创新背景
针灸是针法和灸法的总称,中国古人利用金属针具或艾炷、艾卷,在人体特定的部位进针施灸,用以治疗疾病,解除病痛,创立了独具特色的人体经络腧穴理论。针灸疗法的特点是治病不靠吃药,只是在病人身体的一定部位(穴位)用针刺入,达到刺潋神经并引起局部反应,或用火的温热刺激烧灼局部,以达到治病的目的。穴位和经脉难以用现代解剖的理论来解释,破解针灸所运用的人体解剖机制,有助促进疾病治疗发展。
创新过程
2021年,哈佛大学、复旦大学和中国中医科学院多名研究人员组成团队,对针灸的神经解剖学机制进行分析研究,成果《电针驱动迷走肾上腺轴的神经解剖学基础》发表在医学顶刊《Nature》上。研究对小鼠后肢穴位进行微弱电刺激和低强度针刺激,能激活抗炎通路,促进抗炎作用。
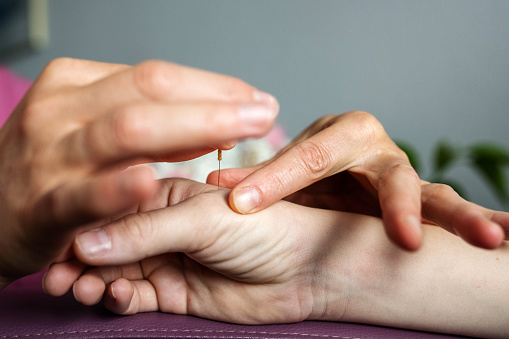
实验小鼠是一对对照组,一组是正常小鼠,另一组杀死了分泌多巴胺和甲肾上腺素的嗜铬细胞或去甲肾上腺素能神经元被杀死。研究人员通过对患脓毒血症小鼠的后肢足三里穴位进行电针刺激,进入结缔组织,激活一组有髓鞘表达Prokr2蛋白的感觉神经元。电针是用针刺入结缔组织后,在针上通以感应人体生物电的微量电流波。
这组神经元可以调节迷走神经-肾上腺反射,特异性还可以支配四肢的深层筋膜组织,达到抑制炎症的效果。迷走神经-肾上腺轴是迷走神经给肾上腺传输信号的一条信号通路,信号传输会刺激肾上腺释放多巴胺。低强度电针刺激此通路只能通过后肢电针,无法通过腹部穴位刺激。表明在不同部位给予神经元刺激,激活的神经通路有各自的指向,抑制炎症效果不同。
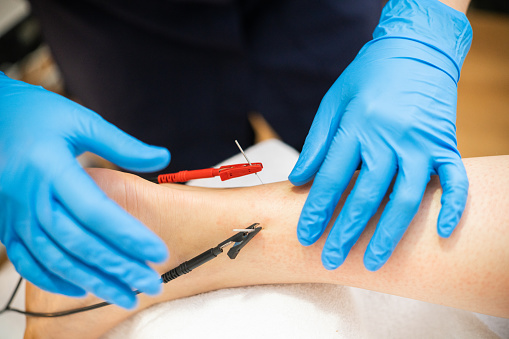
同时,强度不同的电针刺激对炎症的抑制效果也不同。高强度电针刺激腹部和后肢穴位,会激活启发脾脏里的去甲肾上腺素能神经纤维,增强抑制效果。此外,刺激的时机把握也极为重要。在疾病开始和细胞因子风暴之前加以治疗,炎症抑制程度极高,可将小鼠存活率提高60%。如果错过最佳时机,病症和炎症反应会加重。
研究为电针灸刺激足三里穴位(ST36)有全身抗炎效果找到了现代神经解剖学的基础。进一步对电针灸治疗进行研究对于多种疾病炎症抑制和慢性疾病控制将有积极作用。专业领域人士表示,用电针灸刺激特定部位可以调节某些身体机能并治疗疾病,属于近年来新型医学领域的一种,它的深入发展对于医学发展具有良好的推动作用。
创新关键点
用电针代替针,从特定身体部位进行新行生物电子医疗,解析针灸的现代神经解剖学机制。
创新价值
解析针灸治疗原理,发展电针灸医疗方式,推动调节身体机能和治疗疾病的医学新方法发展。
Neuroanatomical principles crack acupuncture therapy
In 2021, a team of researchers from Harvard University, Fudan University and the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences will form a team to analyze and study the neuroanatomical mechanism of acupuncture and moxibustion. And and the result “A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal-adrenal axis “ have published in the top medical journal "Nature".Weak electrical stimulation and low-intensity acupuncture stimulation of acupuncture points on the hind limbs of mice can activate the anti-inflammatory pathway and promote the anti-inflammatory effect.
