创新背景
在过去的许多年里,数码相机已经无处不在,几乎渗透到现代生活的方方面面——嵌入智能手机、智能眼镜、安全监控系统、自动驾驶汽车和面部识别技术。随着大量的图像数据被这些摄像头捕捉到,隐私保护问题越来越受到关注。
创新过程
为了解决这个问题,由加州大学洛杉矶分校萨缪里工程学院Volgenau工程创新教授Aydogan Ozcan领导的研究团队设计了一款智能相机,它只拍摄相关物体的照片,同时防止其他细节被捕获。
这项研究展示了通过使用人工智能构建摄像头来实现隐私保护和安全成像的新模式,这种新模式不需要任何数字后处理,目前应用程序中的算法会模糊个人面部或加密社会安全号码等敏感数据。
在图像拍摄后删除这些数据有被黑客攻击或暴露原始、未修改图像的风险,特别是如果图像存储在云计算中。其他解决这一问题的方法使用定制的相机来隐藏敏感的可识别信息,但同时降低和牺牲所需对象的图像质量。

该相机由多达7个可传输的3d打印表面组成,每个表面都由光波长尺度下的数万个衍射特征组成。利用基于深度学习的训练,该团队制作和组装了这些连续层的结构。当来自目标光场的输入对象出现在相机镜头前时,它们被捕获为高质量的图像,而当输入对象属于其他不需要的类别时,它们被光学擦除,形成随机的低强度图案,成为图像背景中的噪点。
由于不需要的物体类别的特征信息在相机输出时通过光衍射被光学擦除,所以这款人工智能设计的相机从不记录这些信息。这可以优化隐私保护,因为任何试图访问相机的记录图像将无法重建原始对象。该功能还可以减少相机的数据存储和传输负载,因为不记录不需要的物体的图像。
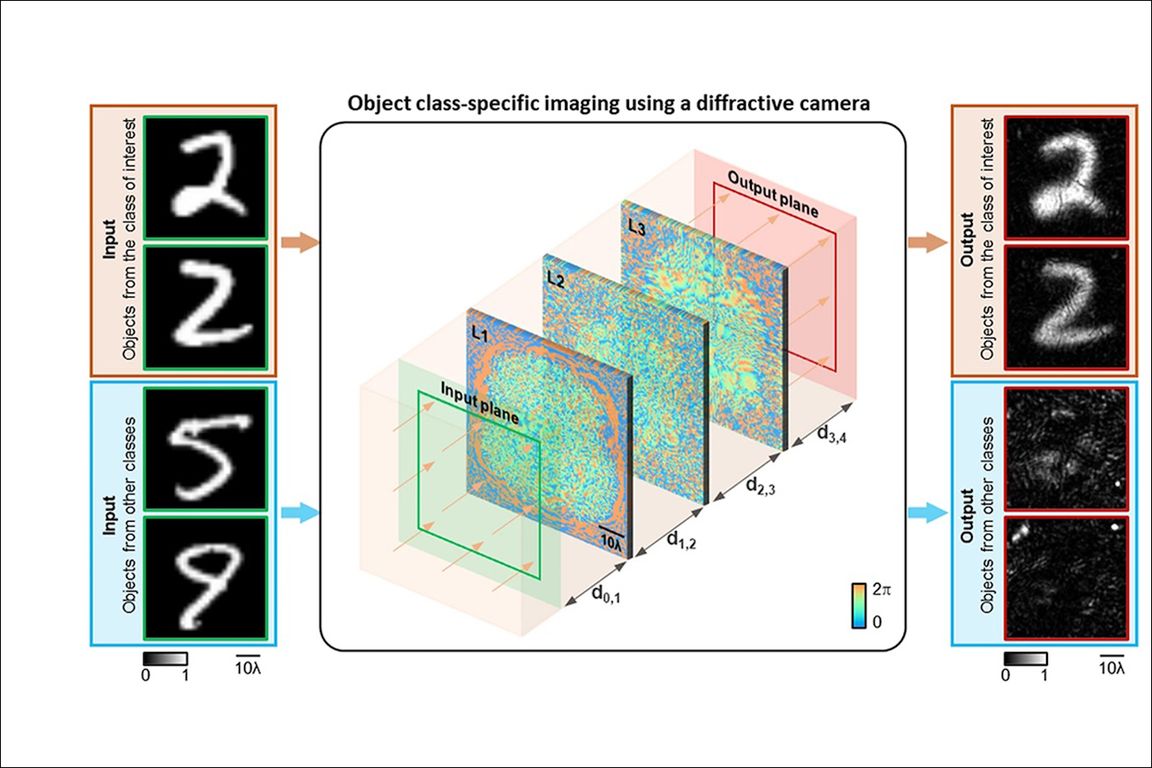
为了展示这种独特的数据专用相机,加州大学洛杉矶分校的研究团队构建了一个3d打印相机,使用太赫兹波照亮手写数字,并训练相机只捕捉一类手写数字,忽略其他数字。
在实验过程中,智能相机能够成像的输入对象只有手写数字“2”,同时立即删除所有其他手写数字从输出图像。该团队还证明,该相机能够成像特定类型的衣服,如裤子,而忽略了其他服装项目从相机的输出。研究团队在不同的光照条件下测试了它的设计,这些光照条件之前没有包括在相机的训练中,结果表明,相机能够适应照明的广泛变化。
创新关键点
利用基于深度学习的训练,该团队制作和组装了这些连续层的结构。当来自目标光场的输入对象出现在相机镜头前时,它们被捕获为高质量的图像,而当输入对象属于其他不需要的类别时,它们被光学擦除,形成随机的低强度图案,成为图像背景中的噪点。
创新价值
除了特定数据的成像,基于人工智能的相机设计也可以用于构建加密相机,在保留原始图像的同时提供额外的一层安全。使用人工智能优化的衍射层,这种相机可以光学执行选定的线性变换,专门针对感兴趣的目标物体。只有那些有权获得解密密钥的人才能恢复物体的原始图像。另一方面,不需要的物体的信息被不可逆地删除,因为人工智能设计的相机在输出时就删除了它们。因此,即使解密密钥应用于这些记录的图像,它也会产生类似噪声的、无法识别的特征。
除了照明灯,智能相机不需要任何外部电源进行计算,并以光速运行,使其快速、数据和节能。这种技术特别适用于特定任务、注重隐私和节省电力的成像应用程序。
这种衍射相机设计的核心人工智能训练可以使未来的成像系统在计算和数据传输方面消耗的能量减少数量级。
New privacy cameras use energy-efficient AI to capture objects at the speed of light
To solve this problem, a team of researchers led by Aydogan Ozcan, Volgenau Professor of Engineering Innovation at UCLA's Samuri School of Engineering, designed a smart camera that only takes pictures of relevant objects while preventing other details from being captured.
The study demonstrates a new model for privacy protection and secure imaging by using AI to build cameras that don't require any digital post-processing, as algorithms in current apps blur a person's face or encrypt sensitive data like social security numbers.
Deleting this data after the image has been taken runs the risk of being hacked or exposing the original, unaltered image, especially if the image is stored in the cloud. Other approaches to this problem use custom cameras to hide sensitive identifiable information, but at the same time degrade and sacrifice the image quality of the desired object.
