创新背景
为了加深对大脑的理解,神经科学家必须能够非常详细地绘制负责处理感觉信息或形成新记忆等任务的神经回路。
创新过程
加州理工学院的一组研究人员描述了一种新方法,可以实时观察特定大脑回路中所有数千到数百万个神经元的活动。
这项新技术被称为“集成神经光子学”,它使用微小的光学微芯片阵列,可以被植入大脑的任何深度,结合荧光分子报告器和光遗传驱动器,分别对神经元进行光学监测和控制它们的活动。这些阵列发射出微尺度的光束来刺激它们周围的转基因神经元,同时记录这些细胞的活动,揭示它们的功能。
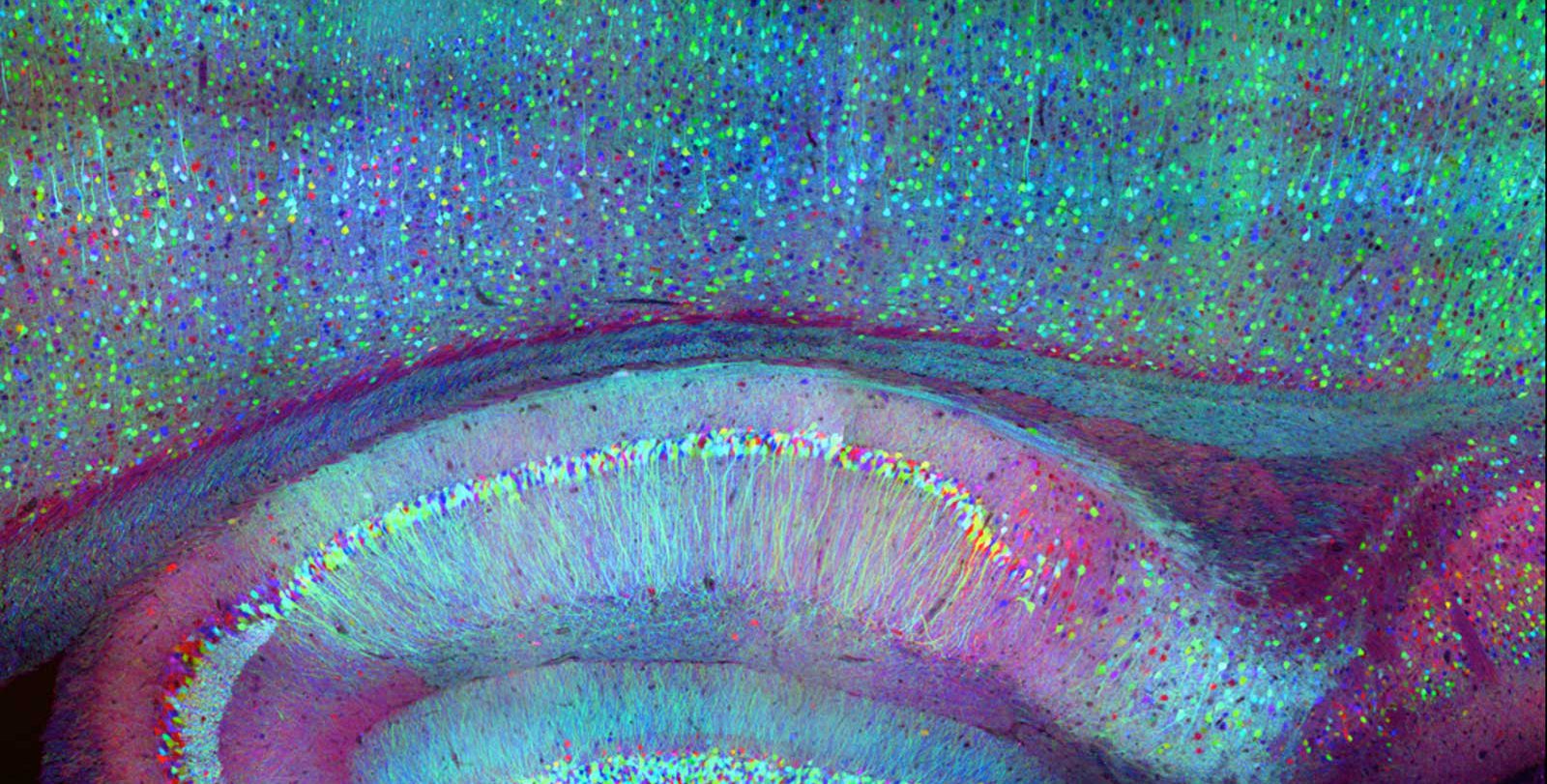
近年来,神经科学家已经开始使用光遗传学来研究包括啮齿类动物在内的模型动物中更大的神经元群。在光遗传学中,神经元通过基因工程表达一种特殊的蛋白质标记物,如绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)。绿色荧光蛋白的存在使细胞在蓝光照射下发出绿光,为神经活动提供了一种视觉指标。通过将传感器分子与这些标记融合,研究人员可以通过调节荧光来设计神经元,使其发出局部活动的信号。光遗传学解决了神经科学研究中固有的一些问题,这些问题依赖于植入电极来测量神经元的电活动,由于大脑中所有的电活动,这种研究平均只能可靠地测量单个神经元。因为大脑不使用光进行交流,光遗传学使得追踪大量神经元信号变得更容易。
但目前对大脑的光遗传学研究受到一个重大的物理限制。大脑组织既能散射光又能吸收光,这意味着从大脑外部照射进来的光只能在大脑内传播很短的距离。正因为如此,只有距离大脑表面不到两毫米的区域可以被光学检查。这就是为什么研究得最好的大脑回路通常是传递感觉信息的简单回路,比如老鼠的感觉皮层——它们位于大脑表面附近。简而言之,目前光遗传学的方法还不能很好地洞察位于大脑深处的电路,包括那些涉及高阶认知或学习过程的电路。
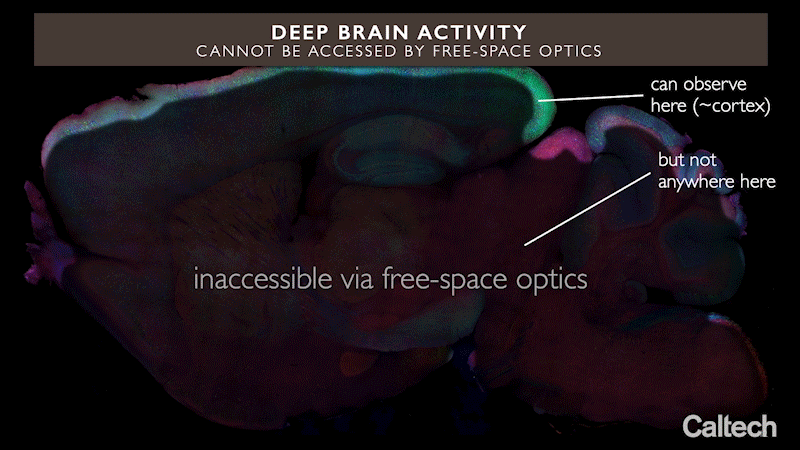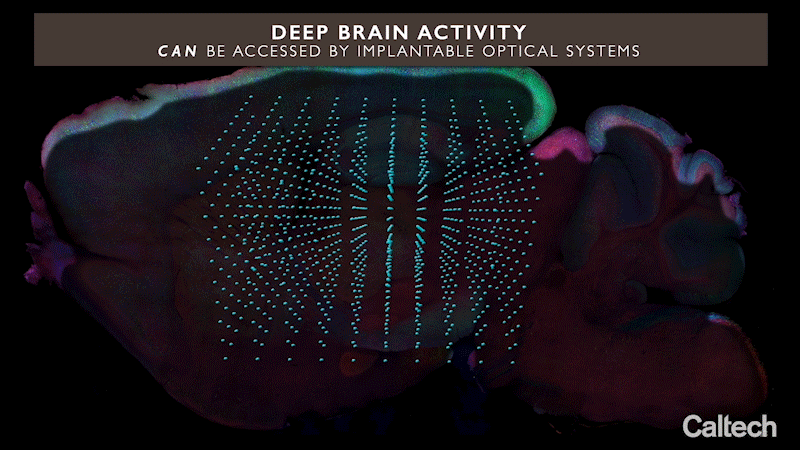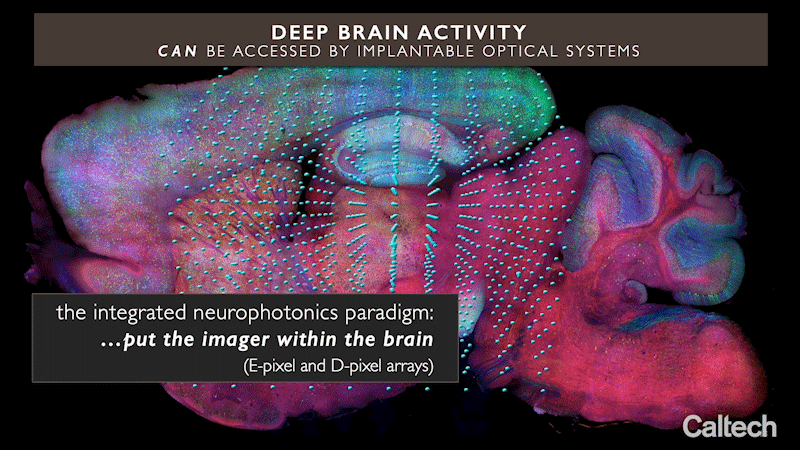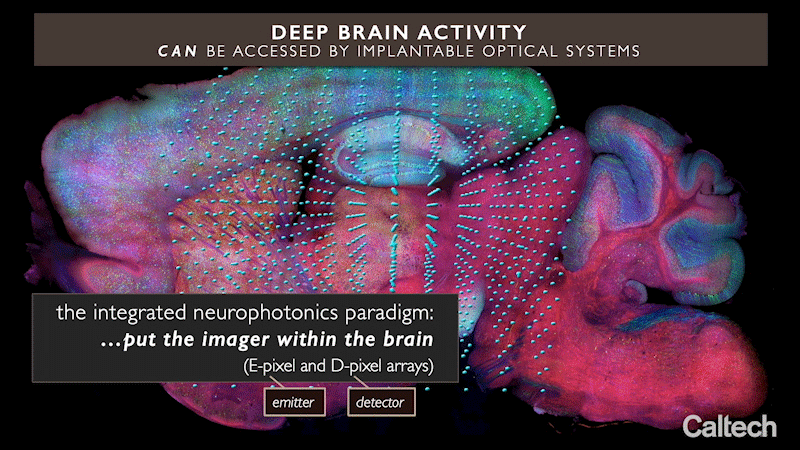
集成神经光子学则绕过了这个问题。在这项技术中,完整成像系统的微尺度元件被植入到大脑深处复杂的神经回路附近,这些神经回路位于诸如海马体(参与记忆形成)、纹状体(控制认知)等区域,以及其他具有前所未有分辨率的基本结构。考虑到类似的功能磁共振成像(fMRI)技术,这种扫描技术目前被用于整个大脑的成像。功能磁共振成像扫描中,每个体素或三维像素的体积通常约为一立方毫米,包含大约10万个神经元。因此,每个体素代表了这10万个细胞的平均代谢活性。
创新关键点
这项新技术使用微小的光学微芯片阵列,可以被植入大脑的任何深度,结合荧光分子报告器和光遗传驱动器,分别对神经元进行光学监测和控制它们的活动。
创新价值
在集成神经光子学这项技术中,完整成像系统的微尺度元件被植入到大脑深处复杂的神经回路附近,这些神经回路位于诸如海马体(参与记忆形成)、纹状体(控制认知)等区域,以及其他具有前所未有分辨率的基本结构。因此,研究人员可以更好的对大脑进行研究。
Innovative development of "integrated neurophotonics" to map brain circuits in real time
A team of Caltech researchers has described a new way to observe the activity of all thousands to millions of neurons in a specific brain circuit in real time.
