创新背景
石墨烯是由碳原子以sp2杂化轨道紧密堆积成单层二维蜂窝状晶格结构的二维原子尺度、六角型的碳同素异形体,其中每个顶点有一个原子。石墨烯与其厚度成比例,它比最坚固的钢大约强100倍。具有良好的导电和导热性能和非线性抗磁性。1962年石墨烯被电子显微镜观察发现以来,科学家们一直在对石墨烯的物理和化学性质进行理论研究。石墨烯已经广泛应用于能源、材料学、生物医学和药物传递等方面,具有光明的应用前景。
创新过程
细胞是生命的单位,运动是生命存在的证明。细胞力学和运动一直是生物学的关键研究方向,2022年4月18日《自然·纳米技术》杂志发表了荷兰代尔夫特理工大学法尔博德·阿里贾尼课题组对于石墨烯研究的论文《用石墨烯鼓探测单个细菌的纳米运动》。成功利用石墨烯捕捉到了单一细菌的低水平噪音,为石墨烯基本力学和细胞运动研究做了进一步探索。
细菌的运动只有在微观尺度上才能被观察到,细菌菌落会在机械悬臂上产生纳米运动。研究人员利用石墨烯对外力的极度敏感,结合大肠杆菌进行实验。实验发现大肠杆菌的鞭毛在运动中会发出轻微的节拍振动,仅在纳米级研究上才能发现,确定菌毛是细菌纳米运动的来源,鞭毛的节拍振动就是单一细菌运动产生的声音。研究人员解释,这种鞭毛的节拍之微小相当于人类拳击手打沙袋时的100亿倍分之一。
研究将细菌附着在石墨烯鼓的表面,发现石墨烯鼓可以探测到细菌鞭毛产生的仅几纳米幅度的随机振动,纳米级的节拍振动被转换为音轨,研究人员就可以检测并听到单个细菌的声音。研究团队实时跟踪施用抗生素时细菌纳米运动的变化,证明了石墨烯鼓对细菌声音的探测可以通过探测单细胞灵敏度对抗生素敏感性进行测试。
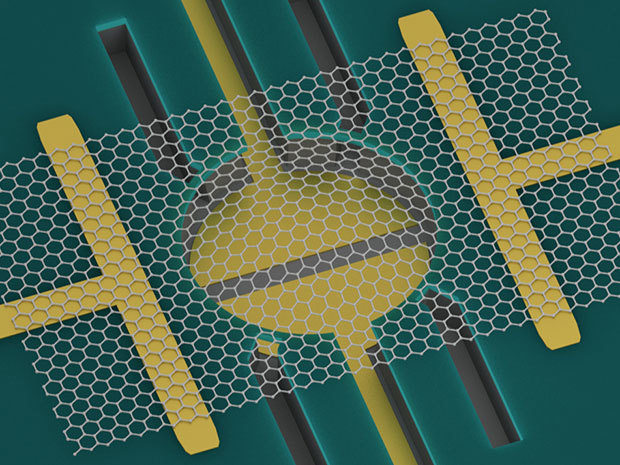
研究人员表示,这项研究推动细胞动力学和石墨烯研究的发展。实验结果可以用于细菌对药物作用的反应,通过观察细菌的振动确定抗生素药物的作用和细菌是否具有抗药性。石墨烯鼓的高灵敏度让这一检测过程只需一个电池就可完成。对抗生素耐药性的检测具有巨大的意义,未来优化这一检测平台,将对人类健康保护产生重要作用。
创新关键点
利用石墨烯高灵敏度探测细菌运动,发展细胞运动力学、石墨烯运用,应对抗生素耐药性问题。
Detection of bacterial movement by graphene
Cells are the unit of life, and motion is the proof of the existence of life. Cell mechanics and motion have always been the key research directions of biology. On April 18, 2022, the journal Nature Nanotechnology published a report on graphene research by Falbaud Arijani's group at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands. Thesis Probing nanomotion of single bacteria with graphene drums. The low-level noise of a single bacterium was successfully captured by graphene, which further explored the basic mechanics and cell movement of graphene.
The motion of bacteria can only be observed at the microscopic scale, and bacterial colonies generate nanomotion on the mechanical cantilever. The researchers used graphene's extreme sensitivity to external forces to conduct experiments in combination with Escherichia coli. Experiments have found that the flagella of E. coli emits slight beat vibrations during movement, which can only be found in nanoscale research. It is determined that the fimbriae are the source of bacterial nanomotion, and the beat vibration of the flagella is the sound produced by the movement of a single bacteria. The researchers explain that the beats of the flagella are 10 billion times smaller than when a human boxer hits a punching bag.
The study attached bacteria to the surface of graphene drums and found that the graphene drums could detect random vibrations of only a few nanometers in amplitude produced by the bacterial flagella. The nanoscale beat vibrations were converted into sound tracks, allowing the researchers to detect and hear a single The sound of bacteria. The research team tracked changes in bacterial nanomotion in real time when antibiotics were administered, demonstrating that the detection of bacterial sounds by graphene drums can be tested for antibiotic susceptibility by probing single-cell sensitivity.
The researchers say the study advances cell dynamics and graphene research. The experimental results can be used to determine the bacteria's response to the action of the drug, by observing the vibration of the bacteria to determine the effect of antibiotic drugs and whether the bacteria are drug-resistant. The high sensitivity of the graphene drum allows this detection process to be completed with just one battery. The detection of antibiotic resistance is of great significance, and optimizing this detection platform in the future will play an important role in the protection of human health.
智能推荐
新材料 | 人造叶绿体有助于将二氧化碳转化为有机物
2022-06-29纳米技术和生物细胞交叉融合实现人造叶绿体并完成批量生产替代。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向高龄父亲精子中miRNA影响胚胎,使子代易出现精神疾病
2022-08-03这项研究发现,高龄雄鼠精子中的miRNA通过引发早期胚胎雌二醇信号通路功能紊乱,导致子代出现焦虑和社交障碍等精神症状表型。该发现对阐释雄性高龄生育导致子代精神异常的分子机理具有重要意义,也为研究精神类疾病的遗传规律提供了新的视角;同时,在全球生育年龄普遍推迟的社会现实下,此发现对于预防子代可能出现的健康风险、维持优生优育的政策提供了一定的理论依据。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向微生物学创新 | 创新应用CRISPR技术提高对水中有害微观寄生虫的检测精度
2022-09-22新南威尔士大学的工程师们发现了一种新的更简单的方法,可以检测水中的微小微生物,这些微生物会导致严重的健康风险,甚至可能导致死亡。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向创新利用"Pathul-seq"技术发现转座元件在胚胎发育中的重要功能
2022-07-27该研究建立了靶向 SVA 的表观基因组编辑系统以及微量细胞多组学分析技术 Pathul-seq,阐明了转座元件上 H3K9me3 依赖性异染色质的重塑在人类早期胚胎发育中的功能及其机制。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向