创新背景
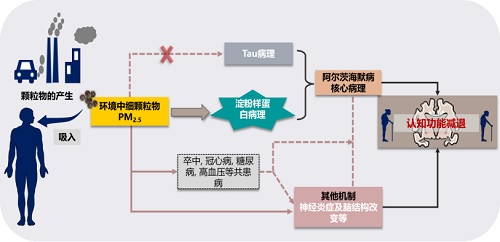
空气污染影响人体健康,危害呼吸和免疫系统,对肺部功能产生消极影响。越来越多的研究证明,空气污染对人的认知能力也有影响,会增加患阿尔兹海默症的几率,但其中的联系机制尚不明确。
创新过程
德国的SALIA研究始于1985年,旨在通过探究空气污染对肺功能、炎症和衰老的影响研究空气污染对人体健康的长期不良影响。研究小组对象由来自南明斯特兰州和鲁尔区的老年妇女组成,通过初步检查和随访结果的比较可以得出不同环境的人的健康状况。

通过观察追踪几何图形轮廓,可以观察到空气污染对老年人的认知障碍尤其是视觉建设能力的影响。德国杜塞尔多夫莱布尼茨环境医学研究所IUF的科学家假设空气污染对老年人认知能力的影响是因为肺功能受损,细小的尘埃颗粒通过循环系统或鼻子进入中枢神经系统,直接造成有害影响。
研究以SALIA研究的587名老年妇女的肺功能和认知能力的情况为基础,通过因果中介分析,证实了成年期的肺功能是影响老年人认知能力的重要因素。肺功能差不仅是老年人认知障碍的危险因素,还部分介导了空气污染对认知的负面影响,其中二氧化氮的最大比例为11%。相关研究成果于2018年发表在《欧洲呼吸杂志》上。
研究人员表示,空气污染因为肺的介导影响大脑,成为认知障碍的威胁因素之一。在成年期维持良好的肺功能也许对健康的大脑衰老很重要。
中国天津医科大学的研究团队对1377名无痴呆症的参试者进行为期21年的追踪研究,评估参试者的功能水平,并根据19项认知测试每年对参试者的全局和特定领域认知功能进行研究。研究发现,肺功能偏低会影响整体认知和局部具体认知功能,肺功能较差会引起认知功能下降,且与较小的全脑、白质和灰质体积以及较大的白质高信号体积有关。研究人员表示,肺功能会通过多种机制影响认知能力。
肺功能和认知能力之间研究为空气污染以肺部为部分介导影响认知能力提供了可参考的证据。空气污染危害人体健康,人体器官之间联系紧密,长期暴露于环境空气污染的居民认知能力和身体健康下降的风险会明显增高。
创新关键点
探索肺部功能及其与大脑的联系,寻找空气污染影响认知障碍的机制和介导。
The effect of air pollution on cognitive impairment may be due to impaired lung function
The SALIA study in Germany began in 1985 with the aim of studying the long-term adverse effects of air pollution on human health by exploring the effects of air pollution on lung function, inflammation and aging. The research team consisted of elderly women from South Münsterland and the Ruhr area, and the health status of people in different environments could be derived from a comparison of the results of preliminary examination and follow-up.
By observing and tracking the contours of geometric figures, the effect of air pollution on cognitive impairment in the elderly, especially visual construction ability, can be observed. Scientists at the IUF Institute for Environmental Medicine in Leibniz, Düsseldorf, Germany, hypothesized that the effect of air pollution on cognitive abilities in the elderly is due to impaired lung function and tiny dust particles entering the central nervous system through the circulatory system or nose, directly causing harmful effects.
Based on the lung function and cognitive abilities of 587 elderly women studied by SALIA, the study confirmed through causal mediating analysis that lung function in adulthood is an important factor affecting cognitive ability in the elderly. Poor lung function is not only a risk factor for cognitive impairment in the elderly, but also partly mediates the negative impact of air pollution on cognition, with the largest proportion of nitrogen dioxide being 11%. The results were published in the European Journal of Breathing in 2018.
The researchers say air pollution is one of the threatening factors for cognitive impairment because the lungs mediate that affect the brain. Maintaining good lung function in adulthood may be important for healthy brain aging.
The research team at Tianjin Medical University in China conducted a 21-year follow-up study of 1377 dementia-free participants, assessing the functional level of the participants, and studying the participants' global and domain-specific cognitive function annually based on 19 cognitive tests. The study found that low lung function affects overall cognition and local specific cognitive function, and poor lung function can cause cognitive decline, and is related to smaller whole brain, white matter and gray matter volume, and larger white matter high signal volume. Researchers say lung function affects cognitive abilities through a variety of mechanisms.
Studies between lung function and cognitive ability provide evidence that air pollution partially mediates cognitive performance in the lungs. Air pollution endangers human health, human organs are closely linked, and the risk of cognitive ability and physical health decline of residents who have been exposed to environmental air pollution for a long time will increase significantly.
智能推荐
非编码区突变导致白血病的发生
2022-07-01该研究为 APL 中首个聚焦于功能性非编码突变的系统性研究工作,通过构建 APL 顺式调控区的突变图谱,鉴定出38个具有潜在功能的非编码区突变位点,并以 WT1 为例首次报道了非编码区突变对于 WT1 表达的影响以及具体的作用机制,同时揭示了一个新的 APL 风险变异位点。该研究强调了非编码区突变在 APL 发病中的重要性,为白血病及其他疾病非编码区功能性突变的筛选鉴定以及功能验证提供了全新的研究思路和策略。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向间歇性禁食通过改变肠道菌群活性促进神经元轴突再生
2022-08-08这项研究发现间歇性禁食能够改变肠道菌群活性,促进3-吲哚丙酸(IPA)的产生,从而显著增强轴突再生。同时,该研究首次证实肠道菌群的代谢产物(例如3-吲哚丙酸)通过免疫介导机制促进感觉轴突再生和功能恢复的能力,是神经元轴突再生所必需的。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向传感器+生物医学 | 利用新型“棉导电线”批量生产带有可穿戴传感器的服装
2022-09-25该研究利用一种棉基导电线纺成新型低成本传感器,并将其缝制到口罩中监测使用者呼吸,缝制到T恤上监测使用者心跳活动。该研究使得这种传感器可以大规模生产,它们已经可以无缝集成,甚至可能帮助诊断和监测未来的疾病治疗,同时也开创了新一代服装可穿戴设备。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向创新利用肠道微生物衍生的鞘脂改善脂肪肝
2022-08-19康奈尔大学的研究团队在实验中对鞘脂进行了标记,发现肠道微生物的代谢产物能够进入肝脏和结肠,并进一步发现鞘脂分子通过改善呼吸能够调节肝脏的脂肪酸过载。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向