创新背景
为了更好地理解跨越血管壁的工作机制,有必要进行详细的观察:血管壁由一层细胞组成,是血流和肿瘤组织之间的屏障,肿瘤组织被许多小血管渗透。这些细胞之间的狭窄空间允许某些分子通过血管壁。这些细胞间隙的大小是由血管壁的细胞调节的,它们可以暂时足够宽,甚至允许细菌通过血管壁。
创新过程
世界各地的科学家都在研究抗癌药物如何最有效地到达目标肿瘤。一种新发现是使用改造过的细菌作为“渡船”,将药物通过血液运送到肿瘤。苏黎世联邦理工学院的研究人员现在已经成功地控制了某些细菌,使它们能够有效地穿过血管壁并渗透到肿瘤组织中。
研究人员选择了一种细菌,这种细菌由于含有氧化铁颗粒而具有天然的磁性。这些磁螺旋体属的细菌对磁场有反应,可以由体外的磁铁控制。

在细胞培养物和小鼠中,在肿瘤上施加旋转磁场可以提高细菌穿过癌生长部位附近血管壁的能力。在血管壁处,旋转磁场推动细菌作圆周运动前进。
在实验和计算机模拟的帮助下,研究人员能够证明,使用旋转磁场推动细菌是有效的,原因有三:首先,通过旋转磁场的推进力是通过静态磁场推进力的十倍。后者只是设定了方向,细菌必须依靠自己的力量移动。
第二个也是最关键的原因是,细菌在旋转磁场的驱动下不断运动,沿着血管壁移动。这使得它们更有可能遇到血管壁细胞之间短暂打开的间隙,与其他推进类型相比,在其他推进类型中,细菌的运动不太探索。
第三,与其他方法不同的是,细菌不需要通过成像来追踪。一旦磁场定位在肿瘤上,它就不需要重新调整。
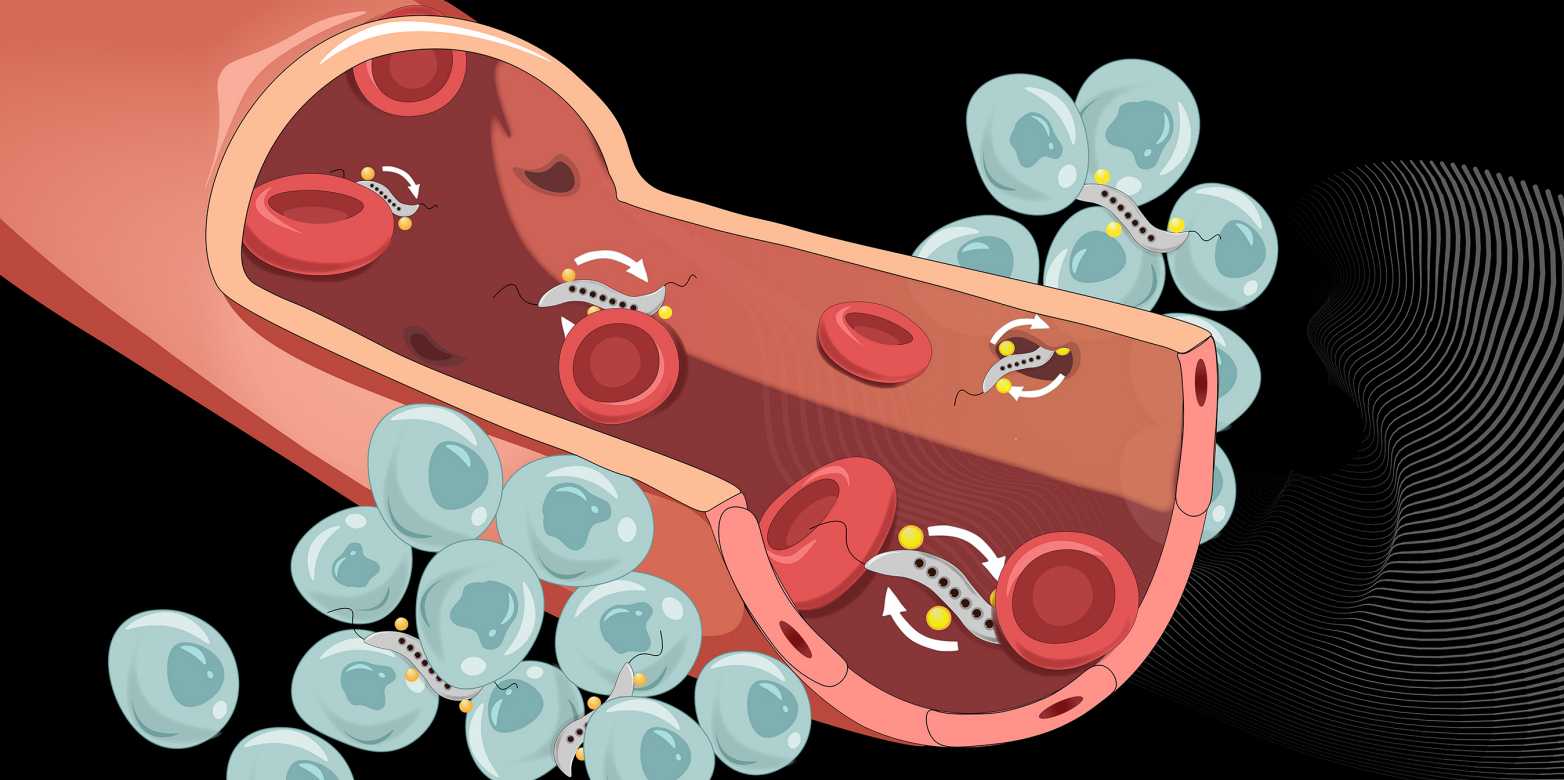
磁性细菌(灰色)可以挤压穿过狭窄的细胞间间隙,穿过血管壁并对抗肿瘤。
同时,研究人员利用了细菌的自然和自主运动,一旦细菌穿过血管壁进入肿瘤,它们就可以独立地向肿瘤内部深处迁移。由于这个原因,科学家们使用外部磁场的推进只持续了一个小时——足够让细菌有效地穿过血管壁到达肿瘤。
这种细菌未来可能携带抗癌药物。在他们的细胞培养研究中,苏黎世联邦理工学院的研究人员通过将脂质体(类脂肪物质的纳米球)附着在细菌上模拟了这种应用。他们用荧光染料标记这些脂质体,这使他们能够在培养皿中证明,细菌确实将它们的“货物”运送到了癌变组织中,并在那里积累。在未来的医疗应用中,脂质体将被药物填充。
创新关键点
用于癌症研究的大肠杆菌没有磁性,因此不能被磁场推动和控制。一般来说,细菌的磁性反应性是一种非常罕见的现象。磁旋菌是少数具有这种特性的细菌属之一。
创新价值
目前有多个研究项目正在调查大肠杆菌对肿瘤的疗效。未来,利用合成生物学修饰细菌是可能的,以优化它们的治疗效果,减少副作用,并使它们更安全。
Innovative use of "magnetic bacteria" can penetrate blood vessel walls to fight tumors
Scientists around the world are studying how cancer drugs can most effectively reach their target tumors. One new discovery is the use of engineered bacteria as a "ferry" to deliver drugs through the bloodstream to tumors. Researchers at ETH Zurich have now managed to control certain bacteria so that they can efficiently cross blood vessel walls and penetrate tumor tissue.
The researchers chose a type of bacteria that has natural magnetic properties due to the presence of iron oxide particles. These spirochetes are responsive to magnetic fields and can be controlled by magnets outside the body.
In cell cultures and mice, applying a rotating magnetic field to a tumor improves the ability of bacteria to cross the walls of blood vessels near the site of cancer growth. At the blood vessel wall, a rotating magnetic field pushes the bacteria forward in a circular motion.
