
创新背景
机器人水下监测大大提高了对水生环境的监测和保护效率,但还是需要使用船只对水生环境做全面估测。使用无人机技术结合机器人,或许可以简化机器人工作,完成具有挑战性的任务。
创新过程
伦敦帝国理工学院结合机器人和无人机技术,开发出名为“称为 水下样本采集多环境双机器人(MEDUSA)”的新双机器人无人机,可以到达困难地区收集水生图像、样本和指标等,对生态和水生研究具有重要的积极作用。
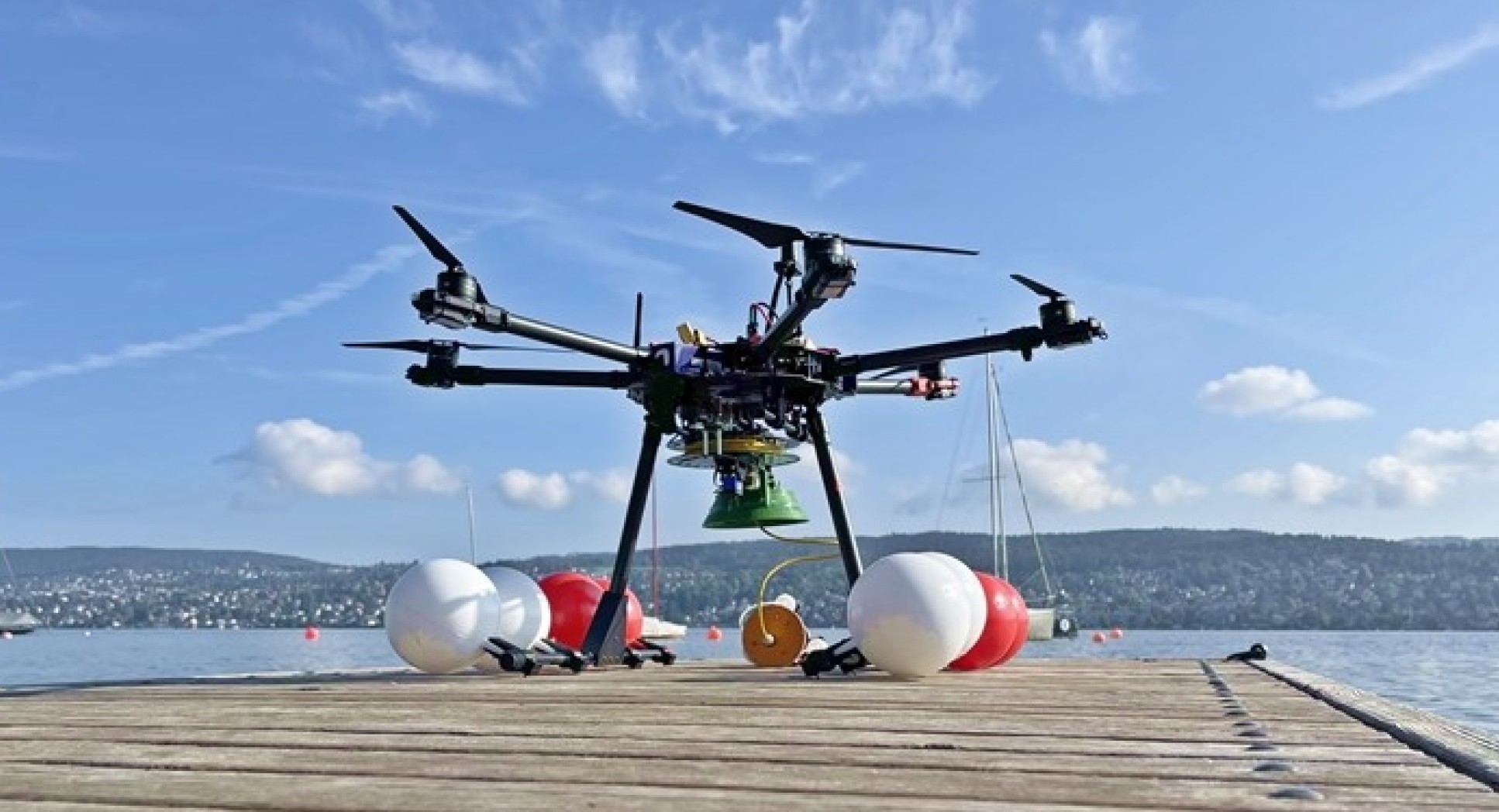
无人机采用遥控多旋翼飞行升力产生叶片,可以像直升飞机叶片一样围绕中心垂直桅杆旋转。MEDUSA使用多旋翼保障了它可以在高有效载荷的情况下飞越障碍物进行长途旅行,并在困难的地形中机动。
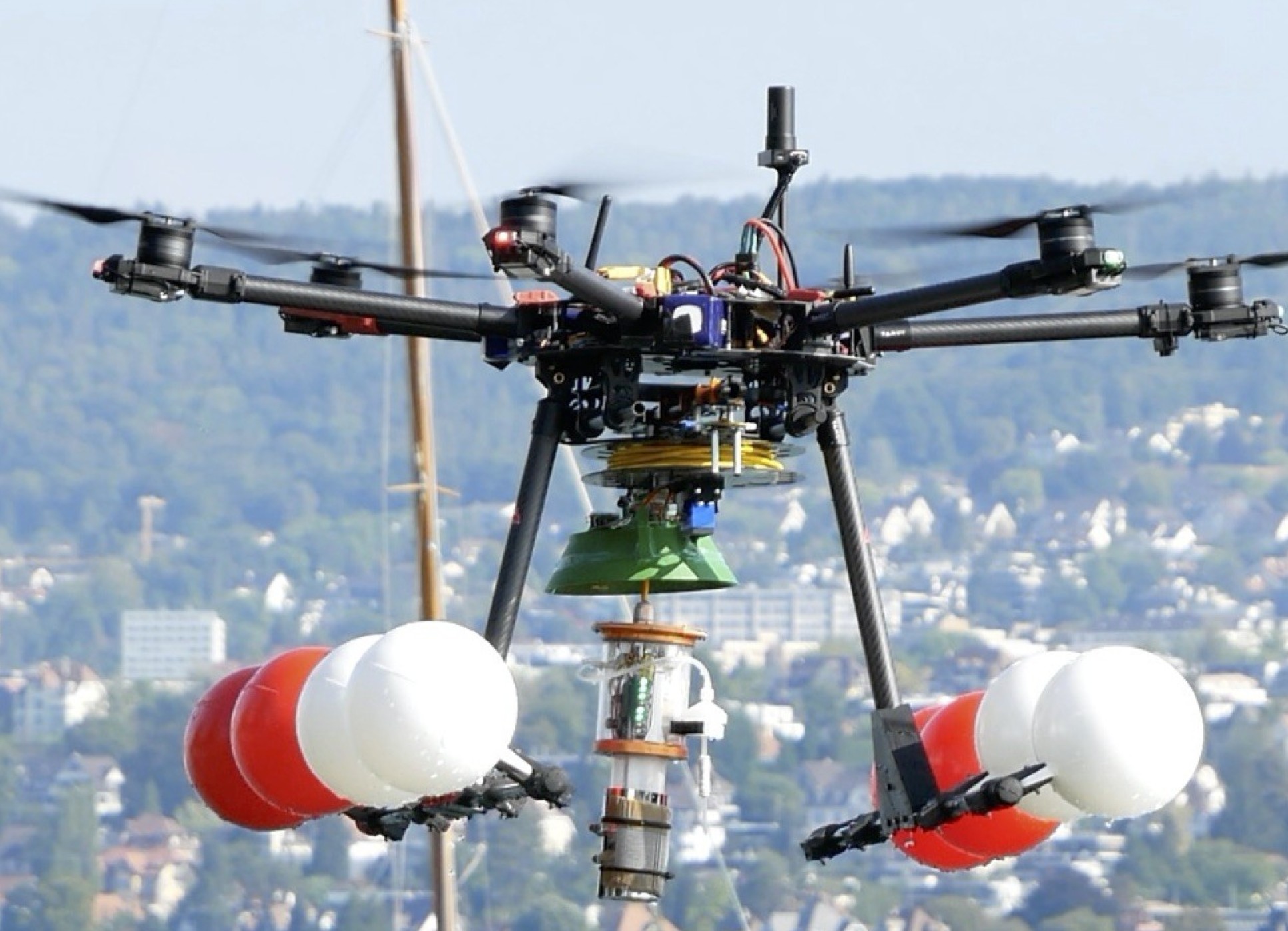

多旋翼无人机可以飞行到一个机器人难以到达的水生环境,降落在水面上将其带有的摄像头和传感器系留移动到10米深度的水下,进行吊舱部署。无人机操作员使用浮力控制和喷射器远程调整吊舱深度和在水中的三维位置,操作人员可以受到来自吊舱的实时视频和传感器反馈,进行实时水生环境监测。无人机采集到样本以后就会盘绕系绳,在起飞并飞回之前与吊舱团聚。
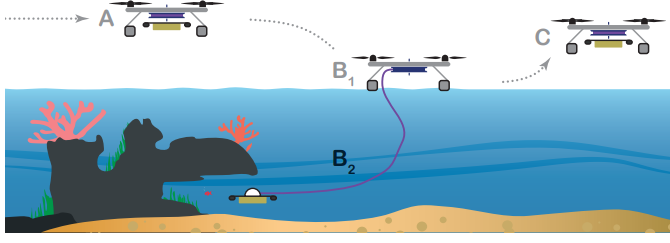
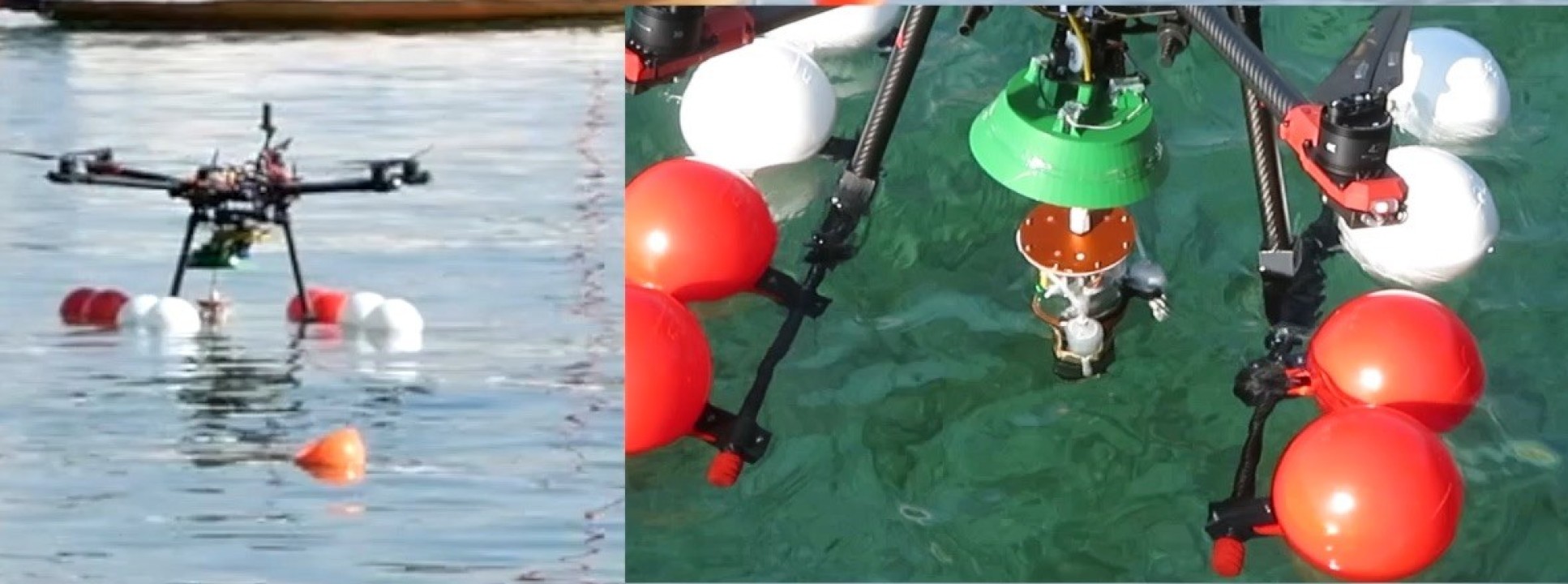
水下吊舱设计是全新的,无人机根据行业标准设计,令MEDUSA系统可以使用工业操作框架轻松构建和部署。研究人员已经在实验室环境和瑞士湖泊的野外环境中测试了MEDUSA,它有效提高了在水生环境中快速部署监控无人机的能力,有助于降低人类前往难以到达的水生环境的风险,还可以帮助监测和维护海上基础设施,如水下能源管道和漂浮风力涡轮机等。
创新关键点
开发可以长途飞行的多旋翼无人机,有效深入难以到达的地区监测水生环境。
创新价值
