创新背景
声学设备利用机械优势执行有用的任务,让设备工作可靠、紧凑、高效耐用的时候保持周期性运动。将机械设备的优势带入量子领域或许会促进量子技术发展,并开发机械设备新的用途。
创新过程
斯坦福大学的研究人员借用当前机械设备的原理和优势,将微小的纳米机械振荡器与一种能够以量子比特或量子“位”信息的形式存储和处理能量的电路耦合,将机械系统的好处带入极小尺度的量子领域,为未来基于量子物理学的技术开发了一种新设备。该设备的量子比特可以让研究人员操纵及谐振荡器的量子态,进而发生各种量子力学效应。基于新设备的结合量子力学和机械设备的优势,研究人员试图建立类似的可利用量子设备和机械量子力学系统。
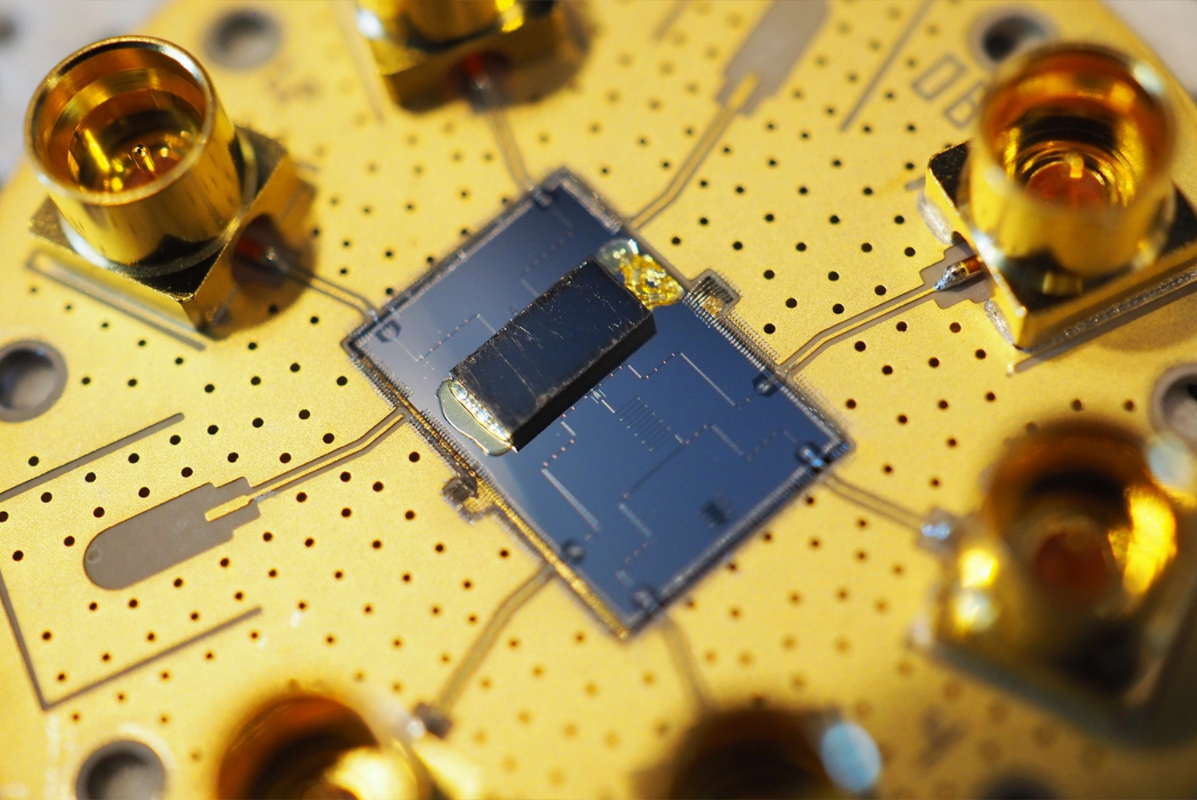
研究使用斯坦福大学的纳米共享设施,通过专用设备在两个硅计算机芯片上以纳米级分辨率制造硬件组件,然后粘合两个芯片,使底部芯片上的组件对应上半部分芯片的三明治式组件。底部芯片上带有一个铝制超导电路作为器件的量子比特。
微波脉冲被发送到电路上会产生对设备信息量子位进行编码的光子。叠加的量子力学现象的量子系统同时存在于多个量子态中,直到被系统测量。所以量子机械设备中的量子位可以同时表示0和1的加权组合,和传统将比特储存为表示0或1的电压的电气设备不同。压电材料铌酸锂制成晶体,可以将电场力转换为运动。顶部芯片包含两个由悬挂的桥状晶体结构组成、长度仅为几十纳米的纳米机械谐振器,量子比特光子传递的电场就被转换为声子的量子振动能量。

研究人员表示,通过在设备中结合不同形式的能量,声波被量子化成声子粒子,研究创造了一种混合量子技术。声子的产生允许每个纳米机械振荡器像寄存器一样工作,由量子位提供数据,作计算机中最小的数据保存元件。振荡器和量子比特一样相应地处于叠加状态,可以同时代表1和0。超导电路使研究人员能够准备、读出和修改存储在寄存器中的数据。
器件中光子和谐振器除了叠加还利用了量子纠缠进行连接。在量子力学里,几个粒子在彼此相互作用后,各自的特性综合成为整体性质,无法单独描述各个粒子的性质,只能描述整体系统的性质,导致量子纠缠很难在实验中被创建。多个量子比特的操纵使量子全部处于叠加和纠缠状态,一对二的冲击力为基于量子技术的计算和传感提供动力。

为了证明这些量子效应,研究人员创造一个量子比特作为光子,将其存储在底部芯片的电路中。电路与顶部芯片上的一个机械振荡器被允许交换能量,剩余的信息会传输到第二个机械设备。 研究以电路作为量子机械纠缠的工具将先后使用的两个机械谐振器相互纠缠在一起。声音以离散的单位出现,且单个声音粒子可以在两个纠缠的宏观物体之间共享,每个物体都有数万亿个原子同时移动或不移动。
