创新背景
去教堂的人听到的声音受许多因素的影响,包括风琴的位置,听者站在哪里,柱子、长凳或其他物品之间是否有障碍物,墙壁是什么材料,窗户或门的位置,等等。听到声音可以帮助人们想象他们的环境。
创新过程
麻省理工学院和MIT- ibm沃森人工智能实验室的研究人员也在探索使用空间声学信息来帮助机器更好地想象它们的环境。他们开发了一种机器学习模型,可以捕捉房间中的任何声音如何在空间中传播,使该模型能够模拟听众在不同位置会听到什么。
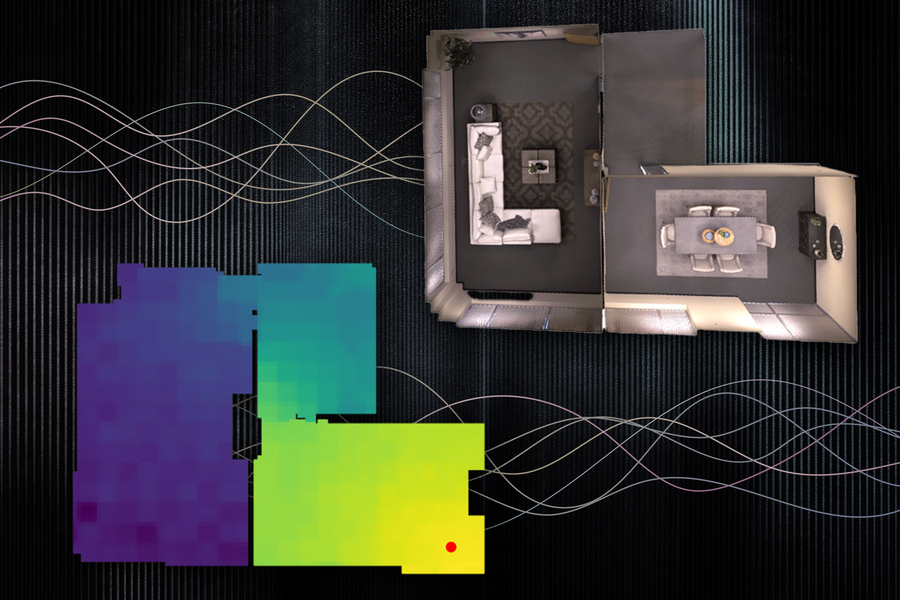
在此图像中,声音发射器由红点标记。如果听众站在不同的位置,颜色显示音量:黄色更大声,蓝色更安静。
通过对场景的声学进行精确建模,该系统可以从声音记录中了解房间的底层3D几何结构。研究人员可以使用他们的系统捕获的声学信息来建立一个房间的精确视觉渲染,类似于人类在估计其物理环境属性时使用声音的方式。
声音和视觉
研究人员发现,视觉模型受益于光度一致性这一特性,而这一特性不适用于声音。如果一个人从两个不同的位置看同一个物体,这个物体看起来大致相同。但是对于声音,改变位置,人们听到的声音可能会因为障碍物、距离等而完全不同。这使得预测音频非常困难。
研究人员通过将声学的两个特性纳入他们的模型来克服这个问题:声音的相互性质和局部几何特征的影响。
声音是相互的,这意味着如果一个声音的来源和听者交换位置,这个人听到的是不变的。此外,人们在某个特定区域听到的东西在很大程度上受到当地特征的影响,例如听者和声源之间的障碍。
为了将这两个因素纳入他们的模型(称为神经声场(NAF)),他们用一个网格来增强神经网络,捕捉场景中的物体和建筑特征,如门口或墙壁。该模型对网格上的点进行随机采样,以了解特定位置的特征。
创新关键点
在计算机视觉研究中,一种称为隐式神经表示模型的机器学习模型已被用于从图像生成流畅、连续的3D场景重建。这些模型利用神经网络,其中包含层层相互连接的节点或神经元,处理数据以完成任务。
麻省理工学院的研究人员使用了相同类型的模型来捕捉声音是如何在场景中连续传播的。
创新价值
除了在虚拟现实和增强现实方面的潜在应用,该技术还可以帮助人工智能代理更好地理解周围的世界。例如,通过对环境中声音的声学特性建模,水下探测机器人可以感知到比仅靠视觉更远的东西。
The innovative development of "neuroacoustic fields" can use acoustics to accurately model the scene
Researchers at MIT and the MIT-IBM Watson Artificial Intelligence Laboratory are also exploring the use of spatial acoustic information to help machines better imagine their environment. They developed a machine learning model that captures how any sound in a room travels through space, allowing the model to simulate what listeners would hear in different locations.
By accurately modeling the acoustics of the scene, the system can learn the underlying 3D geometry of the room from the sound recordings. The researchers can use the acoustic information captured by their system to build an accurate visual rendering of a room, similar to the way humans use sound when estimating properties of their physical environment.
Sound and Sight
The researchers found that visual models benefit from a property called photometric consistency, which does not apply to sound. If a person looks at the same object from two different locations, the object will look roughly the same. But with sound, changing location, the sound people hear may be completely different due to obstacles, distance, and so on. This makes predicting the audio very difficult.
The researchers overcome this problem by incorporating two properties of acoustics into their model: the mutual nature of sound and the influence of local geometric features.
Sounds are mutual, meaning that if the source of a sound switches places with the listener, the person hears the same thing. Moreover, what people hear in a particular area is heavily influenced by local characteristics, such as barriers between the listener and the sound source.
To incorporate these two factors into their model (called Neuroacoustic field (NAF)), they augment the neural network with a grid that captures objects and architectural features in the scene, such as doorways or walls. The model randomly samples points on a grid to learn the characteristics of a particular location.
智能推荐
利用光声学技术提高检测方法的便捷度
2022-08-14利用光声学原理,使用光使材料发出声音,帮助优化各领域的检测方式,提高检测速度和便捷性。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向通过计算机模型探究鸟类发声机制,帮助人类开展喉咙手术研究
2022-08-16基于鸟类发声和人类发声机制的相似性,利用计算机模型探究鸟类声音的产生,进而钻研人类声音的生理机制,为喉咙手术提供具有参考性的新见解。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向声学创意 | 以声学功能设计建筑形态
2022-07-06创新以声学功能作建筑的首要元素,融合自然与人为的声音,突破原有的建筑类型。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向