创新背景
细胞固有的运动和多种生物化学和生物物理信号的发生关系密切,化学和物理信号的发生协同着调节细胞的行为和功能。柔性传感器、检测器在近年来广泛应用于生物监测,但细胞信号监测领域器件还处于新阶段,传感器研发需要考虑性能和材料平衡,既保证监测准确又不损伤细胞。
创新过程
2022年4月22日《德国应用化学》期刊发表了武汉大学研究团队对于心肌细胞电化学和电生理监测的研发成果论文《用于搏动心肌细胞电化学和电生理监测的软电极》。

新电极的柔软性达到新的高度,含有电纺聚基纳米网,具有优异导电性、电化学性能和细胞生物相容性。电极在可自支撑的纳米网络上使用静电纺丝技术,增强传感器的电化学感知性能和稳定性,通过改变静电纺丝过程参数和添加不同的催化剂于电纺溶液中,可控制纳米定向网络结构并把握电化学性能。
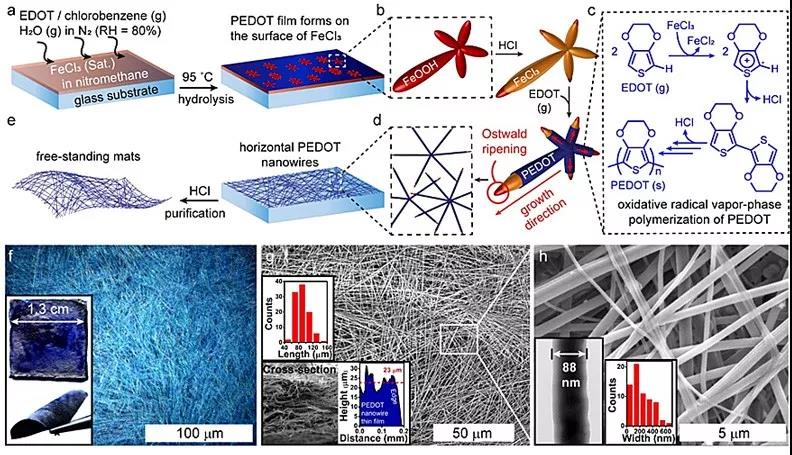
软电极可以在保持心肌细胞自身节律性收缩运动不受影响的情况下实时监测细胞运动中的化学和电生理信号。研究在超柔软电极表面上培养大鼠原代心肌细胞,细胞运动自主有序地进行,和原生心肌细胞一样收缩伸展,带动下层电极同步变形,并且心肌细胞在电极表面上充分舒展方便研究观察。
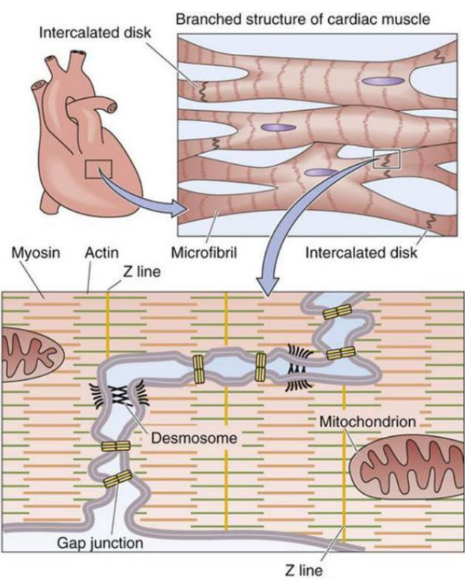
在此基础上,软电极完成细胞自主运动的实时监测,发现运动过程中释放的信号分子和电生理活动,并探究了其中的关系,发现两者相互作用影响心跳。软电极为监测细胞运动的化学和物理信息提供了新的途径,对推动生物科学和细胞研究意义深远,未来或许也能拓展心脏相关的医学领域研究。
创新关键点
在纳米网络上采用高可控性的静电纺丝技术,监测心肌细胞化学物理信息同时保证细胞自主无影响运动。
Ultra-soft electrodes monitor cardiomyocyte electrical signals
On April 22, 2022, the German Journal of Applied Chemistry published the research and development results paper "Soft Electrodes for Electrochemical and Electrophysiological Monitoring of Beating Cardiomyocytes" by the Wuhan University research team on the electrochemical and electrophysiological monitoring of cardiomyocytes.
The new electrodes reach new heights of flexibility and contain electrospun poly-based nanomesh with excellent electrical conductivity, electrochemical performance, and cellular biocompatibility. Electrospinning technology is used for electrodes on self-supporting nanonetworks to enhance the electrochemical sensing performance and stability of the sensor. The nanooriented network structure can be controlled by changing the parameters of the electrospinning process and adding different catalysts to the electrospinning solution. And grasp the electrochemical performance.
Soft electrodes allow real-time monitoring of chemical and electrophysiological signals in cell movement while keeping the cardiomyocyte's own rhythmic contraction movement unaffected. In this study, primary rat cardiomyocytes were cultured on the surface of ultra-soft electrodes. The cells moved in an autonomous and orderly manner. They contracted and stretched like native cardiomyocytes, driving the underlying electrodes to deform synchronously. The cardiomyocytes were fully stretched on the electrode surface to facilitate research and observation.
On this basis, the soft electrode completes the real-time monitoring of the autonomous movement of cells, discovers the signal molecules and electrophysiological activities released during the movement, and explores the relationship between them, and it is found that the interaction between the two affects the heartbeat. Soft electrodes provide a new way to monitor the chemical and physical information of cell movement, which has far-reaching significance for promoting biological science and cell research, and may also expand research in the field of heart-related medicine in the future.
智能推荐
真菌学创新 | 酵母菌“后来者杀戮”生存策略创新研究
2022-11-15酵母所具有“后来者杀戮”生存策略的发现有助于科学研究者了解单细胞微生物的行为、单细胞生物到多细胞生物的进化机制。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向生命科学创新 | “CAHS蛋白”研究全新揭示缓步动物在极端脱水条件下的生存机制
2022-10-31与细胞或生物体的干燥保存相关的机制的研究可能对许多未来的应用起作用。新机制的发现有助于找到改善细胞材料和生物分子在干燥状态下保存的方法,延长用于研究的材料的保质期。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向细胞生物学创新 | 创新发现ERG28蛋白质有助于调节胆固醇的产量
2022-11-07研究人员发现,一种先前特征不明显的蛋白质在胆固醇生成中起着支持作用。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向大脑前额叶皮层中有毒副产物的积累导致认知疲劳
2022-08-17巴黎 Pitié-Salpêtrière 医院和巴黎大脑研究所的研究团队经过两组对比实验分析发现,持续的高强度工作不仅会导致瞳孔扩张的减少,还会造成更高水平的谷氨酸积累。这项研究的结果否定了以往认为疲劳是大脑制造的幻觉的理论,表明了认知工作会导致真正的大脑功能的改变,即有害物质的积累。因此,疲劳确实会是一种让人停止工作的信号,但目的不同:它是为了保持大脑功能的完整性。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向