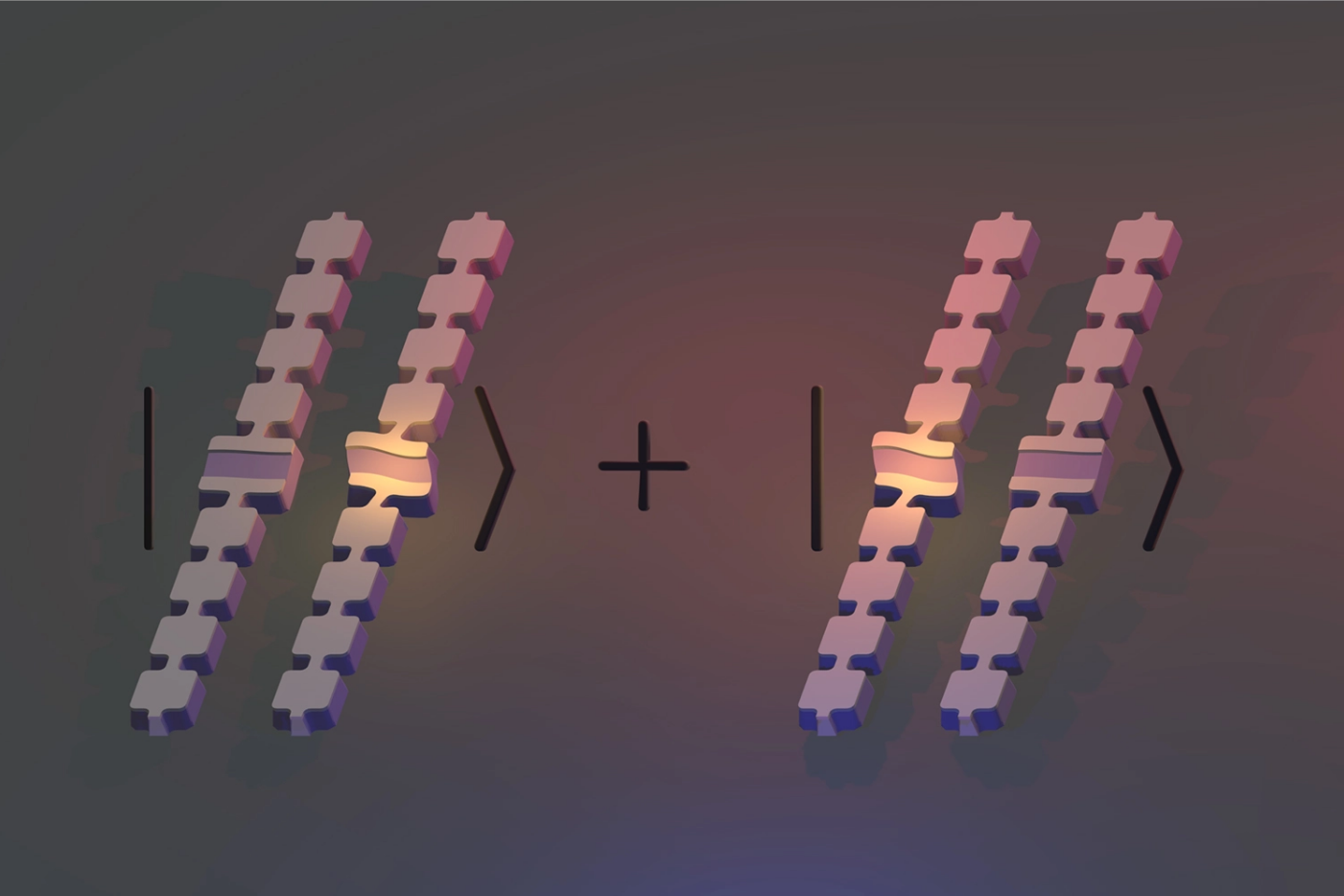
量子叠加和纠缠所需要的条件都具有高度要求,它甚至容易受到热或其他能量形式的轻微干扰,因此赋予所提出的量子传感器件极高的灵敏度。为了能够进行最终的实际计算,持续纠缠或相干的周期需要更长的时间。研究通过精进制造工艺和优化所涉及的材料,每年将系统性能提高近10倍以实现更长的相干时间。
创新关键点
将机械设备的优势带入量子领域,基于微小机械设备开发精密量子技术。
创新价值
有望增强计算机和传感系统的精确性并提高反应速度,为开发未来基于量子物理学的技术和相关设备助力。
Develop new devices in the quantum field based on the advantages of mechanical equipment
Borrowing the principles and advantages of current mechanical devices, researchers at Stanford University couple tiny nano-mechanical oscillators with a circuit capable of storing and processing energy in the form of qubits or quantum "bit" information, bringing the benefits of mechanical systems into the quantum realm at a very small scale, developing a new device for future technologies based on quantum physics. The device's qubits allow researchers to manipulate and resonate the quantum state of the resonator to produce various quantum mechanical effects. Based on the advantages of combining quantum mechanics and mechanical devices with the new device, the researchers sought to build similar systems of usable quantum devices and mechanical quantum mechanics.
