创新背景
随着世界人口的不断增长,水资源短缺是人类需要克服的巨大问题,水覆盖了全球四分之三的面积,但只有大约一半的一半是可用的淡水。
创新过程
受仙人掌刺形状的启发,研究人员开发微型结构允许一种新创造的材料昼夜从空气中收集饮用水,并将两种集水技术合二为一。
这种材料是一种微结构水凝胶膜,它可以通过太阳能蒸汽水产生和雾收集两种独立的过程产生水,通常需要两个独立的设备。雾收集指在夜间沿海低洼的云上布满水滴时,聚合并收集这些雾滴把雾变成饮用水。
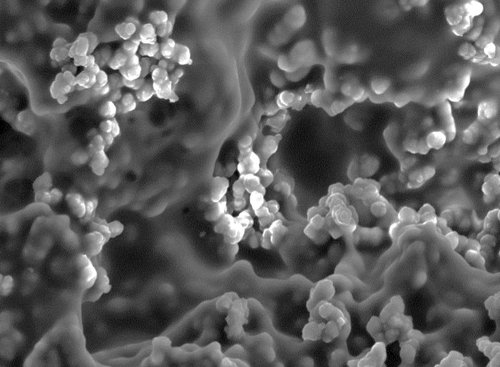
凝胶基质的多孔结构
太阳能蒸汽发电是另一种收集水的技术。它在沿海地区的效果特别好,因为它还能够净化水,尽管它在白天而不是晚上工作。在这种方法中,来自太阳的热量使水蒸发成蒸汽,水蒸气可以凝结成饮用水。
由于这两种技术在如此不同的条件下工作,它们通常需要不同的材料和设备才能工作。加州理工学院开发的一种材料可以将它们组合成一个设备进行全天淡水收集。
研究人员创造了一种由排列的小刺组成的膜,它类似于圣诞树,但实际上是受仙人掌刺形状的启发。仙人掌独特地适应了干旱气候,这些刺被称之为“微树”,吸引悬浮在空气中的微小水滴,让它们沿着脊柱底部滑落,并与其他水滴结合成相对重的水滴,最终汇聚成一个可以利用的蓄水池。
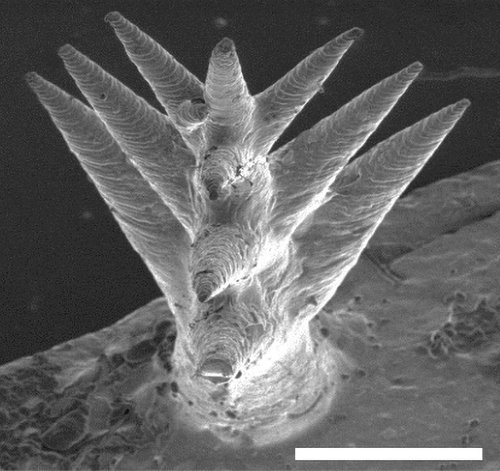

刺是由水凝胶制成的,亲水性聚合物网络能够自然地吸引水。由于它们的体积很小,所以可以打印在极薄的薄膜上。在白天,水凝胶膜吸收阳光加热下面的水,变成蒸汽。然后蒸汽重新凝结在一个透明的盖子上,在那里它可以被收集。在夜间,透明罩折叠起来,水凝胶膜暴露在潮湿的空气中捕捉雾。因此,这种材料可以从蒸汽和雾中收集水分。
在夜间进行的一项操作测试中,从55-125平方厘米面积的材料样本中,可以从雾中收集约35毫升的水。在白天的测试中,这种材料能够收集大约125毫升的太阳能蒸汽。

具有代表性的制备PVA / PPy凝胶微树阵列的图像。
水凝胶本身是一种聚乙烯醇/聚吡罗(PVA/PPy)复合凝胶,这是一种无毒且灵活的材料,用于电容器、可穿戴应变和温度传感器以及电池等众多应用领域。
为了优化微型树的设计,研究人员利用计算机建模,计算了微型树木内部的热量分布,以帮助确定最有效地从空气中吸收水分的大小和形状。
创新关键点
研究人员创造了一种由排列的小刺组成的膜,它类似于圣诞树,但实际上是受仙人掌刺形状的启发。刺是由水凝胶制成的,亲水性聚合物网络能够自然地吸引水。
创新价值
加州理工学院开发的一种新材料可以将两种集水技术组合成一个设备进行全天淡水收集,极大提高了对水资源的利用,可缓解水资源短缺的问题。
The new material can be used to collect fresh water throughout the day through a microstructured hydrogel film
Inspired by the shape of cactus spines, researchers have developed tiny structures that allow a newly created material to collect drinking water from the air day and night, and combine two water-harvesting technologies in one.
