创新背景
在过去的几十年里,电池的研究主要集中在可充电锂离子电池上。从电动汽车到便携式电子产品,锂离子电池的应用非常广泛,在价格和容量方面都有了显著的提高。但非充电电池在许多重要用途中发挥着至关重要的作用,如心脏起搏器等植入式医疗设备,但在此期间几乎没有改进。
创新过程
麻省理工学院的研究人员提出了一种新方法来提高这些不可充电电池的能量密度,这种技术可以使使用寿命增加50%,或者在给定的功率或能量容量下,相应减小体积和重量,同时提高安全性,几乎不增加成本。
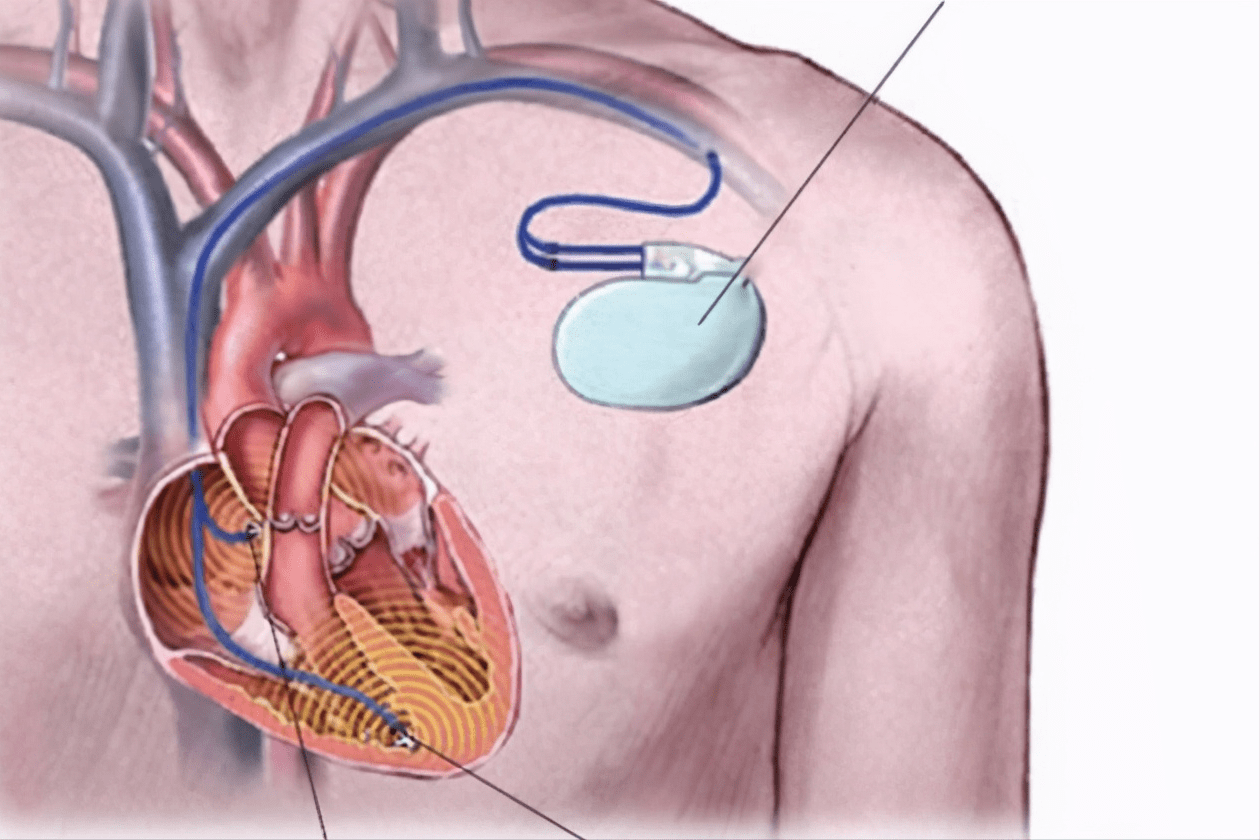
更换起搏器或其他医疗植入物中的电池需要外科手术,因此电池寿命的任何延长都可能对患者的生活质量产生重大影响。一次电池被用于这些重要的应用,因为在给定的尺寸和重量下,它们可以提供大约三倍于充电电池的能量。
这种容量上的差异使得一次电池在充电不可能或不切实际的应用中至关重要。这种新材料在人体温度下工作,因此适合用于医疗植入物。除了可植入设备,随着进一步的发展,电池可以在更低的温度下有效工作,应用还可以包括运输跟踪设备中的传感器,例如,确保食品或药品运输的温度和湿度要求在整个运输过程中得到适当保持。或者,它们可能被用于远程操作的空中或水下航行器,需要在很长一段时间内随时准备部署。
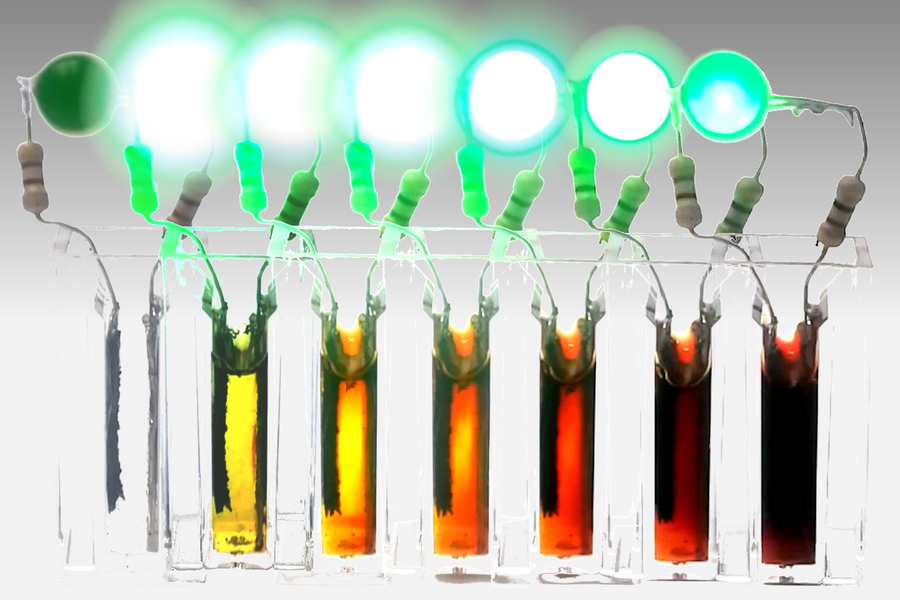

延时系列图像显示新型电池在几天内完全放电。在放电过程中,电池单元中的新“阴极电解液”材料被化学覆盖成红色化合物,因此放电越多颜色越深。
该团队创新的关键是一种新型电解质——这种材料位于电池的阴极和阳极之间,并允许载流子从一侧通过到另一侧。通过使用一种新的液体氟化化合物,研究小组发现他们可以将阴极和电解质的一些功能结合在一种化合物中,称为catholyte。
除了这种新化合物,理论上还有其他材料可以在大容量电池中发挥类似的阴极作用,但这些材料的固有电压较低,无法与传统起搏器电池(一种被称为CFx的电池)中的其余材料相匹配。因为电池的总输出不能超过两种电极材料中较低的那一种,额外的容量就会因为电压不匹配而浪费掉。但是这种新材料的电压与CFx的电压非常一致。

在传统的CFx电池中,液体电解质是必不可少的,因为它允许带电粒子从一个电极穿过到另一个电极。但这些电解质实际上在化学上是不活跃的,这意味着大约50%的电池关键部件,主要是电解质,是非活性材料。因此,在使用氟化catholyte材料的新设计中,自重可以减少到20%左右。
创新关键点
这种新材料的一大优势是,它可以很容易地集成到现有的电池制造过程中,作为一种材料的简单替代。
创新价值
研究人员表示,在未来的道路上,其他应用可能也会利用这种新材料,比如可以远程读取的智能水表或燃气表,或者像EZPass应答器这样的设备,延长它们的使用寿命。为无人驾驶飞机或水下交通工具提供动力需要更高的动力,因此可能需要更长的时间来开发。其他用途还包括用于远程设备的电池,如石油和天然气钻井平台,包括下放到井下监测条件的设备。
The innovative use of catholyte to develop new materials could make implantable batteries last longer
Researchers at MIT have come up with a new way to increase the energy density of these non-rechargeable batteries, a technique that could increase service life by 50 percent, or a corresponding reduction in size and weight for a given amount of power or energy capacity, while improving safety at almost no additional cost.
Replacing a battery in a pacemaker or other medical implant requires surgery, so any extension of battery life can have a significant impact on a patient's quality of life. Primary batteries are used for these important applications because they can provide approximately three times as much energy as rechargeable batteries for a given size and weight.
