创新背景
目前对于新冠肺炎引起的呼吸衰竭,一般使用氧气、氦气和一氧化氮等无害气体来进行治疗。急性新冠肺炎症状和新冠肺炎愈后的症状会有呼吸衰竭引起的低氧血症,这是肺通气受阻引起的血液含氧不足,动脉血氧分压低于同龄人的正常下限。除了用气体治疗,目前也会采用外源性表面活性剂和一些抗病毒和抗细胞因子药物的特定变体进行治疗。但这些治疗方式是否能根本消除病症以及后续反应尚无明确结论。新冠病毒在人体反应严重时会引起呼吸衰竭和神经错乱,亟需研发合适的治疗方式帮助恢复机体呼吸能力,保证减弱病毒对呼吸和神经的伤害。
创新过程
托木斯克国家研究医学中心药理学和再生医学研究所副主任弗拉基米尔·乌杜特表示,真正治疗呼吸衰竭和低氧血症,需要执行一项能让血氧饱和度增加的程序。弄清楚这种效果是如何实现的,并了解清楚肺受损时改善氧气供应的机制。
2020年年底,托木斯克大学科研人员发现,吸入氙气可以治疗新冠肺炎带来的呼吸功能损伤,缓解呼吸衰竭问题,甚至改善精神错乱和压力巨大的状况。2022年,俄罗斯科学院托木斯克国家研究医学中心药理学和再生医学研究所的科学家证实,氙气吸入可有效治疗肺部通气功能障碍,并利用3D打印研发了一种可执行该过程的设备,构成完整的技术系统。
氙是一种非金属元素,在常温常压下无色、无嗅、无味,化学性质极不活泼,极具惰性。空气和温泉气体中都存在氙,也可以从液态空气中与氪一起被分离得到。氙除了在照明技术上的应用,医学也常利用它的惰性,用于深度麻醉剂、医用紫外线、标准气、特种混合气等。因为氙气趋向许多特定受体,可以调节神经组织的兴奋性,起到催眠和抗压作用,从而阻止神经性疾病。

在肺泡和毛细血管之间,存在气体交换和表面活性剂。表面活性剂排列在肺泡内,时保护肺泡呼气时不因低表面张力而关闭的物质。新冠肺炎会损伤气体交换和表面活性剂,造成呼吸衰竭和血液缺氧。
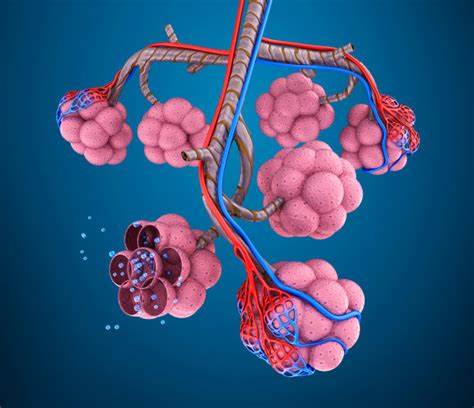
根据氙气的特性,研究者们发现,对于新冠肺炎造成的破坏,氙气可以恢复肺泡和毛细血管之间的气体交换和表面活性剂,从而达到治疗效果。这样一来,氙气吸入可以帮助从空气中吸入氧气转移到血液中,治疗呼吸衰竭,重开肺部通气。这种效果可以通过传统的脉搏血氧仪看到。
吸入氙气的设备尚且没有成熟技术可以生产,目前可以利用3D打印制作成本低廉。氙气治疗为新冠引起的呼吸衰竭提供新的治疗方式,可以更进一步帮助恢复低血氧症引起的精神错乱。
创新关键点
利用化学元素特性考虑治疗新冠病情的新方式。
Xenon inhalation can help treat respiratory failure caused by COVID-19
Vladimir Udut, deputy director of the Institute of Pharmacology and Regenerative Medicine of the Tomsk National Research Medical Center, said that the real treatment of respiratory failure and hypoxemia requires a procedure that increases blood oxygen saturation. Find out how this effect is achieved and understand the mechanisms that improve oxygen supply when the lungs are damaged.
At the end of 2020, researchers at Tomsk University discovered that inhaling xenon can treat respiratory damage caused by new coronary pneumonia, relieve respiratory failure, and even improve mental confusion and stress. In 2022, scientists from the Institute of Pharmacology and Regenerative Medicine of the Tomsk National Research Medical Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences confirmed that xenon inhalation can effectively treat lung ventilation dysfunction, and developed a device that can perform the process using 3D printing. , constitute a complete technical system.
Xenon is a non-metallic element that is colorless, odorless and tasteless under normal temperature and pressure, and is extremely inert and inert in chemical properties. Xenon is present in both air and hot spring gases, and can also be isolated from liquid air along with krypton. In addition to the application of xenon in lighting technology, medicine often uses its inertness for deep anesthetics, medical ultraviolet rays, standard gas, special mixed gas, etc. Because xenon gas tends to many specific receptors, it can regulate the excitability of nerve tissue, play a hypnotic and anti-stress effect, thereby preventing neurological diseases.
Between the alveoli and capillaries, there is gas exchange and surfactants. Surfactants line the alveoli and protect the alveoli from closing due to low surface tension during exhalation. COVID-19 impairs gas exchange and surfactants, causing respiratory failure and hypoxia of the blood.
Based on the properties of xenon gas, the researchers found that for the damage caused by new coronary pneumonia, xenon gas can restore gas exchange and surfactant between alveoli and capillaries, thereby achieving therapeutic effects. In this way, xenon inhalation can help transfer oxygen from the air to the bloodstream, treat respiratory failure, and reopen the lungs. This effect can be seen with conventional pulse oximeters.
There is no mature technology to produce xenon-inhaling equipment, and 3D printing is currently available at low cost. Xenon therapy offers a new treatment modality for respiratory failure caused by Covid-19, which could go one step further to help restore delirium caused by hypoxemia.
智能推荐
药物摄入可能会增加高温引起的心肌梗死风险
2022-08-02耶鲁大学的陈凯团队通过对2494名患者的数据进行研究分析,认为服用抗血小板药物和β受体阻滞剂这两种常规心血管疾病治疗药物,将会提升患者非致命高温相关的心脏病风险。这一发现可以有助于开发针对性策略,降低与温度上升有关的心血管疾病负担。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向改变治疗顺序有可能改善乳腺癌治疗和护理
2022-08-02改变乳腺癌治疗顺序,确定改变顺序对于可改善现有治疗和护理效率。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向物联网+临床医学 | 结合手机和智能手表的新型可穿戴技术为量化神经疾病病情提供客观依据
2022-09-21该研究开发了一种能够与手机和智能手表结合的新型可穿戴技术。这项数字化卫生技术使帕金森患者能够在家进行病情监测,有效地缓解了因病情频繁波动导致难以准确判断病情进展的问题,也为客观量化神经疾病的病情提供了依据。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向肿瘤学创新 | 创新利用“玻璃气泡”纳米载体提升胰腺癌治疗效果
2022-11-09研究人员开发了一种技术,通过纳米级颗粒装载伊立替康(一种被批准为胰腺癌药物方案一部分的化疗药物)和3M-052(一种可以增强免疫活性并帮助克服肿瘤耐药性的研究药物)对胰腺肿瘤进行联合治疗。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向