新技术帮助监测水生环境质量,有助于寻找可能对人类健康构成危害的微生物和藻类大量繁殖的迹象,并在未来可用于监测北极海温度变化等气候线索。
Using UAVs for Aquatic Environment Monitoring
Combining robotic and drone technologies, Imperial College London has developed a new dual-robot drone called the Multi-Environmental Dual Robot for Underwater Sample Collection (MEDUSA), which can reach difficult areas to collect aquatic imagery, samples and metrics It has an important positive effect on ecological and aquatic research.
The drone uses a remote-controlled multi-rotor to fly lift-generating blades that can rotate around a central vertical mast like helicopter blades. MEDUSA's use of multi-rotors allows it to travel long distances over obstacles with high payloads and maneuver in difficult terrain.
The multi-rotor drone can fly to an aquatic environment that is difficult for robots to reach, land on the surface and tether its cameras and sensors to a depth of 10 meters underwater for pod deployment. The drone operator uses buoyancy controls and jets to remotely adjust the pod depth and 3D position in the water, and the operator can receive real-time video and sensor feedback from the pod for real-time aquatic environment monitoring. Once the drone collects the sample, it coils the tether and reunites with the pod before taking off and flying back.
The underwater pod design is completely new, and the drone is designed according to industry standards, allowing the MEDUSA system to be easily constructed and deployed using an industrial operating framework. Researchers have tested MEDUSA in laboratory settings and in the field in Swiss lakes, and it effectively improves the ability to rapidly deploy surveillance drones in aquatic environments, helping to reduce the risk of humans traveling to hard-to-reach aquatic environments, and also It can help monitor and maintain offshore infrastructure such as underwater energy pipelines and floating wind turbines.
智能推荐
结合人工智能驱动的智能监听设备守护自然森林
2022-06-30智能监听设备为地球的未来带来更多希望。通过收集和分析声音数据,它们也在彻底改变环境科学,即生物声学。生物声学,意味着研究人员通过人工智能可以更系统、更有效地监控和研究物种的行为和多样性。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向使用“信念稀疏化算法”可简化自动化设备在不确定情况下的决策过程
2022-09-02新发现为通过简化解决决策问题奠定了基础,并证明了这些方法能够在不损失重大结果的情况下节省相当多的计算时间。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向新型“MIMO雷达”系统可快速识别探测无人机
2022-09-05采用多天线技术开发高分辨率且无需旋转的新雷达,可快速捕捉飞行中的不同类型无人机,完成探测无人机任务。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向创新使用无人机技术简化排雷过程
2022-09-05创新将先进的无人机技术用于排雷工作,检测覆盖传统排雷方法无法覆盖的范围,简化排雷工作,增加排雷操作员的技术安全性。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向