创新背景
传统使用的扬声器依靠电流通过线圈时产生磁场,磁场影响扬声器膜和其上方得空气产生声音,让人听到音频器件得声音。在此基础上,研究者们研发出便携轻巧得薄膜扬声器,不需依靠支撑物,自由弯曲就能发出声音。但这样的薄膜扬声器安装在某个表面时,振动会受到阻碍,从而影响声音产生。
创新过程
根据已有扬声器的问题,麻省理工学院的研究团队研发出一种极薄的薄膜扬声器,厚度仅如寻常纸张,大小如手掌,重量约和10美分硬币一样,它克服了以往薄膜扬声器受到表面阻碍的问题,可以将任何表面变成音源。2022年4月成果论文《基于压电微圆顶阵列的超薄柔性扬声器》发表在《IEEE工业电子汇刊》电子期刊上。
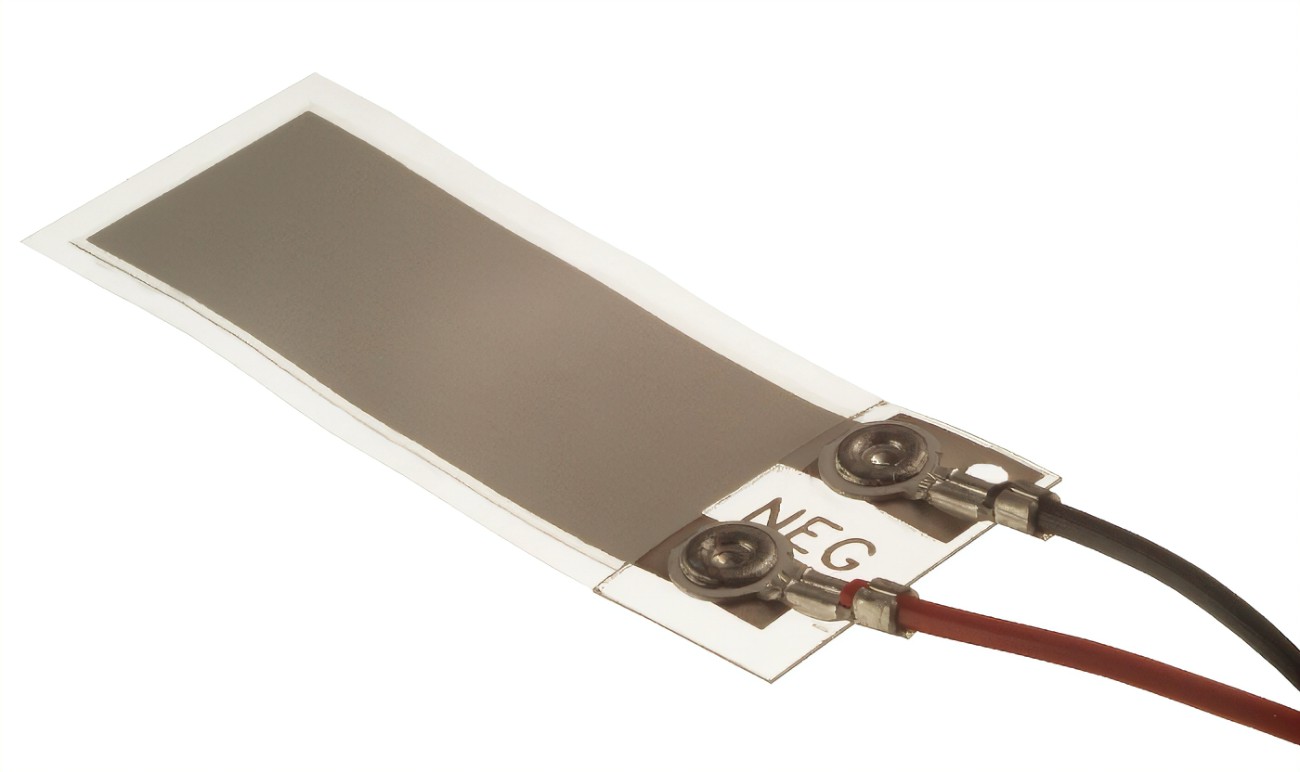
无论将薄膜安装在什么表面,都能产生高质量的声音,声音输入与输出的偏差很小,失真畸变的影响非常小。因为新薄膜扬声器的振动不是以往的整个材料振动,而是薄膜层上的微小圆顶振动,减小了来自结合表面的阻碍。而且,因为它非常轻薄,操作所需的能量功率极小,只是传统扬声器的一小部分,很适合应用于小型便携、电池寿命有限的智能设备上。

新超薄扬声器的制造使用了一种成型的压电薄膜材料来简化扬声器设计。研究人员在PET轻型塑料薄片上用激光钻出小孔,在穿孔的PET层的底部铺上一层只有8微米厚的PVDF薄膜,这是一种极薄的高分子敏感压电材料。两者组合成薄片,然后在薄片上方施加真空,下方施加高温热源。
PVDF层化学稳定性强,压电常数大。真空和高温热源对它原本的稳定外形造成影响,产生的压力差使它膨胀。PVDF无法强行穿过PET薄片,只能在没有被PET阻挡的小孔处,突起微小的圆顶。然后,在PVDF的另一侧铺上另一层PET层,间隔圆顶和结合表面。
微小圆顶的宽度和厚度都极小,每个圆顶单独振动发声,人耳能听见的声音必须众多的小圆顶一起振动才能产生。这些圆顶与安装表面的结合被间隔层保护,能够自由振动。间隔层也保护圆顶免受磨损和冲击,增强了扬声器的耐用性。当电压施加在薄膜上时,圆顶振动带动薄膜移动,然后移动其上方的空气并产生声音。

超薄的薄膜扬声器可以用在嘈杂的环境中,如飞机驾驶舱,通过产生相同振幅但相位相反的声音,帮助消除噪音。也可用于沉浸式娱乐,为娱乐提供完整沉浸的三维音频。并且,成千上万的微小圆顶振动使扬声器有足够高的共振频率,可以用于超声波成像方面应用,以更高的频率产生更高分辨率的图像。
研究人员表示,制作扬声器过程非常简单直接。如果将来能把它与卷对卷加工工艺结合起来,扬声器可以大量制造,像墙纸一样覆盖墙壁、汽车或飞机内部。如果在薄膜的振动圆顶上覆盖一层反射表面,或许可以为未来发光现实技术提供思路。通过激活可伸缩的振动表面,精确地生成空气的机械运动,可以为各种技术提供新的方式和思路。
创新关键点
结合PVDF薄膜和PET塑料薄片,使扬声器摆脱整块材料振动的传统模式,只让微小圆顶振动带动空气振动产生失真小的声音。
Make extremely thin speakers from thin films and plastic sheets to overcome surface obstacles and reduce sound distortion
Based on the problems of existing speakers, a research team at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has developed an extremely thin film speaker, which is only as thick as ordinary paper, about the size of a palm, and weighs about the same as a 10-cent coin. The problem of surface obstruction can turn any surface into a sound source. In April 2022, the result paper "An Ultra-Thin Flexible Loudspeakers Based on a piezoelectric Micro-Dome Array" was published in the electronic journal "IEEE Transactions of Industrial Electronics".
No matter what surface the film is mounted on, it produces high-quality sound with very little deviation from sound input to output and very little effect of distortion distortion. Because the vibration of the new membrane speaker is not the vibration of the entire material in the past, but the vibration of the tiny dome on the membrane layer, which reduces the resistance from the bonding surface. And, because it is so thin and light, it requires very little energy and power to operate, a fraction of that of traditional speakers, making it ideal for small, portable smart devices with limited battery life.
