创新背景
蛋白质是细胞组成的关键部分,是生命活动的主要承担者,没有蛋白质就没有生命。了解蛋白质的生命作用机制,需要先了解蛋白质的三维结构。蛋白质功能认识对于病理学、制药都具有重要意义。
创新过程
2022年4月,《自然·通讯生物学》发表了美国欧道明大学和兰州大学研究人员合作研发的有助利用冷冻电镜技术成像解析蛋白质三维结构的新算法成果《使用两个球形嵌入从低温 EM 投影图像进行 3D 重建》,是一种基于球面嵌入的蛋白质三维重构算法。
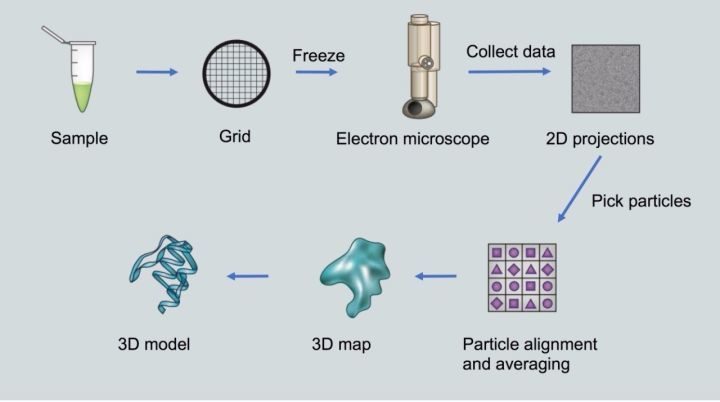
冷冻电镜技术是继X射线晶体学成像和核磁共振之后又一高效率进行蛋白质结构解析的技术,通过冷冻运动中的生物分子,即可在原子层面上进行高分辨成像,突破了以往生物分子研究的成像局限。冷冻电镜测定蛋白质结构的主流技术是单颗粒分析。通过三维重构算法,单颗粒分析可以从冷冻电镜获得的同一种蛋白质分子大量二维投影图像中计算出蛋白质的三维结构。
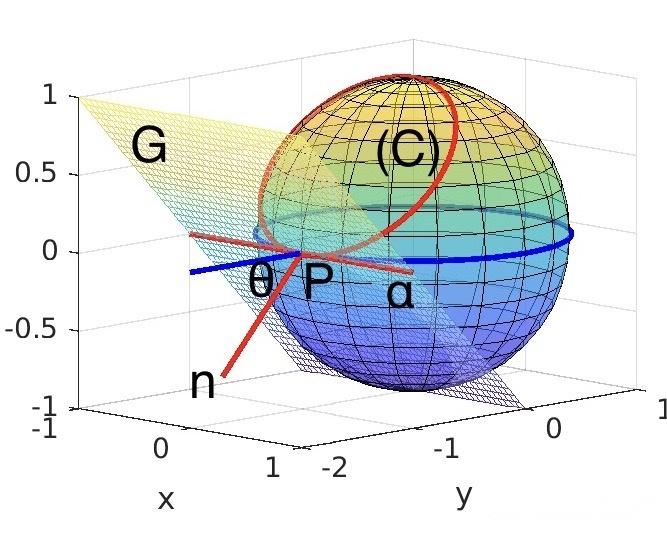
现有的算法大多是基于模板匹配或期望最大化的参数估计算法,重构出的蛋白质结构容易出现错误。三维重构的核心问题是估计每个投影图像的投影方向,保证投影方向不影响结果的可靠性。研究团队使用球面嵌入,球面是三维空间中完全圆形的几何物体。然后充分利用全体投影图像在投影方向以及等价线方面的全体一致性约束,在三维空间中获得满足全体投影图像一致性约束的投影方向估计,避免投影方向的误差,计算出蛋白质的三维结构。

这种方法对初始化数据依赖性小,尽量从数据内部挖掘约束条件,提高了重构结果的可靠性和准确性。实验使用模拟数据集和两组真实数据集评价算法。模拟数据由大肠杆菌70S核糖体对应的蛋白质结构通过计算机模拟投影生成。真实数据使用了从EMPIAR数据库中的的恶性疟原虫80S核糖体数据集和Hedgehog受体补丁与纳米抗体TI23复合物的冷冻电镜图像。

实验结果证明,球面嵌入算法可以更准确地估计投影方向,在噪声比较高的情况下能有效降低投影估计的误差。该算法重构不同噪声水平和不同数量的投影图像时,结果具有更高的分辨率,更加接近于真实结构,对蛋白质三维结构解析提供新的有效算法,推动蛋白质研究向前发展。进一步研究确定并扩展,将对人体疾病原理的药物设计也起到重要作用。
创新关键点
利用冷冻电镜技术,加入球面嵌入减小投影误差,帮助解析蛋白质结构。
Resolve protein three-dimensional structure based on spherical embedding
In April 2022, "Nature Communication Biology" published the results of a new algorithm jointly developed by researchers from Lanzhou University and Old Dominion University, which helps to use cryo-electron microscopy to image and analyze the three-dimensional structure of proteins”3D reconstruction from cryo-EM projection images using two spherical embeddings" ,is a protein three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm based on spherical embedding.