This difference in capacity makes a single battery crucial in applications where recharging is impossible or impractical. The new material works at human temperatures, making it suitable for use in medical implants. In addition to implantable devices, with further development allowing batteries to operate effectively at lower temperatures, applications could also include sensors in transport tracking devices, for example, to ensure that temperature and humidity requirements for food or medicine shipments are properly maintained throughout the journey. Or they may be used for remotely operated air or underwater vehicles that need to be ready for deployment over a long period of time.
Key to the team's innovation is a new electrolyte -- a material that sits between the battery's cathode and anode and allows charge carriers to pass from one side to the other. By using a new type of liquid fluorinated compound, the team found they could combine some of the functions of the cathode and electrolyte in a single compound called catholyte.
In addition to the new compound, there are other materials that could theoretically perform a similar cathodic role in high-volume batteries, but these have a low inherent voltage that doesn't match the rest of the material in a conventional pacemaker battery, a type of battery known as a CFx. Because the total output of the battery cannot exceed the lower of the two electrode materials, the extra capacity is wasted because of the voltage mismatch. But the voltage of the new material is very consistent with that of CFx.
In conventional CFx batteries, a liquid electrolyte is essential because it allows charged particles to pass from one electrode to the other. But these electrolytes are actually chemically inactive, meaning that about 50 percent of the key parts of the battery, mostly electrolytes, are inactive materials. Thus, in the new design using fluorinated catholyte materials, the self-weight can be reduced to about 20%.
智能推荐
新材料 | 将固体聚合物与电解质相融合后利用3D打印技术定制其形状
2022-09-21来自新南威尔士大学悉尼分校的一个团队开发了一种将坚固、高导电的固体聚合物电解质3D打印成定制形状的方法。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向利用高性能水凝胶驱动材料模拟肌肉结构和功能
2022-07-28受肌肉结构的启发,宾夕法尼亚州立大学的研究人员研创出一种纤维驱动器的新设计。它模拟了肌肉纤维的结构,并在能效、驱动应变和机械性能等多个方面比其他现有驱动器更优越。这一结果发表在《自然·纳米技术》(Nature Nanotechnology)杂志上。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向铁基磁性纳米纤维有助于提升微机电系统性能
2022-08-18利用静电纺丝获得铁基纳米纤维,施加电厂和聚合物溶液使纤维具有磁性并进行自组织,成为可用于微机电系统的磁性材料。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向新材料 | 阻断氧气使陶瓷复合材料快速修复
2022-06-29添加物质让陶瓷复合材料在高温中能阻断氧气,自我修复。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向