The experimental mice were a control pair, one was normal mice, and the other was killed by killing chromaffin cells or noradrenergic neurons that secrete dopamine and norepinephrine. The researchers used electroacupuncture to stimulate the Zusanli acupoint in the hindlimb of mice with sepsis to enter the connective tissue and activate a group of myelinated sensory neurons that express the Prokr2 protein. Electroacupuncture is a micro-current wave that induces bioelectricity in the human body after the needle is inserted into the connective tissue.
This group of neurons can regulate the vagus-adrenal reflex, and can specifically innervate the deep fascia of the limbs to inhibit inflammation. The vagus-adrenal axis is a signaling pathway through which the vagus nerve transmits signals to the adrenal glands, which stimulate the release of dopamine from the adrenal glands. Low-intensity electroacupuncture to stimulate this pathway can only be done through hindlimb electroacupuncture, not through abdominal acupuncture points. It shows that when neurons are stimulated in different parts, the activated neural pathways have their own directions, and the effect of inhibiting inflammation is different.
At the same time, electroacupuncture stimulation with different intensities had different inhibitory effects on inflammation. High-intensity electroacupuncture stimulates acupuncture points on the abdomen and hind limbs, which activates noradrenergic nerve fibers in the spleen and enhances the inhibitory effect. In addition, the timing of stimulation is also extremely important. Treatment before the onset of the disease, and before the cytokine storm, has a very high degree of inhibition of inflammation and can increase the survival rate of mice by 60%. Symptoms and inflammatory responses are exacerbated by missing the best poetry collections.
The study found a modern neuroanatomical basis for the systemic anti-inflammatory effect of electroacupuncture on the Zusanli acupoint (ST36). Further research on electroacupuncture therapy will have a positive effect on the inhibition of inflammation in various diseases and the control of chronic diseases. Professionals said that stimulating specific parts with electroacupuncture can regulate certain bodily functions and treat diseases. It is one of the new medical fields in recent years.
智能推荐
美国认知神经科学学会Michael Gazzanigas演讲:意识的本能(3)
2022-09-14认知神经科学协会(CNS)致力于发展思维和大脑研究,旨在研究认知的心理,计算和神经科学基础,认知神经科学这个词现在已经存在了将近三十年,它确定了一种跨学科的方法 来理解思想的本质。认知神经科学学会每年春季都举行一次年度会议。会议的目的是召集来自世界各地的研究人员,以分享认知神经科学方面的最新研究。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向利用新型脑损伤计算机模型预测患者脑出血情况
2022-09-01帝国理工学院的研究团队开发了一种新型的创伤性脑损伤(TBI)机器模型,能够以超高的分辨率绘制大脑中的血管网络。这个新的机器模型为头部损伤导致脑出血的方式提供了见解,有助于改善脑外伤的诊断和预防。还可以帮助医护人员预测患者的头部损伤导致的脑出血情况,挽救患者的生命。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向FSP1还原酶推动非典型维生素K循环,抑制铁死亡
2022-08-15本研究不仅发现了维生素K是一种新的铁死亡抑制剂,还揭示了维生素K代谢在血液凝固中的最后一个谜团,并阐明了维生素K能够为法华林解毒的分子机制,即FSP1作为维生素K的还原酶,将其还原为维生素K对苯二酚(VKH2),从而缓解法华林导致的毒副作用。这项研究将有助于解释维生素K在生命进化中的作用,也为开发针对铁死亡相关疾病的新型治疗策略铺平了道路。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向临床医学创新 | 开发新型“纳米孔封锁传感器”可帮助检测早期癌症
2022-09-29来自新南威尔士大学的研究人员经创造了首个“纳米孔封锁传感器”的早期版本,它可以在快速的单分子水平上分析疾病生物标志物。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向