创新背景
斯坦福大学博士后学者莫奇尔·明科夫(Momchil Minkov)曾遇到一个他急于解决的难题。他的非线性光学领域的核心是将光从一种颜色转换为另一种颜色的装置,这一过程对电信、计算和基于激光的设备和科学领域的许多技术都很重要。但是明科夫想要一种同时捕捉两种颜色光的装置,这是一项复杂的壮举,可以极大地提高光变化过程的效率。
创新过程
任何接触过绿色激光笔的人都见过非线性光学的作用。在激光指针内部,一个晶体结构将激光从红外转换为绿色。(绿色激光对人们来说更容易看到,但制造纯绿色激光的组件不太常见)。这项研究的目的是在一个更小的空间中实现类似的波长减半转换,由于光束之间复杂的相互作用,这可能会导致能源效率的大幅提高。
该团队的目标是使用光子晶体腔来实现两束激光的共存,该腔可以将光聚焦在微观体积内。然而,现有的光子晶体腔通常只限制一个波长的光,它们的结构高度定制以适应这一波长。

研究人员提出了一种微观结构,可以将激光从红外线变为绿色,并捕获两种波长的光以提高这种转变的效率。这种类型的结构可以帮助推进电信和计算技术。
因此,研究人员没有制造一种统一的结构来完成所有的工作,而是设计了一种结构,它结合了两种不同的方式来限制光线,一种是控制红外光,另一种是控制绿光,所有这些都仍然包含在一个微小的晶体中。
事实证明,采用不同的方法来包含每种光比使用一种机制来处理两个频率要容易得多,而且在某种意义上,这完全不同于人们为实现这一壮举所需要做的事情。
在解决了它们两部分结构的细节之后,研究人员列出了四个条件,这将指导同事们建造一个能够容纳两种不同波长光的光子晶体腔。他们的结果读起来更像一个食谱,而不是示意图,因为光操纵结构对许多任务和技术都很有用,因此它们的设计必须灵活。
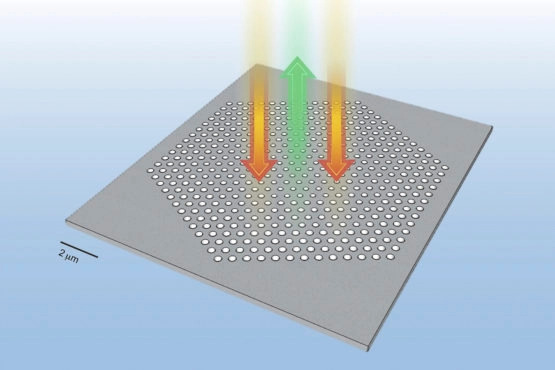
研究人员设计的插图。这种微观板结构中的孔被布置和调整大小,以控制和保持两个波长的光。此图像上的比例尺为二微米,即百万分之二米。
如果电信频道是一条高速公路,在不同波长的光之间切换就等于快速换道以避免减速——而一个容纳多个频道的结构意味着更快的切换。非线性光学对量子计算机也很重要,因为这些计算机的计算依赖于纠缠粒子的产生,而纠缠粒子的形成过程与范实验室的晶体形成过程相反,即由一个绿色光粒子产生成对的红色光粒子。
研究人员用带孔的平板结构,通过排列这些孔,他们可以控制和保持光线。他们移动和调整这些小洞的十亿分之一米,这关乎着研究的成功与失败。
创新关键点
研究人员没有制造一种统一的结构来完成所有的工作,而是设计了一种结构,它结合了两种不同的方式来限制光线,一种是控制红外光,另一种是控制绿光,所有这些都仍然包含在一个微小的晶体中。
创新价值
该项研究开发了新型微观晶体,可大大提高两种颜色光的转换效率,进而提高电信和量子计算的速率。
Innovative design of "light-trapping and color-changing crystals" could speed up quantum computing
Anyone who has ever touched a green laser pointer has seen nonlinear optics in action. Inside the laser pointer, a crystal structure converts the laser light from infrared to green. (Green lasers are easier for people to see, but components to make pure green lasers are less common). The aim of this research is to achieve a similar wavelength halving conversion in a much smaller space, which could lead to a large increase in energy efficiency due to the complex interactions between the beams.
The team's goal is to achieve the coexistence of two laser beams using a photonic crystal cavity, which can focus light in a microscopic volume. However, existing photonic crystal cavities are typically restricted to only one wavelength of light, and their structures are highly customized to fit this wavelength.
So instead of making a uniform structure to do all the work, the researchers designed one that combines two different ways to limit light, one to control infrared light and the other to control green light, all still contained in a tiny crystal.
It turns out that taking a different approach to including each light is much easier than using a single mechanism to handle both frequencies, and in a sense completely different from what one would need to do to achieve such a feat.
After working out the details of their two-part structure, the researchers laid out four conditions that would guide colleagues to build a photonic crystal cavity capable of accommodating two different wavelengths of light. Their results read more like a recipe than a schematic, because light-manipulated structures are useful for many tasks and techniques, so their design must be flexible.
If telecom channels were a highway, switching between different wavelengths of light would amount to fast lane changes to avoid slowing down - and a structure that accommodates multiple channels means faster switching. Nonlinear optics is also important for quantum computers because their calculations rely on the generation of entangled particles, which is the opposite of the crystal formation process in Van's laboratory, where pairs of red light particles are generated from a single green light particle.
The researchers used plate structures with holes. By arranging the holes, they could control and hold light. They move and adjust these tiny holes by billionths of a meter, which can make or break a study.
智能推荐
DTU研究人员创造性地将量子计算机用于电网计算
2022-09-05科技正在迅速发展,将量子计算机用于电力系统计算可以做到普通计算机做不到的事情。这意味着未来将可以开发基于可再生能源的安全稳定电力系统所需的工具。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向量子计算+原子物理 | 创新利用“碱土原子”实现量子特定计算
2022-10-24加州理工学院的一个量子物理学家团队在使用一种更复杂的中性原子(位于元素周期表第二列的碱土原子)的研究上取得了进展。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向创新量子技术应用于诊断和治疗心脏疾病
2022-08-04伦敦大学学院研究人员开发的量子技术可以对心脏等活器官的传导率进行无创成像,这有可能彻底改变心房纤颤的诊断和治疗。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向