The new technology, called "integrated neurophotonics," uses arrays of tiny optical microchips, which can be implanted at any depth in the brain, in combination with fluorescent molecular reporters and optogenetic drivers to optically monitor neurons and control their activity, respectively. These arrays emit microscale beams of light to stimulate the transgenic neurons around them, while recording the activity of these cells and revealing their functions.
In recent years, neuroscientists have begun to use optogenetics to study larger populations of neurons in model animals, including rodents. In optogenetics, neurons are genetically engineered to express a specific protein marker, such as green fluorescent protein (GFP). The presence of green fluorescent protein causes cells to glow green in response to blue light, providing a visual indicator of neural activity. By fusing sensor molecules with these markers, researchers can engineer neurons to signal local activity by tuning their fluorescence. Optogenetics addresses some of the problems inherent in neuroscience research that rely on implanted electrodes to measure the electrical activity of neurons, which on average can only reliably measure a single neuron because of all the electrical activity in the brain. Because the brain doesn't use light to communicate, optogenetics has made it easier to track signals from large numbers of neurons.
But current optogenetic research into the brain suffers from a major physical limitation. Brain tissue can both scatter and absorb light, meaning that light coming in from outside the brain can travel only a short distance inside the brain. Because of this, only areas less than two millimeters from the surface of the brain can be optically examined. That's why the best-studied brain circuits are often simple circuits that transmit sensory information, like the sensory cortex in mice -- they're located near the surface of the brain. In short, current optogenetic approaches do not provide good insight into circuits located deep within the brain, including those involved in higher-order cognitive or learning processes.
Integrated neurophotonics circumvents this problem. In this technique, microscale elements of a complete imaging system are implanted near complex neural circuits deep in the brain in areas such as the hippocampus (involved in memory formation), the striatum (which controls cognition), and other basic structures with unprecedented resolution. This scanning technique is currently used to image the whole brain, considering similar functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) technology. In fMRI scans, each voxel, or three-dimensional pixel, is typically about a cubic millimeter in volume and contains about 100,000 neurons. Thus, each voxel represents the average metabolic activity of these 100,000 cells.
智能推荐
神经科学创新 | 在基因中创新引入神经保护蛋白可延缓ALS进展
2022-11-17加州大学圣地亚哥分校开发了一种新型基因治疗方法,在家族性渐冻症(ALS)的人化小鼠和大鼠模型中,明显推迟了疾病的发病时间。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向神经科学创新 | 动物天生的节拍同步创新研究
2022-11-15精确地随着音乐节拍移动被认为是人类与生俱来的技能,研究表明老鼠也有这种能力。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向利用微型硅探头可高清记录大脑活动
2022-08-08由伦敦大学学院的科学家们组成的一个团队开发了一种新的设备,它可以让研究人员以一种前所未有的方式绘制控制行为和决策的复杂神经网络的活动,从而彻底改变我们对大脑的认识。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向