The material is a microstructured hydrogel film that can produce water through two separate processes, solar steam water generation and fog collection, typically requiring two separate devices. Fog harvesting is the process of aggregating and collecting water droplets from low-lying coastal clouds at night to turn the fog into drinking water.
Solar steam is another technique for capturing water. It works particularly well in coastal areas because it also purifies water, although it works during the day rather than at night. In this method, heat from the sun evaporates water into steam, which can condense into drinking water.
Because the two technologies work under such different conditions, they often require different materials and equipment to work. A material developed at Caltech can combine them into a single device for all-day freshwater harvesting.
The researchers created a membrane of arranged spines that resembles a Christmas tree but is actually inspired by the shape of the spines of a cactus. Uniquely adapted to dry climates, these spines, known as "microtrees," attract tiny droplets of water suspended in the air, allowing them to slide down the base of their spine and combine with other droplets to form relatively heavy droplets, eventually pooling into a usable reservoir.
The spines are made of hydrogels, networks of hydrophilic polymers that naturally attract water. Because of their small size, they can be printed on extremely thin films. During the day, the hydrogel membrane absorbs sunlight and heats the water underneath, turning it into steam. The steam then recondenses on a transparent lid, where it can be collected. At night, the clear hood folds up and the hydrogel film is exposed to moist air to capture fog. As a result, the material can collect water from steam and fog.
In an operational test conducted at night, about 35 milliliters of water could be collected from the fog from a sample of material covering an area of 55-125 square centimeters. In daytime tests, the material was able to collect about 125 milliliters of solar steam.
The hydrogel itself is a polyvinyl alcohol/polypirro (PVA/PPy) composite gel, a non-toxic and flexible material used in numerous applications such as capacitors, wearable strain and temperature sensors, and batteries.
To optimize the design of the miniature trees, the researchers used computer modeling to calculate the heat distribution inside the miniature trees to help determine the size and shape that most efficiently absorbs water from the air.
智能推荐
新技术+基础设施 | 主动维修基础设施,提高维修管理效率
2022-08-17利用现代数字化技术帮助精简基础设施维修措施并进行主动预防性维护,降低维修成本,提高维修效率,进而优化公共事业管理、城市管理和工程管理模式。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向应用新材料技术解决溶聚丁苯橡胶进口难题
2022-07-27青岛能源所(山东能源研究院)针对中国合成橡胶严重依赖进口的问题和石化下游C4~C5烯烃的高值化转化利用迫切需求,通过设计合成新型铁系催化剂,创制了铁系丁戊橡胶新材料,开发了具有自主知识产权的催化剂技术和催化聚合技术。他们与巴陵石化合作,首次实现了铁系丁戊橡胶百吨级间歇聚合和连续聚合中试放大试验,目前正在进行3万吨/年的产业化示范研究。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向创新应用发光二极管设计新型“智能纹身”
2022-08-02伦敦大学学院和意大利理工学院的科学家们利用电视和智能手机屏幕上的发光技术创造了一种临时纹身,为一种具有广泛潜在用途的新型“智能纹身”铺平了道路。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向创造性利用人工智能优化污水处理模式
2022-08-01结合人工智能和污水处理工程,分析水污染物的分子机制,开发可以筛选识别相关分子的人工智能模型,有效筛查污染物,实现水资源的循环利用。
涉及学科涉及领域研究方向