创新背景
量子系统中材料与光相互作用的能力为其提供了重要的功能,例如量子系统之间远程通信和未来需要开发的光量子计算机都取决于量子系统与光有效交互的能力。但目前,很难找到一种可以充分利用光的量子特性的材料。
创新过程
法国国家科学研究中心、斯特拉斯堡大学、德国卡尔斯鲁厄理工学院和法国巴黎国立高等化工学校的研究人员组成团队合作研究,发现基于稀土铕的新材料具有作为光子量子系统组成部分的潜力,将对开拓光量子系统有重要作用,相关研究成果《稀土分子晶体中的超窄光学线宽》发表在2022年3月9日出版的《自然》。
理想状态下,建立通过光纤进行信息和通信处理功能的量子系统必须带有一个有光和信息存储单元接口的存储器。信息在单元内进行处理,单元以自旋形式存在。
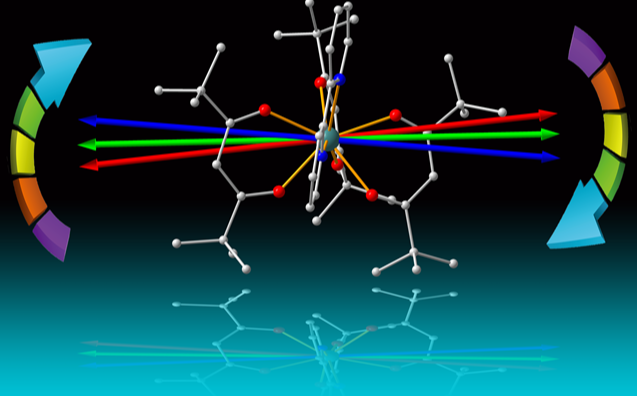
目前一些分子晶体已被证明是具有优异量子特性的新材料。晶体由目前在量子技术中已知的稀土离子和分子系统组合产生。稀土离子(REIs)是有前途的固态系统,拥有自旋均匀线宽的潜力、等效长寿的命量子态和对窄光学的显示,用于在量子水平上构建光物质界面,可以用于光子量子系统和技术。分子系统通常缺乏自旋(存储或计算单元),或者存在的光学线太宽,无法在自旋和光之间建立可靠的联系。
研究证明铕分子晶体超窄的线宽可以化为长寿命的量子态,证明这些分子晶体内存储的光脉冲。铕分子晶体可进行超窄的光学跃转换,光学线宽只在几万赫兹范围内,使用原子频率进行光的相干存储和离子相互作用可实现对离子的光学控制和与光的最佳交互,在量子通信和处理器方面具有巨大的价值。
研究采用光学寻址技术,提高读出速度并防止电信号的干扰。量子计算执行过程中一个量子比特的叠加状态必须持续一段时间,即所谓的相干时间。分子中的核自旋使量子叠加态具有较长的相干时间,进而更好地屏蔽干扰。分离频率允许对多个分子分别定位,在分子材料中达到了超过此前将近1000倍的光学相干性,以此使核自旋态能够以一种特定的方式被光学操纵。

研究人员表示,光子可以在更大的距离上传输量子信息,进而连接量子计算机或安全地传输信息。在光子结构中整合新的铕分子也许可以实现这一点,并增强光学跃迁。
创新关键点
结合分子晶体、稀土离子和光的特性,研究铕分子晶体对于光量子技术的作用。
创新价值
新材料在量子水平上实现自旋和光之间的联系,为光在量子系统中发挥作用有积极作用,并为计算机和量子存储器的新架构铺平了道路。
Development of new optical quantum materials based on rare earth europium
Researchers from the French National Scientific Research Center, the University of Strasbourg, the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology in Germany and the Ecole Nationale Supérieure des École Des Beseurs des Chemicals in Paris, France, have found that new materials based on rare earth europium have the potential to be part of photonic quantum systems and will play an important role in the development of optical quantum systems.
Ideally, a quantum system for information and communication processing via optical fiber must have a memory with an interface to optical and information storage units. The information is processed within the cell, which exists in spin form.
At present, some molecular crystals have been shown to be new materials with excellent quantum properties. Crystals are produced by a combination of rare earth ions and molecular systems currently known in quantum technology. Rare earth ions (REIs) are promising solid-state systems with the potential for spin uniform linewidths, life-cycle states of equivalent longevity, and displays of narrow optics for building optical interfaces at the quantum level that can be used in photonic quantum systems and technologies. Molecular systems often lack spin (storage or computing units), or the optical lines present are too wide to establish a reliable link between spin and light.
Studies have proved that the ultra-narrow line width of europium molecular crystals can be reduced to long-life quantum states, and proved that the light pulses stored within these molecular crystals have been proved. Europium molecular crystals can perform ultra-narrow optical leap conversion, optical line width is only in the range of tens of thousands of hertz, the use of atomic frequencies for coherent storage of light and ion interaction can achieve optical control of ions and optimal interaction with light, which has great value in quantum communication and processors.
Optical addressing technology is used to improve the readout speed and prevent interference of electrical signals. The superposition state of a qubit during the execution of quantum computing must last for a certain period of time, the so-called coherence time. The nuclear spin in the molecule gives the quantum superposition state a longer coherence time, which in turn better shields interference. The separation frequency allows multiple molecules to be individually localized, achieving nearly 1,000 times more optical coherence in the molecular material than previously, allowing the nuclear spin state to be optically manipulated in a specific way.
The researchers say photons can transmit quantum information over larger distances, which in turn can be connected to quantum computers or securely transmitted. Integrating new europium molecules into photonic structures may be possible to achieve this and enhance optical transitions.
智能推荐
利用量子时间反转来测量振动原子
2022-07-28创新利用量子理学的时间反转现象从原子震动的变化中增强信号,提高原子振动测量的精确度。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向在金晶体的原子光滑表面上压缩声子极化子
2022-08-05使用高灵敏度光学显微镜测量图像声子极化子的光场,观察到中红外光波;将超光滑单晶金片用作h-BN基底的自产金晶体的原子光滑表面,为压缩声子极化子且不减损其寿命提供可能。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向将涡旋光子束缚在简并光学腔中,创新拓扑量子模拟方法
2022-06-29基于简并腔中涡旋光子人工合成维度,研发拓扑量子模拟新方案。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向将微小金刚石晶体创新应用于引力波探测器
2022-08-04伦敦大学学院领导的一项新研究表明,微小的钻石晶体可以用作一种非常灵敏的小型引力波探测器,能够测量引力波。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向