创新背景
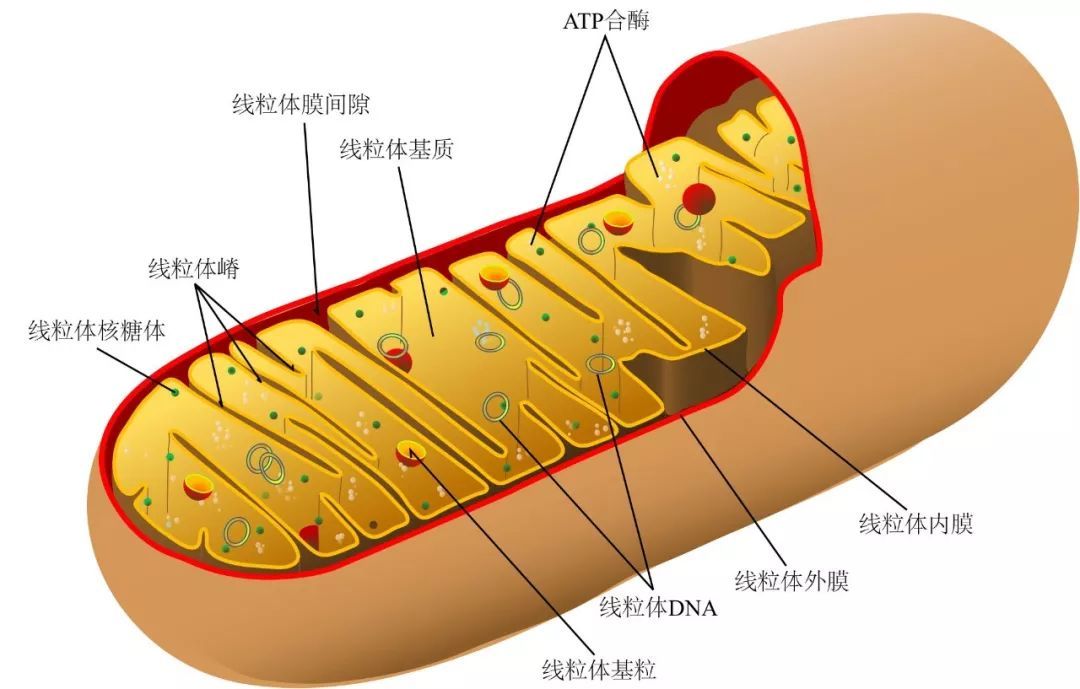
自20世纪60年代发现第一个限制性内切酶,科技逐渐深入基因编辑领域进行对DNA的操控,取得了诸多有效成果,但对于线粒体DNA的研究始终存在不足。线粒体是细胞能量生产的场所,细胞在其中进行有氧呼吸,是细胞的动力源。它时存在于大多数细胞中的由两层膜包被的细胞器,拥有自身的遗传物质和遗传体系。补全线粒体DNA的短板将有效帮助治疗遗产性疾病。
创新过程
2022年4月26日出版的《细胞》杂志发表了韩国基础科学研究所(IBS)针对线粒体DNA研发出的新基因编辑平台——类转录激活因子效应相关脱氨酶(TALED),可以突破以往的基因编辑局限,实现线粒体中A到G碱基的转换。
此前哈佛大学和麻省理工学院组成的研究团队在2020年,创建胞嘧啶碱基编辑器(DaCBE),可实现线粒体DNA的C到T碱基转换,但这项技术仅局限于TC程序,对已确认致病性线粒体点突变的纠正仅达到10%。新的A到G碱基转换对于已知致病性突变的纠正率可达到43%。
TALED主要由功能不同的3部分组成:一是DaCBE用到的DNA结合蛋白转录激活子样效应子,它能够靶向DNA序列,进入线粒体后与之序列结合。二是创新性使用腺嘌呤脱氢酶(TadA8e),这是从大肠杆菌腺嘌呤脱氢酶改造而来的,可以促进A到G碱基的转化。此前并未有人将其使用在线粒体DNA碱基转换上。三是名为DddAtox的胞嘧啶脱氨酶。线粒体DNA是裸露的DNA双链分子,根据研究人员猜想,DddAtox可以短暂分开双链线粒体DNA,使TadA8e进入其中获取访问,实现A到G碱基的高速转化。
研究人员表示,TadA8e是一种已知仅对单链DNA具有特异性的蛋白质。以前从未有人想过把它用在线粒体中进行碱基编辑,因为它应该只对单链DNA具有特异性。正是这种跳出传统的思维局限真正帮助我们发明了TALED。
研究成果补全了线粒体DNA碱基转换的短板,进一步深入可以帮助构建疾病可能模型并有效治疗线粒体DNA带来的遗传性疾病。
创新关键点
跳出思维局限,创新利用TadA8e进入双链DNA进行碱基转换。
TadA8e helps complete the shortcomings of mitochondrial gene editing
The "Cell" magazine published on April 26, 2022 published a new gene editing platform developed by the Korea Institute of Basic Science (IBS) for mitochondrial DNA-Transcription activator-like effect-related deaminase (TALED), which can break through the previous The limitation of gene editing is to realize the conversion of A to G bases in mitochondria.
In 2020, a research team composed of Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology created a cytosine base editor (DaCBE), which can realize the C-to-T base conversion of mitochondrial DNA, but this technology is limited to the TC program. Correction of confirmed pathogenic mitochondrial point mutations reaches only 10%. The new A-to-G base transition can correct up to 43% of known pathogenic variants.
TALED is mainly composed of three parts with different functions: one is the DNA-binding protein transcription activator-like effector used by DaCBE, which can target the DNA sequence and bind to the sequence after entering the mitochondria. The second is the innovative use of adenine dehydrogenase (TadA8e), which is modified from Escherichia coli adenine dehydrogenase, which can promote the conversion of A to G bases. It has not been used before in mitochondrial DNA base switching. The third is a cytosine deaminase called DddAtox. Mitochondrial DNA is a naked DNA double-stranded molecule. According to the researchers' speculation, DddAtox can briefly separate the double-stranded mitochondrial DNA, allowing TadA8e to enter it for access, and achieve high-speed conversion of A to G bases.
TadA8e is a protein known to be specific only for single-stranded DNA, the researchers said. It had never been thought of before for base editing in mitochondria, since it should only be specific for single-stranded DNA. It is this out-of-conventional thinking that really helped us invent TALED.
The research results complement the shortcomings of mitochondrial DNA base conversion, and further research can help build possible disease models and effectively treat genetic diseases caused by mitochondrial DNA.
智能推荐
新材料 | 人造叶绿体有助于将二氧化碳转化为有机物
2022-06-29纳米技术和生物细胞交叉融合实现人造叶绿体并完成批量生产替代。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向新材料 | 创造性利用石墨烯探测细菌运动
2022-06-29利用石墨烯高灵敏度探测细菌运动,发展细胞运动力学、石墨烯运用,应对抗生素耐药性问题。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向细胞学创新 | 使用LLPS创新发现分子分离受到细胞大小调节影响
2022-10-31对分子分离影响因素的新发现有助于生物技术和人造细胞工程发展,可以模仿生物细胞的功能并执行各种任务,推动细胞对病毒做出反应,可推动开发人造皮肤以测试化妆品,或制造食品防腐剂,帮助多个行业避免其产品中人造细胞特性的意外变化。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向微生物学创新 | 创新应用CRISPR技术提高对水中有害微观寄生虫的检测精度
2022-09-22新南威尔士大学的工程师们发现了一种新的更简单的方法,可以检测水中的微小微生物,这些微生物会导致严重的健康风险,甚至可能导致死亡。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向