Cryo-electron microscopy is another high-efficiency technology for protein structure analysis after X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance. By freezing biomolecules in motion, high-resolution imaging can be performed at the atomic level, breaking through previous research on biomolecules. imaging limitations. The mainstream technique for protein structure determination by cryo-EM is single particle analysis. Through a three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm, single particle analysis can calculate the three-dimensional structure of a protein from a large number of two-dimensional projection images of the same protein molecule obtained by cryo-electron microscopy.
Most of the existing algorithms are parameter estimation algorithms based on template matching or expectation maximization, and the reconstructed protein structures are prone to errors. The core problem of 3D reconstruction is to estimate the projection direction of each projected image to ensure that the projection direction does not affect the reliability of the results. The research team used the embedding of spherical surfaces, which are completely circular geometric objects in three-dimensional space. Then make full use of the overall consistency constraints of the overall projection image in the projection direction and the equivalent line, obtain the projection direction estimation that satisfies the consistency constraints of the overall projection image in the three-dimensional space, avoid the error of the projection direction, and calculate the three-dimensional structure of the protein.
This method has little dependence on the initialization data, and tries to mine the constraints from the data, which improves the reliability and accuracy of the reconstruction results. Experiments use simulated datasets and two sets of real datasets to evaluate the algorithm. The simulated data were generated by computer simulation projection of the protein structure corresponding to the E. coli 70S ribosome. The real data used the P. falciparum 80S ribosome dataset from the EMPIAR database and cryo-EM images of the Hedgehog receptor patch in complex with the nanobody TI23.
The experimental results show that the spherical embedding algorithm can estimate the projection direction more accurately, and can effectively reduce the error of projection estimation in the case of high noise. When the algorithm reconstructs different noise levels and different numbers of projection images, the results have higher resolution and are closer to the real structure. It provides a new effective algorithm for protein three-dimensional structure analysis and promotes the development of protein research. Further research to identify and expand will also play an important role in drug design for human disease principles.
智能推荐
研究发现逆向TCA循环可将二氧化碳转化为氨基酸、糖和脂质
2022-08-04在细菌内发现逆转的三羧酸循环,逆向TCA循环令二氧化碳成为微生物碳源。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向生命科学理论创新 | 通过研究“fusogens”蛋白推测细胞受精过程起源于30亿年前
2022-09-02研究通过对来自不同环境的基因序列进行生物信息研究,证明Fsx1蛋白具有融合蛋白的作用,合理推测精子细胞和卵细胞融合的细胞机制起源于30亿年前。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向发育生物学创新 | 重建“细胞框架”以探究胚胎发育的复杂过程
2022-11-23使用高级数学建模,创建来自众多生物体的细胞类型的详细图谱,探究“原肠胚”的发育过程,精准跟踪细胞的发育和分化。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向PABP/R-motif介导的蛋白重编程新机制
2022-08-04该研究揭示了不同于经典的eIF2α磷酸化介导的蛋白重编程机制,同时因为R-motif同样广泛存在于果蝇、小鼠和人体的胁迫相关mRNA的5’端前导序列中,本研究发现的蛋白翻译起始调控机制可能同样广泛存在于其他真核生物体中。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向