With the help of experiments and computer simulations, the researchers were able to show that using a rotating magnetic field to propel bacteria is effective for three reasons: First, the force of propulsion through a rotating field is ten times greater than that through a static field. The latter simply sets the direction, and the bacteria must move under their own power.
The second and most crucial reason is that bacteria are constantly moving, driven by rotating magnetic fields, along the walls of blood vessels. This makes them more likely to encounter transiently open gaps between cells in the vessel wall, compared to other propulsion types, where bacterial movement is less explored.
Third, unlike other methods, bacteria do not need to be tracked by imaging. Once the magnetic field is positioned on the tumor, it does not need to be readjusted.
At the same time, the researchers took advantage of the natural and autonomous movement of bacteria, which can independently migrate deep inside the tumor once they have crossed the blood vessel wall and entered the tumor. For this reason, the scientists' boost using an external magnetic field lasted only an hour - long enough for the bacteria to efficiently cross the blood vessel wall to reach the tumor.
The bacteria could one day carry anti-cancer drugs. In their cell culture study, the ETH Zurich researchers mimicked this application by attaching liposomes, nanospheres of fat-like material, to bacteria. They labeled these liposomes with a fluorescent dye, which allowed them to demonstrate in a Petri dish that the bacteria had indeed delivered their "cargo" to the cancerous tissue, where it accumulated. In future medical applications, liposomes will be filled with drugs.
智能推荐
新型人工智能驱动算法可以检测大脑“指纹”中的自闭症
2022-08-15斯坦福大学的研究人员开发了一种算法,可以通过观察大脑扫描来判断一个人是否患有自闭症。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向开发微型机器人使药物靶向输送更精准
2022-08-15斯坦福大学的一名机械工程师创造了多功能无线机器人,以最大限度地提高健康结果,并将手术的侵入性降到最低。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向肿瘤学创新 | 新型磁疗法可增强乳腺癌的治疗效果
2022-09-30开创新型磁疗法增强对乳腺癌的治疗作用,优化磁性方案,更有效地杀死癌细胞,从而推动癌症治疗发展。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向生物医学工程创新 | 自组装纳米纤维可防止炎症造成的损伤
2022-09-29杜克大学的生物医学工程师开发了一种自组装纳米材料,可以通过激活免疫系统中的关键细胞来帮助限制炎症疾病造成的损伤。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向