecond, and can also make long-term measurements in a matter of days.
Combining the advantages of traditional microscopy with deep learning, optics and biology, the new microscope can decipher the spatial distribution of refractive index and discover quantitative relationships between the spatial distribution of refractive index and the main structures in cells. And, no matter what type of cell, this relationship is constant.
The researchers said that the molecular image information extracted by the deep learning model is consistent with the molecular image information obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space by up to 97% or more, which is an indistinguishable level with the naked eye, showing that the new microscope has higher performance.
智能推荐
AI+精密测量 | 里德堡原子和神经网络交叉融合推动精密测量
2022-06-30里德堡原子和神经网络交叉结合提高微波测量准确性。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI+能源化学 | 利用机器学习帮助提高锂离子电池和燃料电池的性能
2022-09-01帝国理工学院的研究人员将机器学习与能源储存相结合,开发出了一种名为“深度卷积生成对抗网络”(DC-GANs)的新技术。研究团队的发现将帮助能源领域的研究人员设计和制造优化电极,以提高电池性能。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI+算法理论 | 利用微控制器训练AI模型可降低隐私暴露风险
2022-10-10一项新技术使AI模型能够不断从智能手机和传感器等智能边缘设备上的新数据中学习,从而降低能源成本和隐私风险。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI+农业 | 利用气候智能型农业实现更多灌溉
2022-08-24由加州大学戴维斯分校(UC Davis)领导的一个国际团队正致力于将危地马拉的9000个农村家庭与改善的水管理和气候智能型农业战略联系起来,以提高粮食安全并减少贫困。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向