创新背景
3D打印是一种以数字模型文件为基础,运用粉末状金属或塑料等可粘合材料,通过逐层打印的方式来构造物体的技术,常在模具制造、工业设计等领域被用于制造模型,对传统制造业有深刻影响。但3D打印的从上到下的逐层打印方式限制了它的效率,如果能够打破逐层建构限制,3D打印的性能会更上一层楼。
创新过程
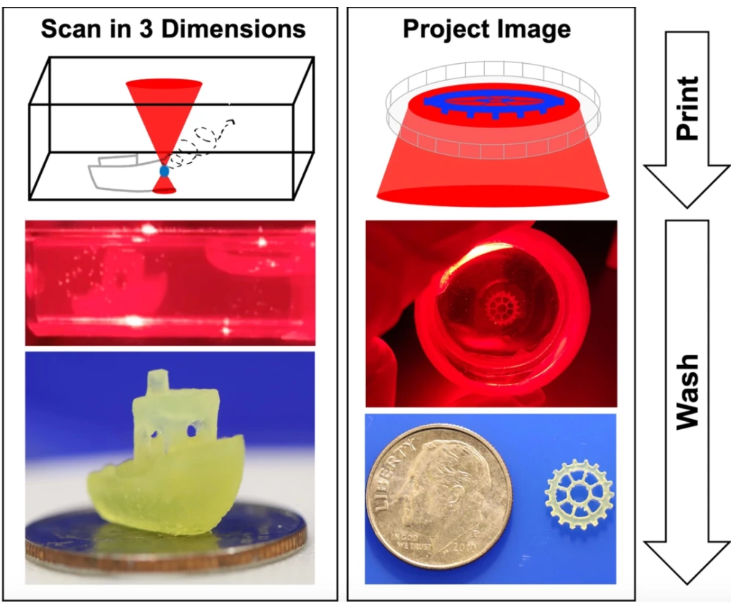
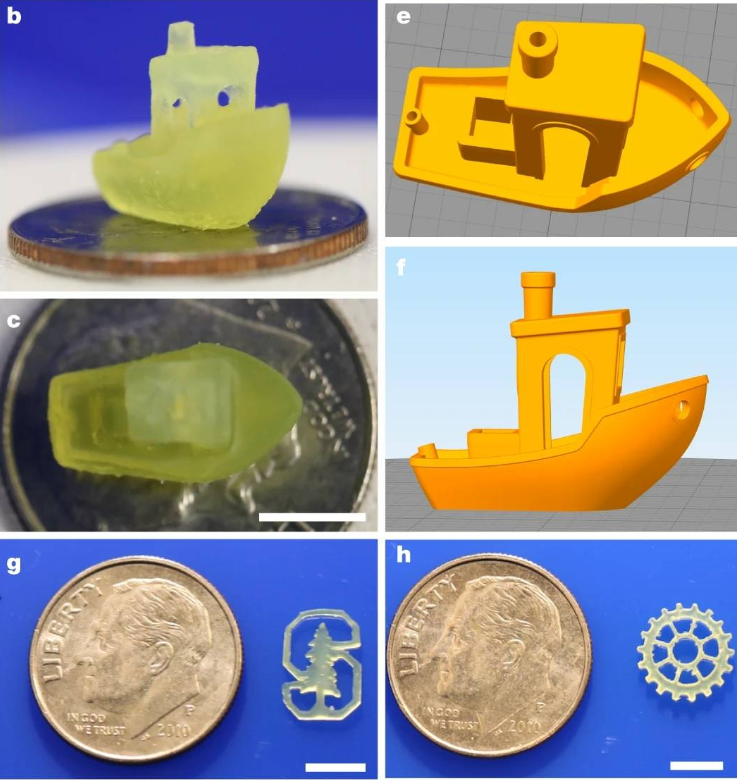
斯坦福大学和哈佛大学研究员合作开发了一种在固定体积的树脂内打印3D物体的方法,研究成果《用于体积 3D 打印的三重态融合上转换纳米胶囊》于2020年4月发表在《自然》上。打印物体完全由厚树脂支撑,减轻3D打印结构支撑需求压力,可以节省材料减少打印时间,以更轻松地打印日益复杂的设计。
研究把感光性的树脂填满容器,用透镜聚焦激光,从容器透明的顶部和侧面照射光线,当树脂暴露在高能蓝色激光下就会聚合固化。为了避免凝胶状树脂受蓝光影响固化成光线形状,研究采用“三重态融合上转换”的技术,先从低能红光开始照射,促进光的波长转换。通过四处移动光源,树脂的不同部分接受光线刺激,可以逐渐构建出一个三维物体。
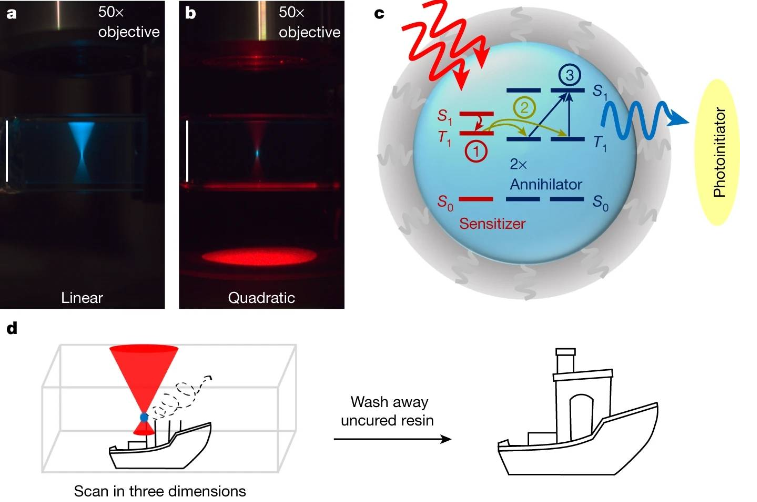
设计将纳米材料分散在树脂中,这是一种含有微小二氧化硅涂层液滴的纳米胶囊,比人类头发宽度小1000倍。红光从任意方向聚集到胶囊上,发生一连串能量转移,从低能红色光子转化为高能蓝色光子。
研究人员表示,新技术非常相近虽然和传统双光子打印机接近,但所需激光功率要小的多。研究正在继续改进,探索同时打印多个点的可能性,这将让打印以更高的分辨率和更小的比例进行,数倍提高打印效率。
新的方法如果向着太阳能电池板方向和光反应方向探索,三重聚变上转换或许能帮太阳能电池板更高效运行,将低能光转换成可用的高能波长;纳米技术可以用于光刺激研究,帮助精准定位治疗。
创新关键点
综合利用激光、纳米材料和树脂实现3D打印无逐层结构支撑。
Laser + resin breaks through the limitations of 3D printing
Stanford University and Harvard University researchers have collaborated to develop a method for printing 3D objects within a fixed volume of resin. The research result, "Triplet fusion upconversion nanocapsules for volumetric 3D printing," was published in Nature in April 2020. superior. The printed object is entirely supported by thick resin, which relieves the need for structural support in 3D printing, which can save material and reduce printing time to more easily print increasingly complex designs.
The research fills the container with photosensitive resin, uses a lens to focus the laser, and irradiates light from the transparent top and sides of the container. When the resin is exposed to high-energy blue laser light, it will polymerize and solidify. In order to prevent the gelatinous resin from being cured into the shape of light due to the influence of blue light, the research adopts the technology of "triple state fusion and up-conversion", which starts from low-energy red light to promote the wavelength conversion of light. By moving the light source around, different parts of the resin are stimulated by light, gradually building a three-dimensional object.
