创新背景
制药开发所需的时间、能源和人力资源庞大,开发新技术提高药业开发和评估速度,对制药和医学发展至关重要。
创新过程
哥本哈根大学的黑扎吉斯团队和南丹麦大学斯蒂芬·沃格尔副教授合作研究出名为“基于DNA介导融合的单粒子组合脂质纳米容器融合”的方案(缩写为SPARCLD),是一种可以数百万倍提高疫苗开发速度的新技术。相关论文Single-particle combinatorial multiplexed liposome fusion mediated by DNA发表在《自然-化学》上。

此技术借助DNA纳米技术,人为设计并产生有用的核酸结构,在比针头还小的区域内使用类似肥皂泡的纳米容器,在容器中混合多种成分,可以合成和分析4万种以上不同的分子,在7分钟内提供结果。1纳米即10的负9次方米,相当于4倍的原子,比单个细菌还要小得多。类肥皂泡状的纳米容器中运用合成生物学和合成化学建立人为的分子系统,大约40000多个纳米容器可以安装在一平方毫米中。在纳米尺度范围上进行疫苗开发,可以大幅度节省制药资源。
黑扎吉斯用一升水和海洋的水量对比新技术和以往技术之间的差距。据他解释,新技术所采用的均是已有的学科元素,没有一个元素是全新的,他们以前从未无缝完美地结合在一起。该技术创造性地将高跨度学科元素组合起来,集纳米技术、合成生物化学、组合化学和机器学科等于一体,在已有学科元素基础上研发出提高疫苗开发速度的新技术,可以前所未有的节省人力、材料、能源和精力。
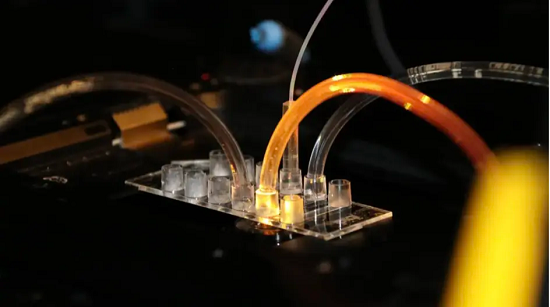
研究负责人表示,参与聚合物等长分子合成的行业和学术团体都可以采用该方法,包括与药物开发相关的配体行业,帮助极速高效地筛选数千种候选分子提高疫苗和药品生产潜力。
该技术可进一步集成,允许直接添加相关应用程序,运用于其他方面。比如合成生物技术工具CRISPR的RNA字符串,或筛选、检测和合成用于制备应对未来大流行所需疫苗的替代RNA。并且,将SPARCLD设置允许与组合后读数相结合,用于蛋白质—配体反应的组合,例如与CRISPR相关的反应。
创新关键点
在现有学科元素的基础上探究组合可能性,医学、化学、生物学和物理学学科交叉,利用已有元素开发新技术,帮助疫苗开发速度数百万倍增长。
By seamlessly combining existing disciplinary elements, vaccine development is millions of times faster
Hezakis' team from the University of Copenhagen and Associate Professor Stephen Vogel of the University of Southern Denmark collaborated on a protocol called "DNA-mediated fusion-based fusion of single-particle combinatorial lipid nanocontainers" (abbreviated as SPARCLD),is a new technology that can speed up million of vaccinum development times .Related paper published in "Nature-Chemistry"——Single-particle combinatorial multiplexed liposome fusion mediated by DNA.
Using DNA nanotechnology, the technology uses a soap bubble-like nano-container in an area smaller than a needle, where multiple components are mixed, and more than 40,000 different molecules can be synthesized and analyzed, providing results in 7 minutes. A nanometer is 10 minus 9 square meters, which is much smaller than a single bacterium.
Vaccine development at the nanoscale can greatly save pharmaceutical resources. Hezakis used a liter of water to compare the gap between the new technology and the previous technology. According to him, the new technology uses elements of existing disciplines, none of which is completely new, but they have never been so seamlessly integrated. The technology combines high-span disciplinary elements, integrating nanotechnology, synthetic biochemistry, combinatorial chemistry and machine disciplines, and develops new technologies to improve the speed of vaccine development on the basis of existing disciplinary elements, which can save manpower and materials. , energy and energy.
The study leader said the approach could be adopted by both industry and academic groups involved in the synthesis of long molecules such as polymers, including the ligand industry associated with drug development.
The technology can be further integrated, allowing related applications to be added directly for use in other areas. Such as the RNA strings of the synthetic biotechnology tool CRISPR, or the screening, detection and synthesis of surrogate RNAs for the preparation of vaccines needed to deal with future pandemics. Also, the SPARCLD setup allows combining post-combinatorial reads for combinatorial protein-ligand reactions, such as those associated with CRISPR.
智能推荐
新型强效核糖核苷抑制剂用于治疗新冠肺炎
2022-06-30美国默沙东的一项研究显示,服用新型抗新冠病毒药物莫努匹拉韦(Molnupiravir)3天后可消除新冠病毒,对SARS-CoV-2(新冠病毒)原始毒株、Delta和Omicron均有效,而接受安慰剂治疗的参与者需要5天甚至更长时间才能达到这个目标。该研究将在2022年的欧洲临床微生物学和传染病大会上发表,由默沙东制药公司的Julie Strizki博士及其同事开展。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向临床药学创新 | 研究发现裸盖菇素可改善抑郁症症状
2022-09-02伦敦帝国理工学院的研究团队对近60名接受抑郁症治疗的患者的脑部扫描进行了两项分析,其中包括针对难治性抑郁症的开放标签试验,以及一项针对更普遍抑郁症的随机对照试验。这两项实验证明,裸盖菇素辅助治疗能够增加患者的大脑连通性,改善抑郁症症状,而且这种效果是传统抗抑郁药物所达不到的。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向Mena蛋白影响乳腺癌细胞对化疗的耐药性
2022-08-07该研究发现了一种名为Mena的蛋白质,表明了紫杉醇治疗三阴性乳腺癌的机制,并发现ERK通路抑制剂与紫杉醇共同使用能够更有效地治疗乳腺癌。这一发现可以帮助医生根据患者肿瘤中的Mena水平来选择治疗方法,同时也为Mena蛋白水平较高的患者的治疗提供了新的药物组合方式,提高了该疾病患者的生存率。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向基于DNA纳米的药物开发新技术减少制药时间
2022-06-29由哥本哈根大学的黑扎吉斯团队和南丹麦大学斯蒂芬·沃格尔副教授合作完成的,被命名为“基于DNA介导融合的单粒子组合脂质纳米容器融合”(SPARCLD)的研究解决方案,可在比针头还小的区域内,合成和分析超过4万种不同的分子,有望大幅减少制药公司的材料、能源和经济成本和时间。该方法通过使用类似肥皂泡的纳米容器,借助DNA纳米技术,可在容器中混合多种成分。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向