The camera consists of up to seven transferable 3D-printed surfaces, each made up of tens of thousands of diffraction features at the wavelength scale of light. Using deep learning-based training, the team made and assembled the structure of these continuous layers. When input objects from the target light field appear in front of the camera lens, they are captured as high-quality images, while when input objects fall into other unwanted categories, they are optically erased to form random low-intensity patterns that become noise in the background of the image.
The AI-designed camera never records features of unwanted object classes because they are optically erased by optical diffraction as the camera outputs them. This can optimize privacy protection, as any recorded image that attempts to access the camera will not be able to reconstruct the original object. This feature also reduces the camera's data storage and transmission load by not recording images of unwanted objects.
To demonstrate this unique data-specific camera, the UCLA research team built a 3D-printed camera that uses terahertz waves to illuminate handwritten numbers, and trained the camera to capture only one class of handwritten numbers and ignore the others.
During the experiment, the smart camera was able to image the input object only with the handwritten digit "2" while instantly deleting all other handwritten digits from the output image. The team also demonstrated that the camera was able to image specific types of clothing, such as pants, while ignoring other clothing items from the camera's output. The research team tested its design in different lighting conditions that had not previously been included in the camera's training, and showed that the camera was able to adapt to a wide range of changes in lighting.
智能推荐
反思可解释性方法,深入探索机器学习的原理
2022-07-23从可解释性方法的角度探索机器学习模型的工作准确性,拓展人工智能研究使用的注意事项。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向AI算法 | 利用激光清除树叶联系,创新森林防火方法
2022-06-29将激光清除树叶的技术引入森林火灾燃烧媒介切断,控制森林火势蔓延,有效进行森林保护和消防事业。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向通过自监督学习实验发现AI模型与人脑的相似性
2022-07-28Meta AI、美国哥伦比亚大学、多伦多大学等的研究人员完成了一个关于深度学习模型和人脑之间相似性的研究。研究发现,AI模型Wav2Vec 2.0与人类大脑处理语音的方式非常相似,甚至AI也像人类一样,对“母语”有更强的辨别能力,如法语模型就比英语模型更容易感知来自法语的刺激。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向人工智能+古文字学 | 人工智能帮助研究古文字文本
2022-07-28将人工智能运用于古文字学领域,帮助重建古老的文字文本,探索人类的历史文明。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向