Using Stanford's nano-sharing facility, the study fabricated hardware components at nanometer resolution on two silicon computer chips through specialized equipment, and then glued the two chips so that the components on the bottom chip corresponded to the sandwich-style components of the upper half of the chip. The bottom chip has an aluminum superconducting circuit on it as the qubit of the device.
Microwave pulses are sent to noisy circuits that produce photons that encode the qubits of device information. Quantum systems of superimposed quantum mechanical phenomena exist in multiple quantum states simultaneously until they are measured by the system. So qubits in quantum mechanical devices can represent a weighted combination of 0 and 1 at the same time, unlike traditional electrical devices that store bits as voltages representing 0 or 1. The piezoelectric material lithium niobate is made into crystals that convert electric field forces into motion. The top chip contains two nanomagic resonators consisting of a suspended bridge-like crystal structure with a length of only a few tens of nanometers, and the electric field transmitted by qubit photons is converted into quantum vibrational energy of phonons.
The researchers say that by combining different forms of energy in the device, sound waves are quantized into phonon particles, creating a hybrid quantum technique. The generation of phonons allows each nanomachinechanical oscillator to work like a register, providing data from qubits as the smallest data-saving element in a computer. Oscillators, like qubits, are correspondingly superimposed and can represent both 1 and 0 at the same time. Superconducting circuits enable researchers to prepare, read out, and modify data stored in registers.
In addition to superposition, the photon and resonator in the device also use quantum entanglement to connect. In quantum mechanics, after several particles interact with each other, their respective properties are synthesized into a whole property, and the properties of each particle cannot be described separately, but only the properties of the overall system, resulting in quantum entanglement being difficult to create in experiments. The manipulation of multiple qubits makes the quanta all superimposed and entangled, and the one-to-two impact force powers the computation and sensing based on quantum technology.
To demonstrate these quantum effects, the researchers created a qubit as a photon to store in the circuit at the bottom of the chip. The circuit is allowed to exchange energy with a mechanical oscillator on the top chip, and the rest of the information is transmitted to a second mechanical device. The study of circuits as tools for quantum mechanical entanglement entangles two mechanical resonators used successively. Sound appears in discrete units, and a single sound particle can be shared between two entangled macroscopic objects, each with trillions of atoms moving or not moving at the same time.
The conditions required for quantum superposition and entanglement are highly demanding, and it is even susceptible to slight disturbances from heat or other forms of energy, thus giving the proposed quantum sensor device extremely high sensitivity. In order to be able to perform the final practical calculations, the period of continuous entanglement or coherence takes longer. The study improves system performance by nearly 10 times per year to achieve longer coherence times by refining the manufacturing process and optimizing the materials involved.
智能推荐
DTU研究人员创造性地将量子计算机用于电网计算
2022-09-05科技正在迅速发展,将量子计算机用于电力系统计算可以做到普通计算机做不到的事情。这意味着未来将可以开发基于可再生能源的安全稳定电力系统所需的工具。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向量子计算理论创新 | 在量子系统使用“表面代码”可实现连续纠错
2022-09-20苏黎世联邦理工学院的研究人员制造含有“表面代码”的芯片,实现量子系统中的连续快速纠错。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向量子计算+凝聚态物理 | 将介电谐振器创新引入量子计算可将“相干时间”延长百倍
2022-11-02新南威尔士大学的工程师引入一种称为介电谐振器的晶体,可将量子计算处理器可保存信息的时间延长100倍以上。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向量子计算理论创新 | 基于光子和气体作用机制创新量子系统存储数据的方式
2022-11-23创新将光子和气体系统用于量子计算研究,通过光子和两种气体之间的碰撞激发构建稳定的量子存储系统,改善信息存储量。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向