The design disperses the nanomaterial in resin, a nanocapsule containing tiny silica-coated droplets 1,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. Red light is focused onto the capsule from any direction, and a cascade of energy transfers occurs, from low-energy red photons to high-energy blue photons.
The researchers say the new technology is very similar, although close to conventional two-photon printers, but requires much less laser power. Research is continuing to improve, exploring the possibility of printing multiple dots at the same time, which would allow printing at higher resolutions and smaller scales, increasing printing efficiency several times over.
If new methods are explored in the direction of solar panels and light reactions, triple fusion upconversion may help solar panels operate more efficiently, converting low-energy light into usable high-energy wavelengths; nanotechnology can be used for photostimulation research, helping precise positioning treat.
智能推荐
智能制造 | 纳米级精度打印纳米金刚石
2022-06-30通过程序控制的先进打印技术,实现了在任意基底上对含有NV色心的纳米金刚石颗粒的高精度位置操控。该技术将为制造量子讯息处理器和生物传感器等量子器件,开拓出一条实用且具经济效益的出路。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向2021年CES展会 | 科技为用户提供更好的骑行体验
2022-09-08涉及学科涉及领域研究方向P2R-Net新方法根据人体轨迹信息模拟房间内物品摆设
2022-07-27来自慕尼黑工业大学、香港中文大学(深圳)的研究者提出了一种新的场景模拟的方法——P2R-Net :仅仅依靠对3D人体姿态的观察,就能估计与人交互的物体在场景中的摆放位置,该模型的特征是其类别和定向 3D 边框。结果表明,P2R-Net 在 PROX 数据集和 VirtualHome 平台上始终优于基线。该研究入选了 ECCV 2022。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向3D打印或可将玻璃废料变成沙子
2022-06-29采用3D打印混凝土技术将玻璃废料转化为沙子替代品。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向