The new ultra-thin speakers are made using a shaped piezoelectric film material to simplify speaker design. The researchers drilled small holes with a laser in the PET lightweight plastic sheet, and laid a thin film of PVDF, an extremely thin polymer-sensitive piezoelectric material, on the bottom of the perforated PET layer with a thickness of only 8 microns. The two are combined into a sheet, then a vacuum is applied above the sheet and a high temperature heat source is applied below.
The PVDF layer has strong chemical stability and large piezoelectric constant. The vacuum and high temperature heat sources affect its original stable shape, and the resulting pressure differential causes it to expand. PVDF cannot force through the PET sheet, and can only protrude tiny domes at the small holes that are not blocked by the PET. Then, another layer of PET was laid on the other side of the PVDF, spacing the dome and bonding surface.
The width and thickness of the tiny domes are extremely small, and each dome vibrates separately to produce sound. The sound that can be heard by the human ear must be produced by the vibration of many small domes. The combination of these domes with the mounting surface is protected by a spacer layer and is able to vibrate freely. The spacer layer also protects the dome from abrasion and impact, enhancing the speaker's durability. When a voltage is applied to the membrane, the dome vibrates to move the membrane, which in turn moves the air above it and produces sound.
Ultra-thin membrane speakers can be used in noisy environments, such as airplane cockpits, to help cancel noise by producing sounds of the same amplitude but opposite phases. It can also be used for immersive entertainment, providing full immersive 3D audio for entertainment. And, the vibrations of thousands of tiny domes give the loudspeaker a high enough resonant frequency for ultrasound imaging applications, producing higher-resolution images at higher frequencies.
According to the researchers, the process of making the loudspeaker is straightforward. If in the future it can be combined with a roll-to-roll process, the speakers could be mass-produced to cover walls, car or plane interiors like wallpaper.If the vibrating dome of the film is covered with a reflective surface, it may provide ideas for future technology of luminous reality. By activating a stretchable vibrating surface to precisely generate the mechanical motion of air, it could lead to new ways and ideas for a variety of technologies.
智能推荐
智能制造 | 新型“材料显微外科”技术可提高废物回收效率
2022-09-27新南威尔士大学可持续材料研究与技术中心(SMaRT)的“微回收科学”先驱们开发出了一项有望提升先进制造业的新技术。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向新材料 | 新型吸湿材料可减少防护服的热应激
2022-09-30创新利用蒸发冷却原理开发可控制防护服中微环境中的湿度水平的超吸湿性复合膜来,有效处理防护服的热应激。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向医用新材料 | 新型“软骨替代品”可缓解膝盖疼痛
2022-09-27杜克大学的研究人员已经开发出一种凝胶软骨替代品来缓解膝盖疼痛,它甚至比真正的软骨更结实、更耐用。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向