创新背景
人体器官之间相互紧密联系依赖,一种疾病可能引起多个器官共同反应,利用新技术探究人体器官之间的关系,对于治疗疾病意义重大。
创新过程
2022年4月27日出版的《自然·生物医学工程》杂志上发表了美国哥伦比亚大学工程系和医学中心一个研究团队开发的多器官芯片的人体生理模型成果。可以为疾病的个性化治疗提供疾病建模参考和器官功能研究技术。
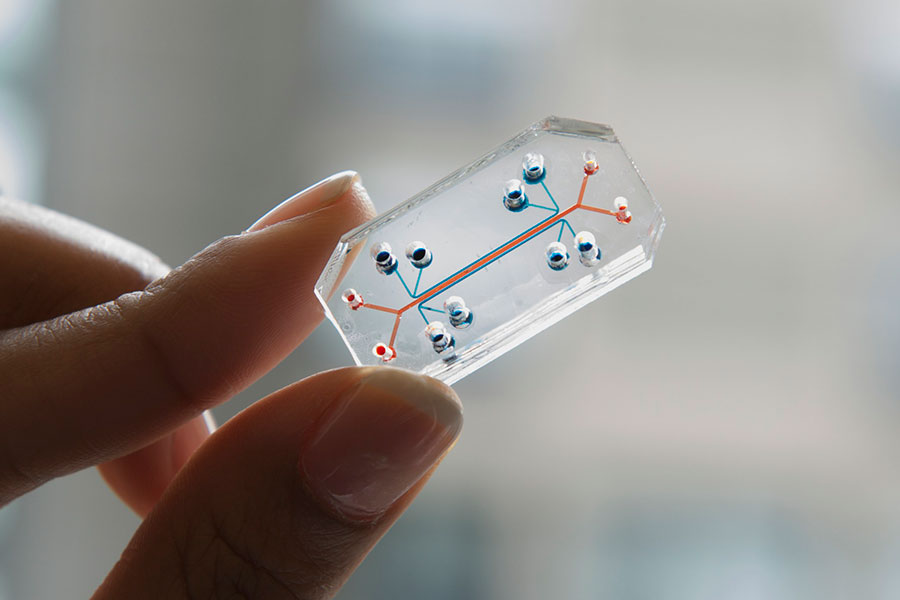

研究从人体器官工作中获取灵感,制造与显微镜载玻片大小芯片,由经过工程改造人体器官组织组成,包括心脏、骨骼、肝脏和皮肤。每个器官组织的胚胎起源、结构和功能特性不同,都受到癌症治疗药物的影响。研究保持它们的独立运行环境,像人体工作一样,通过血管促进循环细胞和生物活性因子流动,连接器官之间的功能,保证能像人体器官一样相互依赖和作用。
研究团队从同一系人类少量血液样本中获得诱导多能干细胞,创建组织模块。用选择性渗透的内皮屏障将它们血管流分开,让它们处于优化的环境中。个体组织环境能够跨越内皮屏障并通过血管循环进行交流。将产生巨噬细胞的单核细胞引入血管循环,帮助模块组织反应损伤或疾病。
团队将已经生长和成熟4到6周的组织在通过血管流动连接后又维持了4周,证明该模型可用于长期研究。并用抗癌药物多柔比星对各组织进行测试,产出相同药物对各器官癌症治疗的效果,展示模型用于研究人类重要疾病和检查抗癌药物的副作用的方法和结果。

多器官芯片具有即插即用的优秀性能,研究开发出多器官芯片计算模型,对药物的吸收、分布、代谢和分泌进行数学模拟,结果证明模型可以正确预测药物作用过程。研究人员表示,多器官芯片准确地预测了心脏毒性和心肌病,这通常需要临床医生减少阿霉素的治疗剂量,甚至停止治疗。
创新关键点
芯片仿人体器官组织工作,深度探究人体工作原理及治疗疾病的过程和效果。
创新价值
模型可以用于药物开发和治疗探究,精准药物治疗效能,帮助心脏疾病的研究和治疗。团队目前正在使用这种芯片的变体继续针对个性化患者进行研究,并为学术和临床实验室开发一种用户友好的标准化芯片,以帮助充分利用其推进生物和医学研究的潜力。
Multi-organ chips help the human body to explore principles
On April 27, 2022, the journal "Nature Biomedical Engineering" published the results of a human physiological model of a multi-organ chip developed by a research team from the Department of Engineering and Medical Center of Columbia University in the United States. It can provide disease modeling reference and organ function research technology for personalized treatment of diseases.
