创新背景
物联网是5G/6G网络的核心组成部分,呈现出指数级增长,预计到2035年将成为万亿台设备的一部分。为了大规模支持物联网设备的连接,建设支持同步通信的实用系统极为重要。
创新过程
韩国科学技术学院电气工程学院的Song Min Kim教授领导领导研究团队,针对物联网设备的需求,利用毫米波反向散射方法,构建开发了一种系统,上万个物联网设备被安排在室内,支持在复杂的通信环境中进行实时同步信号调解的并发通信。研究在知名的移动系统会议ACM MobiSys 2022上发表,以“OmniScatter:使用商品FMCW雷达的灵敏度毫米波反向散射”获得最佳论文奖。

研究使用的毫米波反向散射方法不需要无线创建自己的信号,宽频率范围超过10GHz,可以反射辐射信号,具有极大的扩展性并允许系统在超低功耗下运行。毫米波反向散射系统安装成本较低,为物联网设备提供大规模的互联网连接。
毫米波利用频率在30至300GHz之间的载波,可以纳入5G/6G标准,是下一代通信技术。但由于高频下的信号会减少以及反射损耗,当前的毫米波反向散射系统只能在有限的环境中进行通信,无法在存在各种反射器和障碍物的复杂环境中运行,仅限于需要相对自由排列的大规模物联网设备连接。
研究团队构建的系统开发了一种信号处理方法,在FMCW雷达的高编码增益为基础,可以从根本上分离反向散射信号和环境噪声,同时保持雷达的编码增益。新方法的接收器灵敏度在以往的FMCW雷达的10万倍以上,支持实际环境中的通信。因为雷达解调信号的频率会根据标签的物理位置而变化,研究设计了一个被动为雷达解调信号分配信道的系统,使超低功耗反向散射通信系统能够充分利用10 GHz或更高的频率范围。
新系统可以使用现有商业产品的雷达作为网关,使其易于兼容。因为反向散射系统在10uW或更低的超低功耗水平下工作,只需一节纽扣电池就可以运行40多年,大大降低了安装和维护成本。
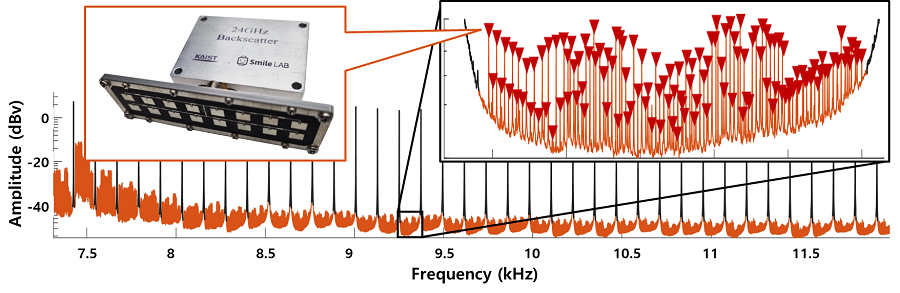
研究证实,新的信号处理方法和分配信道的系统使随机排列的毫米波反向散射设备在具有各种障碍物和反射器的办公室中可以有效通信。研究进一步进行跟踪驱动评估,同时接收了1100台设备发送的信息。
研究人员表示,毫米波反向散射可以操作物联网设备的大规模可扩展性和超低功耗比现有的任何技术都更好,新的系统被积极利用,将实现物联网在未来超连接中的广泛可用性。
创新关键点
针对毫米波反向散射和雷达解调信号的缺陷,开发新的信号处理方式和系统,构建满足物联网设备大规模连接的稳定同步通信系统。
创新价值
新系统的连接性大大超过了5G和6G等下一代通信所需的网络密度,未来将成为超互联的垫脚石。
Use the sensitivity millimeter wave backscatter of FMCW radar to establish a large-scale IoT device connection system
Professor Song Min Kim of the School of Electrical Engineering of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology led the research team to build and develop a system that uses millimeter wave backscattering methods to meet the needs of IoT devices, and tens of thousands of IoT devices are arranged indoors to support concurrent communication in real-time synchronous signal mediation in complex communication environments. The research was presented at the prestigious mobile systems conference ACM MobiSys 2022, which won the Best Paper Award for "OmniScatter: Sensitivity Millimeter Wave Backscatter using Commodity FMCW Radars."
The millimeter wave backscattering method used in the study does not require wireless creation of its own signal, has a wide frequency range of more than 10GHz, can reflect radiated signals, has great scalability and allows the system to operate at ultra-low power consumption. Millimeter wave backscatter systems are less expensive to install and provide large-scale internet connectivity for IoT devices.
Millimeter waves utilize carriers with frequencies between 30 and 300 GHz and can be incorporated into the 5G/6G standard and are next-generation communication technologies. However, due to the reduction of signals at high frequencies and the loss of reflections, current millimeter wave backscattering systems can only communicate in a limited environment, cannot operate in a complex environment with various reflectors and obstacles, and are limited to large-scale IoT device connections that require relatively free arrangement.
The system built by the research team developed a signal processing method that, based on the high coding gain of the FMCW radar, can fundamentally separate backscattered signals and ambient noise while maintaining the coding gain of the radar. The receiver sensitivity of the new method is more than 100,000 times that of previous FMCW radars, supporting communication in real-world environments. Because the frequency of radar demodulation signals varies depending on the physical location of the label, a system that passively assigns channels to radar demodulation signals is designed to enable ultra-low-power backscatter communication systems to take full advantage of the frequency range of 10 GHz or higher.
The new system can use the radar of existing commercial products as a gateway, making it easy to be compatible. Because backscattering systems operate at ultra-low power levels of 10uW or less, they can run for more than 40 years on a single coin cell battery, greatly reducing installation and maintenance costs.
Studies confirm that new signal processing methods and systems for distributing channels enable randomly arranged millimeter wave backscattering devices to communicate effectively in offices with various obstacles and reflectors. The study further performed a track-driven evaluation while receiving information from 1100 devices.
The researchers say millimeter wave backscatter can operate the massive scalability and ultra-low power consumption of IoT devices better than any existing technology, and new systems are actively utilized that will enable the widespread availability of IoT in future hyper-connectivity.
智能推荐
物联网+建筑学 | 将物联网与现代建筑创新融合
2022-06-30物联网创造性地深入建筑学,进一步提高建筑效率并保证节能安全。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向物联网+考古学 | 利用探地雷达发现更新世时期人类足迹和指纹
2022-08-19康奈尔大学的研究团队在犹他州沙漠发现了更新世时期的人类足迹,随后利用探地雷达又发现了隐藏的许多指纹。这项新发现为了解更新世时期的人类生存情况提供了重要信息。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向物联网+农业 | 利用新型探测器测量沙漠中的水分含量
2022-08-23这项研究利用一种称为电容探头的新型仪器,首次表明了水蒸气是如何穿透粉末和颗粒的。这种新型探头可能在制药研究、农业和食品加工,以及行星探索等远远超出沙漠的范围也具有广泛应用的价值。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向物联网+医学 | 新型电子皮肤可通过触觉刺激唤醒植物人
2022-06-29电子技术和医学感知交叉利用,提出电子皮肤毛发刺激触觉唤醒植物人的可能。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向