The research draws inspiration from working with human organs to create and microscope slide-sized chips consisting of engineered tissue from human organs, including heart, bone, liver and skin. The embryonic origin, structure and functional properties of each organ tissue are different and are affected by cancer treatment drugs. The research maintains their independent operating environment, like the work of the human body, promotes the flow of circulating cells and bioactive factors through blood vessels, connects the functions between organs, and ensures that they can rely on and act like human organs.
The research team created tissue modules by obtaining induced pluripotent stem cells from a small blood sample of humans from the same line. Separate their vascular flow with a selectively permeable endothelial barrier, leaving them in an optimized environment. Individual tissue environments are able to cross the endothelial barrier and communicate through the vascular circulation. Introduce macrophage-producing monocytes into the vascular circulation to help modular tissues respond to injury or disease.
The team maintained tissue that had grown and matured for 4 to 6 weeks for an additional 4 weeks after being connected by vascular flow, demonstrating that the model could be used for long-term studies. The anti-cancer drug doxorubicin is also tested on each tissue to produce the effect of the same drug on cancer treatment in each organ, demonstrating the methods and results of the model used to study important human diseases and examine the side effects of anti-cancer drugs.
The multi-organ chip has excellent plug-and-play performance. The multi-organ chip computing model has been researched and developed to mathematically simulate the absorption, distribution, metabolism and secretion of drugs. The results show that the model can correctly predict the drug action process. The researchers said the multi-organ chip accurately predicted cardiotoxicity and cardiomyopathy, which often required clinicians to reduce or even discontinue treatment with doxorubicin.
Models can be used for drug development and treatment exploration, precision drug treatment efficacy, and aid in the research and treatment of heart disease. The team is currently using a variant of this chip to continue research on individualized patients and to develop a user-friendly standardized chip for academic and clinical laboratories to help take full advantage of its potential to advance biological and medical research.
智能推荐
创新利用肠道微生物衍生的鞘脂改善脂肪肝
2022-08-19康奈尔大学的研究团队在实验中对鞘脂进行了标记,发现肠道微生物的代谢产物能够进入肝脏和结肠,并进一步发现鞘脂分子通过改善呼吸能够调节肝脏的脂肪酸过载。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向脑科学理论创新 | 影响儿童阅读障碍的因素在小学前期就已形成
2022-08-09通过调查群体的大脑阅读区域发育状况确定阅读干预的正确时间。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向传感器+生物医学 | 利用新型“棉导电线”批量生产带有可穿戴传感器的服装
2022-09-25该研究利用一种棉基导电线纺成新型低成本传感器,并将其缝制到口罩中监测使用者呼吸,缝制到T恤上监测使用者心跳活动。该研究使得这种传感器可以大规模生产,它们已经可以无缝集成,甚至可能帮助诊断和监测未来的疾病治疗,同时也开创了新一代服装可穿戴设备。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向美国认知神经科学学会Michael Gazzanigas演讲:意识的本能(1)
2022-09-14认知神经科学协会(CNS)致力于发展思维和大脑研究,旨在研究认知的心理,计算和神经科学基础,认知神经科学这个词现在已经存在了将近三十年,它确定了一种跨学科的方法 来理解思想的本质。认知神经科学学会每年春季都举行一次年度会议。会议的目的是召集来自世界各地的研究人员,以分享认知神经科学方面的最新研究。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向